Allowance dApp
Description: This project demonstrates the integration of two smart contracts, RoleContract and AllowanceContract, focusing on role-based access and fund management. It highlights inter-contract calls, where the allowance logic depends on roles retrieved dynamically from the role contract.
Purpose: The purpose of this dApp is to teach state management, access control, and inter smart contract calls on the aelf blockchain. This example models how multi-contract systems work together and call each other to securely manage roles and funds in a blockchain environment. Difficulty Level: Moderate
Step 1 - Setting up your development environment
- Local
- Codespaces
- Basic knowledge of terminal commands
- IDE - Install VS Code
Note for Apple Silicon users:
Ensure that Rosetta is installed, if it is not, use the following command:
softwareupdate --install-rosetta
Install Required Packages
- Install dotnet 8.0.x SDK
- Install aelf contract templates
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
dotnet new --install AElf.ContractTemplates
dotnet new install AElf.ContractTemplates
AELF.ContractTemplates contains various predefined templates for the ease of developing smart contracts on the aelf blockchain.
- Install aelf deploy tool
dotnet tool install --global aelf.deploy
aelf.deploy is a utility tool for deploying smart contracts on the aelf blockchain. Please remember to export PATH after installing aelf.deploy.
ℹ️ Note: If you have installed aelf.deploy and your terminal says that there is no such command available, please uninstall and install aelf.deploy.
Install Node.js and Yarn
Install aelf-command
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
sudo npm i -g aelf-command
npm i -g aelf-command
aelf-command is a CLI tool for interacting with the aelf blockchain, enabling tasks like creating wallets and managing transactions. Provide required permissions while installing aelf-command globally.
- Visit aelf-devcontainer-template.
- Click the
Use this templatebutton. ChooseCreate a new repository. - Enter a suitable repository name. Click
Create repository. - Within the GitHub interface of your new repository, click on
Code. SelectCodespaces. - Click on the
+sign to create a new Codespace. - After some time, your workspace will load with the contents of the repository. You can now continue your development using GitHub Codespaces.
Step 2 - Develop Role Smart Contract
Start Your Smart Contract Project
-
Open your
Terminal. -
Enter the following command to generate a new RoleContract project:
mkdir role-contract
cd role-contract
dotnet new aelf -n RoleContract
Adding Your Smart Contract Code
Now that we have a RoleContract template, we can customize it to implement role-based permissions for various use cases. Below are the core functionalities of the RoleContract:
- Set Admin: Allows the current admin to assign a new admin address.
- Set Parent/Child: Grants parent or child roles with appropriate permissions.
- Retrieve Role Addresses: Methods to fetch the current admin, parent, and child addresses.
- Role-based Access Control: Ensures only admins or parents can assign roles using access validation logic.
This template provides a foundation for building secure systems where role management and hierarchical permissions are essential.
- Enter this command in your
Terminal.
cd src
Defining Methods and Messages
- Rename the file name from
Protobuf/contract/hello_world_contract.prototorole_contract.protomanually or by using the following command:
mv Protobuf/contract/hello_world_contract.proto Protobuf/contract/role_contract.proto
- Open the project with your IDE.
The implementation of file src/Protobuf/contract/role_contract.proto is as follows:
syntax = "proto3";
import "aelf/core.proto";
import "google/protobuf/empty.proto";
import "Protobuf/reference/acs12.proto";
import "aelf/options.proto";
import "google/protobuf/wrappers.proto";
// The namespace of this class
option csharp_namespace = "AElf.Contracts.RoleContract";
service RoleContract {
// The name of the state class the smart contract is going to use to access blockchain state
option (aelf.csharp_state) = "AElf.Contracts.RoleContract.RoleContractState";
option (aelf.base) = "Protobuf/reference/acs12.proto";
rpc Initialize (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.Empty){
}
rpc SetAdmin (aelf.Address) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc GetAdmin (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.StringValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc SetParent (aelf.Address) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc GetParent (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.StringValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc SetChild (aelf.Address) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc GetChild (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.StringValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
}
rpcmethods define the callable functions within the contract, allowing external systems to interact with the contract's logic.messagerepresent the structured data exchanged between the contract and external systems.
Define Contract States
The implementation of the role contract's state inside file src/RoleContractState.cs is as follows:
using AElf.Sdk.CSharp.State;
using AElf.Types;
namespace AElf.Contracts.RoleContract
{
public class RoleContractState : ContractState
{
public BoolState Initialized { get; set; }
public SingletonState<Address> AdminAddress { get; set; }
public SingletonState<Address> ParentAddress { get; set; }
public SingletonState<Address> ChildAddress { get; set; }
}
}
- The
State.csfile on the aelf blockchain smart contract holds the variables that store the contract's data, making sure this data is saved and accessible whenever the contract needs it.
Implement Role Smart Contract
The implementation of the role contract inside file src/RoleContract.cs is as follows:
using AElf.Sdk.CSharp;
using AElf.Types;
using Google.Protobuf.WellKnownTypes;
namespace AElf.Contracts.RoleContract
{
public class RoleContract : RoleContractContainer.RoleContractBase
{
private const string DefaultAdmin = "ENTER_YOUR_PORTKEY_ADDRESS";
public override Empty Initialize(Empty input)
{
if (State.Initialized.Value)
{
return new Empty();
}
State.Initialized.Value = true;
State.AdminAddress.Value = Context.Sender; //Can set Deployer as admin
State.AdminAddress.Value = Address.FromBase58(DefaultAdmin); // Can set YOUR_PORTKEY_ADDRESS as admin
return new Empty();
}
public override Empty SetAdmin(Address input)
{
AssertIsAdmin();
// Set the new admin address
State.AdminAddress.Value = input;
return new Empty();
}
public override Empty SetParent(Address input)
{
AssertIsAdminOrParent();
// Set the parent address
State.ParentAddress.Value = input;
return new Empty();
}
public override Empty SetChild(Address input)
{
AssertIsAdminOrParent();
// Set the chlid address
State.ChildAddress.Value = input;
return new Empty();
}
// Get the current admin address
public override StringValue GetAdmin(Empty input)
{
return State.AdminAddress.Value == null ? new StringValue() : new StringValue {Value = State.AdminAddress.Value.ToBase58()};
}
// Get the current parent address
public override StringValue GetParent(Empty input)
{
return State.ParentAddress.Value == null ? new StringValue() : new StringValue {Value = State.ParentAddress.Value.ToBase58()};
}
// Get the current child address
public override StringValue GetChild(Empty input)
{
return State.ChildAddress.Value == null ? new StringValue() : new StringValue {Value = State.ChildAddress.Value.ToBase58()};
}
private void AssertIsAdmin()
{
Assert(Context.Sender == State.AdminAddress.Value, "Unauthorized(Not Admin) to perform the action.");
}
private void AssertIsAdminOrParent()
{
Assert(Context.Sender == State.AdminAddress.Value || Context.Sender == State.ParentAddress.Value, "Unauthorized (Not Parent or Admin) to perform the action.");
}
}
}
Building Role Smart Contract
- Build the smart contract code with the following command inside
srcfolder:
dotnet build
You should see RoleContract.dll.patched in the directory RoleContract/src/bin/Debug/net.6.0
Step 3 - Deploy Role Smart Contract
Create A Wallet
To send transactions on the aelf blockchain, you must have a wallet.
- Run this command to create aelf wallet.
aelf-command create

- You will be prompted to save your account, please do save your account as shown below:
? Save account info into a file? (Y/n) Y
Make sure to choose Y to save your account information.
ℹ️ Note: If you do not save your account information (by selecting n or N), do not export the wallet password. Only proceed to the next step if you have saved your account information.
- Next, enter and confirm your password. Then export your wallet password as shown below:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export WALLET_PASSWORD="YOUR_WALLET_PASSWORD"
$env:WALLET_PASSWORD = "YOUR_WALLET_PASSWORD"
Acquire Testnet Tokens (Faucet) for Development
To deploy smart contracts or execute on-chain transactions on aelf, you'll require testnet ELF tokens.
Get ELF Tokens
- CLI
- Web
1. Get Testnet ELF Tokens:
To receive testnet ELF tokens, run this command after replacing $WALLET_ADDRESS and $WALLET_PASSWORD with your wallet details:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export WALLET_ADDRESS="YOUR_WALLET_ADDRESS"
curl -X POST "https://faucet.aelf.dev/api/claim?walletAddress=$WALLET_ADDRESS" -H "accept: application/json" -d ""
$headers = @{
"accept" = "application/json"
}
$env:WALLET_ADDRESS = "YOUR_WALLET_ADDRESS"
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://faucet.aelf.dev/api/claim?walletAddress=$env:WALLET_ADDRESS" -Method POST -Headers $headers -Body ""
2. Check ELF Balance:
To check your ELF balance, use:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
aelf-command call ASh2Wt7nSEmYqnGxPPzp4pnVDU4uhj1XW9Se5VeZcX2UDdyjx -a $WALLET_ADDRESS -p $WALLET_PASSWORD -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io GetBalance
aelf-command call ASh2Wt7nSEmYqnGxPPzp4pnVDU4uhj1XW9Se5VeZcX2UDdyjx -a $env:WALLET_ADDRESS -p $env:WALLET_PASSWORD -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io GetBalance
You will be prompted for the following:
Enter the required param <symbol>: ELF
Enter the required param <owner>: **$WALLET_ADDRESS**
You should see the result displaying your wallet's ELF balance.
Go to https://faucet-ui.aelf.dev Enter your address and click Get Tokens.
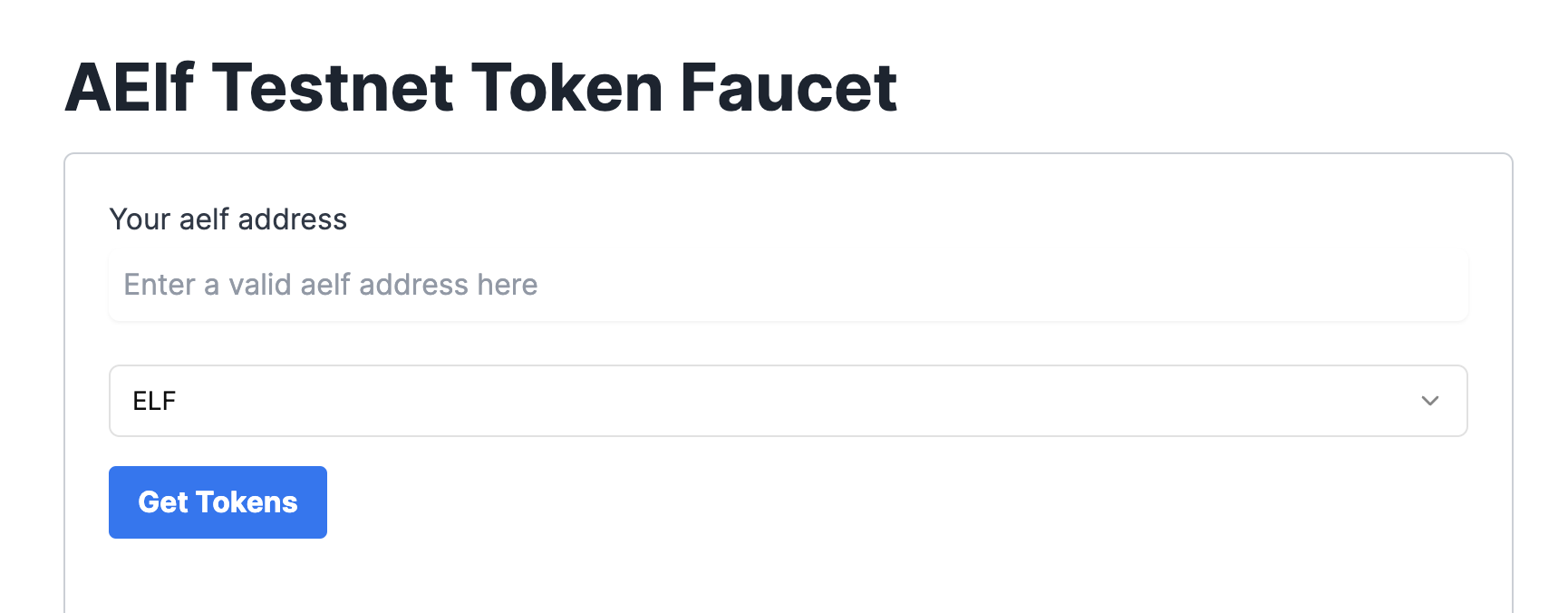
Deploy Smart Contract:
The smart contract needs to be deployed on the chain before users can interact with it.
Run the following command to deploy a contract. Remember to export the path of RoleContract.dll.patched to CONTRACT_PATH.
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export CONTRACT_PATH=$(find ~+ . -path "*patched*" | head -n 1)
aelf-deploy -a $WALLET_ADDRESS -p $WALLET_PASSWORD -c $CONTRACT_PATH -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io/
$CONTRACT_PATH = Get-ChildItem -Recurse -Filter "*patched*" | Select-Object -First 1 -ExpandProperty FullName
$env:CONTRACT_PATH = $CONTRACT_PATH
aelf-deploy -a $env:WALLET_ADDRESS -p $env:WALLET_PASSWORD -c $env:CONTRACT_PATH -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io/
-
Please wait for approximately 1 to 2 minutes. If the deployment is successful, it will provide you with the contract address.
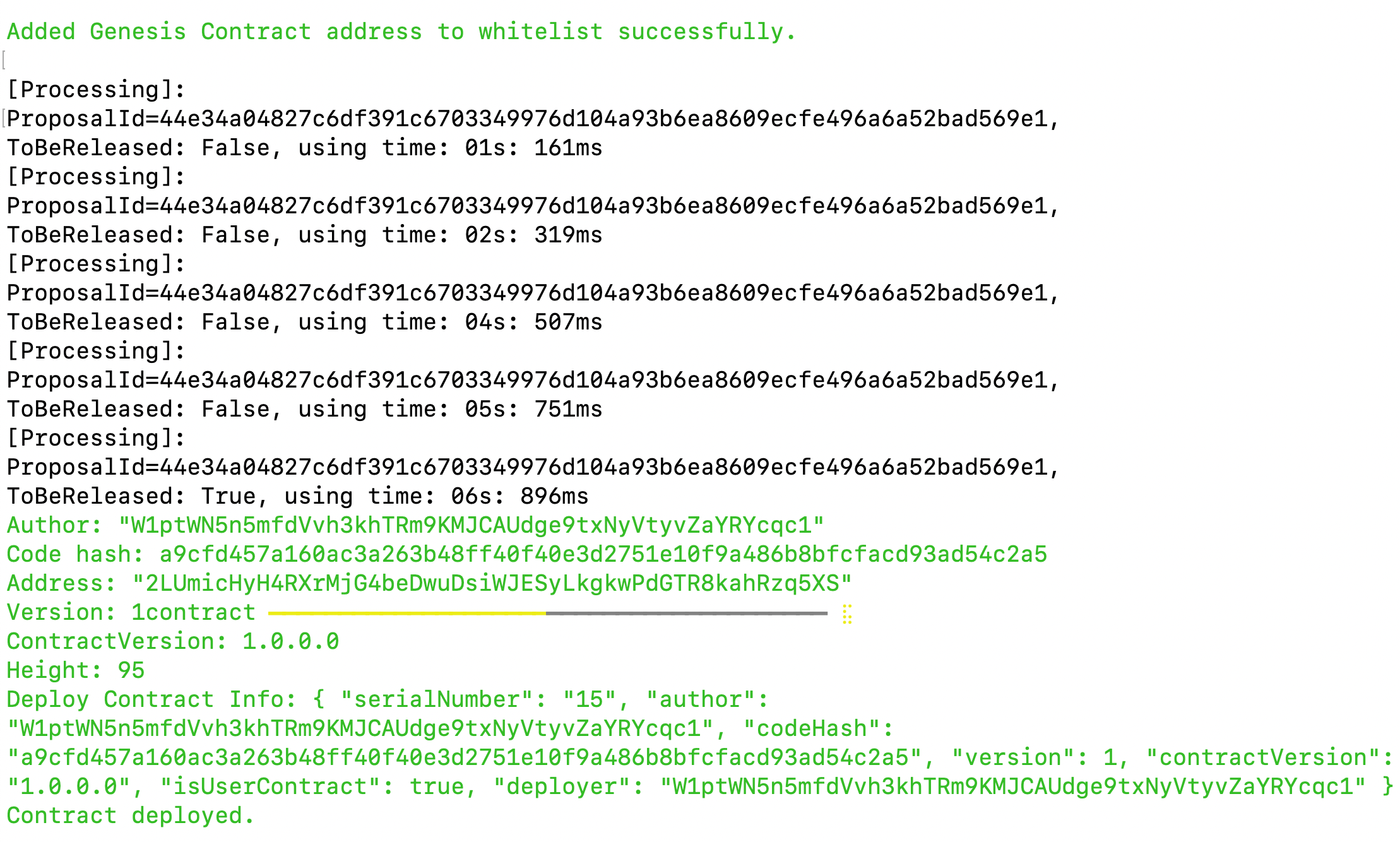
-
Copy the smart contract address from the
addressfield
-
Export your smart contract address:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export CONTRACT_ADDRESS="YOUR_SMART_CONTRACT_ADDRESS e.g. 2LUmicHyH4RXrMjG4beDwuDsiWJESyLkgkwPdGTR8kahRzq5XS"
$env:CONTRACT_ADDRESS="YOUR_SMART_CONTRACT_ADDRESS e.g. 2LUmicHyH4RXrMjG4beDwuDsiWJESyLkgkwPdGTR8kahRzq5XS"
ℹ️ Note: You are to copy the smart contract address as we will be referencing it in the next steps!
🎉 You have successfully deployed your Role smart contract on the aelf testnet! In the next steps, we will be building the frontend components that allow us to interact with our deployed smart contract!
Step 4 - Develop Allowance Smart Contract
Start Your Smart Contract Project
-
Open your
Terminal. -
Enter the following command to generate a new RoleContract project:
cd ../..
mkdir allowance-contract
cd allowance-contract
dotnet new aelf -n AllowanceContract
Adding Your Smart Contract Code
Now that we have an AllowanceContract template, it can be customized to manage funds with role-based permissions. Below are its core functionalities:
- Set Allowance: Increases the current allowance, with permissions verified through parent and child roles fetched from the RoleContract.
- Use Funds: Allows a child role to spend funds, reducing the current allowance.
- Get Allowance: Retrieves the remaining allowance.
- Role-based Permissions: Ensures only authorized roles, like parent of a child can modify or the child use the allowance.
This contract showcases inter-contract calls and role-based fund management, demonstrating how multiple smart contracts work together for secure, controlled financial operations on the aelf blockchain. It helps in understanding how the AllowanceContract calls the RoleContract to check which sender (either of Parent, Child & Admin) is calling the methods of the AllowanceContract to put control on the access of the functions.
- Enter this command in your
Terminal.
cd src
Defining Methods and Messages
- Rename the file name from
Protobuf/contract/hello_world_contract.prototoallowance_contract.proto:
mv Protobuf/contract/hello_world_contract.proto Protobuf/contract/allowance_contract.proto
- Open the project with your IDE.
The implementation of file src/Protobuf/contract/allowance_contract.proto is as follows:
syntax = "proto3";
import "aelf/core.proto";
import "google/protobuf/empty.proto";
import "Protobuf/reference/acs12.proto";
import "aelf/options.proto";
import "google/protobuf/wrappers.proto";
// The namespace of this class
option csharp_namespace = "AElf.Contracts.AllowanceContract";
service AllowanceContract {
// The name of the state class the smart contract is going to use to access blockchain state
option (aelf.csharp_state) = "AElf.Contracts.AllowanceContract.AllowanceContractState";
option (aelf.base) = "Protobuf/reference/acs12.proto";
rpc Initialize (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.Empty){
}
rpc SetAllowance (google.protobuf.Int64Value) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc GetAllowance (aelf.Address) returns (google.protobuf.Int64Value) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc useFunds (google.protobuf.Int64Value) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc IfInitialized (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.BoolValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
}
rpcmethods define the callable functions within the contract, allowing external systems to interact with the contract's logic.messagerepresent the structured data exchanged between the contract and external systems.
Define Contract States
The implementation of the allowance contract state inside file src/AllowanceContractState.cs is as follows:
using AElf.Sdk.CSharp.State;
using AElf.Types;
namespace AElf.Contracts.AllowanceContract
{
public partial class AllowanceContractState : ContractState
{
public BoolState Initialized { get; set; }
public SingletonState<Address> AdminAddress { get; set; }
public SingletonState<Address> ParentAddress { get; set; }
public SingletonState<Address> ChildAddress { get; set; }
public Int32State CurrentAllowance { get; set; }
}
}
- The
State.csfile in an aelf blockchain smart contract holds the variables that store the contract's data, making sure this data is saved and accessible whenever the contract needs it.
Implement Allowance Smart Contract
The implementation of the AllowanceContract inside file src/AllowanceContract.cs is as follows:
using AElf.Sdk.CSharp;
using AElf.Types;
using Google.Protobuf.WellKnownTypes;
namespace AElf.Contracts.AllowanceContract
{
// Contract class must inherit the base class generated from the proto file
public class AllowanceContract : AllowanceContractContainer.AllowanceContractBase
{
private const string RoleContractAddress = "YOUR_ROLE_CONTRACT_ADDRESS"; // tDVW role contract address
public override Empty Initialize(Empty input)
{
// Check if the contract is already initialized
Assert(State.Initialized.Value == false, "Already initialized.");
// Set the contract state
State.Initialized.Value = true;
// Set the owner address
State.AdminAddress.Value = Context.Sender;
// Initialize the role contract
State.RoleContract.Value = Address.FromBase58(RoleContractAddress);
return new Empty();
}
public override Empty SetAllowance(Int64Value input)
{
State.ParentAddress.Value = Address.FromBase58(State.RoleContract.GetParent.Call(new Empty()).Value);
Assert(Context.Sender == State.ParentAddress.Value, "Unauthorized(Not Parent) to perform the action.");
State.ChildAddress.Value = Address.FromBase58(State.RoleContract.GetChild.Call(new Empty()).Value);
State.CurrentAllowance.Value = (int)(State.CurrentAllowance.Value + input.Value) ;
return new Empty();
}
public override Int64Value GetAllowance(Address input)
{
Assert(Context.Sender == State.ChildAddress.Value || Context.Sender == State.ParentAddress.Value, "Unauthorized(Not Parent or Child) to perform the action.");
var allowance = State.CurrentAllowance.Value;
return new Int64Value
{
Value = allowance
};
}
public override Empty useFunds(Int64Value input)
{
State.ChildAddress.Value = Address.FromBase58(State.RoleContract.GetChild.Call(new Empty()).Value);
Assert(Context.Sender == State.ChildAddress.Value, "Unauthorized(Not Child) to perform the action.");
State.CurrentAllowance.Value = (int)(State.CurrentAllowance.Value - input.Value) ;
return new Empty();
}
// Function to check if the allowance contract is already initialized or not
public override BoolValue IfInitialized(Empty input)
{
return new BoolValue { Value = State.Initialized.Value };
}
}
}
Add Inter-Contract Calls
- Now, AllowanceContract needs to create a reference with the RoleContract. First, AllowanceContract will use the
role_contract.protofile inside the Protobuf/reference folder. Copy therole_contract.protofrom the role-contract/src/Protobuf/contract folder.
syntax = "proto3";
import "aelf/core.proto";
import "google/protobuf/empty.proto";
import "Protobuf/reference/acs12.proto";
import "aelf/options.proto";
import "google/protobuf/wrappers.proto";
// The namespace of this class
option csharp_namespace = "AElf.Contracts.RoleContract";
service RoleContract {
// The name of the state class the smart contract is going to use to access blockchain state
option (aelf.csharp_state) = "AElf.Contracts.RoleContract.RoleContractState";
option (aelf.base) = "Protobuf/reference/acs12.proto";
rpc Initialize (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.Empty){
}
rpc SetAdmin (aelf.Address) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc GetAdmin (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.StringValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc SetParent (aelf.Address) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc GetParent (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.StringValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc SetChild (aelf.Address) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc GetChild (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.StringValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
}
- Now, create a file inside
srcfolder and name it asContractReferences.csand add the following code to establish connection between AllowanceContract and the RoleContract.
using AElf.Contracts.RoleContract;
namespace AElf.Contracts.AllowanceContract
{
public partial class AllowanceContractState
{
internal RoleContractContainer.RoleContractReferenceState RoleContract { get; set; }
}
}
Building Allowance Smart Contract
- Build the smart contract code with the following command inside
srcfolder:
dotnet build
You should see AllowanceContract.dll.patched in the directory AllowanceContract/src/bin/Debug/net.6.0
Step 5 - Deploy Allowance Smart Contract
Create A Wallet
To send transactions on the aelf blockchain, you must have a wallet.
- Run this command to create aelf wallet.
aelf-command create

- You will be prompted to save your account, please do save your account as shown below:
? Save account info into a file? (Y/n) Y
Make sure to choose Y to save your account information.
ℹ️ Note: If you do not save your account information (by selecting n or N), do not export the wallet password. Only proceed to the next step if you have saved your account information.
- Next, enter and confirm your password. Then export your wallet password as shown below:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export WALLET_PASSWORD="YOUR_WALLET_PASSWORD"
$env:WALLET_PASSWORD = "YOUR_WALLET_PASSWORD"
Acquire Testnet Tokens (Faucet) for Development
To deploy smart contracts or execute on-chain transactions on aelf, you'll require testnet ELF tokens.
Get ELF Tokens
- CLI
- Web
1. Get Testnet ELF Tokens:
To receive testnet ELF tokens, run this command after replacing $WALLET_ADDRESS and $WALLET_PASSWORD with your wallet details:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export WALLET_ADDRESS="YOUR_WALLET_ADDRESS"
curl -X POST "https://faucet.aelf.dev/api/claim?walletAddress=$WALLET_ADDRESS" -H "accept: application/json" -d ""
$headers = @{
"accept" = "application/json"
}
$env:WALLET_ADDRESS = "YOUR_WALLET_ADDRESS"
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://faucet.aelf.dev/api/claim?walletAddress=$env:WALLET_ADDRESS" -Method POST -Headers $headers -Body ""
2. Check ELF Balance:
To check your ELF balance, use:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
aelf-command call ASh2Wt7nSEmYqnGxPPzp4pnVDU4uhj1XW9Se5VeZcX2UDdyjx -a $WALLET_ADDRESS -p $WALLET_PASSWORD -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io GetBalance
aelf-command call ASh2Wt7nSEmYqnGxPPzp4pnVDU4uhj1XW9Se5VeZcX2UDdyjx -a $env:WALLET_ADDRESS -p $env:WALLET_PASSWORD -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io GetBalance
You will be prompted for the following:
Enter the required param <symbol>: ELF
Enter the required param <owner>: **$WALLET_ADDRESS**
You should see the result displaying your wallet's ELF balance.
Go to https://faucet-ui.aelf.dev Enter your address and click Get Tokens.

Deploy Smart Contract:
The smart contract needs to be deployed on the chain before users can interact with it.
Run the following command to deploy a contract. Remember to export the path of AllowanceContract.dll.patched to CONTRACT_PATH.
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export CONTRACT_PATH=$(find ~+ . -path "*patched*" | head -n 1)
aelf-deploy -a $WALLET_ADDRESS -p $WALLET_PASSWORD -c $CONTRACT_PATH -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io/
$CONTRACT_PATH = Get-ChildItem -Recurse -Filter "*patched*" | Select-Object -First 1 -ExpandProperty FullName
$env:CONTRACT_PATH = $CONTRACT_PATH
aelf-deploy -a $env:WALLET_ADDRESS -p $env:WALLET_PASSWORD -c $env:CONTRACT_PATH -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io/
-
Please wait for approximately 1 to 2 minutes. If the deployment is successful, it will provide you with the contract address.

-
Copy the smart contract address from the
addressfield
-
Export your smart contract address:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export CONTRACT_ADDRESS="YOUR_SMART_CONTRACT_ADDRESS e.g. 2LUmicHyH4RXrMjG4beDwuDsiWJESyLkgkwPdGTR8kahRzq5XS"
$env:CONTRACT_ADDRESS="YOUR_SMART_CONTRACT_ADDRESS e.g. 2LUmicHyH4RXrMjG4beDwuDsiWJESyLkgkwPdGTR8kahRzq5XS"
ℹ️ Note: You are to copy the smart contract address as we will be referencing it in the next steps!
🎉 You have successfully deployed your Allowance smart contract on the aelf testnet! In the next steps, we will be building the frontend components that allow us to interact with our deployed smart contract!
Step 6 - Interact with Your Deployed Smart Contract through dApp
Project Setup
Let's start by cloning the frontend project repository from github.
git clone https://github.com/AElfProject/aelf-samples.git
- Next, navigate to the frontend project directory with this command:
cd aelf-samples/allowance/2-dapp
- Once you're inside the
2-dappdirectory, open the project with your preferred IDE (e.g., VSCode). You should see the project structure as shown below.
Install necessary libraries
- Run this command in the terminal to install all necessary packages and libraries:
npm install
We are now ready to build the frontend components of our Allowance dApp.
Configure Portkey Provider & Write Connect Wallet Function
Now, we'll set up our Portkey wallet provider to allow users to connect their Portkey wallets to the dApp and interact with the smart contract. We'll be interacting with the already deployed RoleContract and AllowanceContract for this tutorial.
Step 1: Locate the File:
- Go to the
src/hooks/useSmartContract.tsfile.
Step 2: Fetch the Smart Contract:
-
Find the comment
//Step A - Function to fetch a smart contract based on deployed wallet address -
Replace the existing
fetchContractfunction with this updated code:
//Step A - Function to fetch a smart contract based on deployed wallet address
const fetchContract = async (address: string) => {
if (!provider) return null;
try {
// 1. get the dAppChain using provider.getChain
const chain = await provider?.getChain("tDVW");
if (!chain) throw new Error("No chain");
// 2. return contract
return chain?.getContract(address);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error, "====error");
return;
}
};
-
Find the comment
// Step B - fetch role-contract -
Replace the existing
getRoleContractfunction with this updated code:
// Step B - fetch role-contract
const getRoleContract = async () => {
//Replace with Address of Deployed Role Smart Contract
const contract = await fetchContract(
"your_deployed_role_smart_contract_address"
);
contract && setRoleContract(contract);
};
-
Find the comment
// Step C - fetch allowance-contract -
Replace the existing
getAllowanceContractfunction with this updated code:
// Step C - fetch allowance-contract
const getAllowanceContract = async () => {
//Replace with Address of Deployed Allowance Smart Contract
const contract = await fetchContract(
"your_deployed_allowance_smart_contract_address"
);
contract && setAllowanceContract(contract);
};
ℹ️ Note: You are to replace the address placeholder with your deployed Role and Allowance smart contract address from "Deploy Smart Contract" steps (Step 3 and 5)!
example: "your_deployed_role_smart_contract_address", "your_deployed_allowance_smart_contract_address"
Explanation:
-
fetchContractFunction: This function fetches a smart contract based on the given chain symbol (e.g., "AELF" or "tDVW") and the contract address.- Check Provider : If no provider is available, the function returns null.
- Fetch Chain : The function fetches chain information using the provider.
- Get Contract : It retrieves the smart contract instance from the chain.
-
getRoleContractFunction: This function fetches the role smart contract. -
getAllowanceContractFunction: This function fetches the allowance smart contract.
AELF represents the mainnet chain and tDVW represents the testnet chain respectively on aelf blockchain.
Step 3. Initialize and Fetch the Smart Contracts:
-
Find the comment
// Step D - Effect hook to initialize and fetch the smart contract when the provider changes -
Replace the existing
useEffectwith this updated code:
// Step D - Effect hook to initialize and fetch the smart contract when the provider changes
useEffect(() => {
getRoleContract();
getAllowanceContract();
}, [provider]); // Dependency array ensures this runs when the provider changes
Explanation:
useEffectHook : This hook initializes and fetches the smart contracts when the provider changes.- Check Provider : If no provider is available, the function returns null.
- Fetch Contracts : It fetches and sets the smart contracts.
By following these steps, we'll configure the Portkey provider to connect users' wallets to our dApp and interact with the Role and Allowance smart contracts including assigning specific roles and allowance related functionalities. This setup will enable our frontend components to perform actions like Set Roles , Get Roles , Set Allowance , Get Allowance and Spend Allowed Funds.
Configure Connect Wallet Function
Step 1: Locate the File
- Go to the
src/components/layout/header/index.tsxfile.
Step 2: Write the Connect Wallet Function
-
The
header/index.tsxfile is the header of our allowance dApp. It allows users to connect their Portkey wallet with the allowance dApp. -
Before users can interact with the smart contract, we need to write the
Connect Walletfunction. -
Find the comment
// Step E - Connect Portkey Wallet. -
Replace the existing connect function with this code snippet:
// Step E - Connect Portkey Wallet
const connect = async (walletProvider?: IPortkeyProvider) => {
const accounts = await (walletProvider ? walletProvider : provider)?.request({
method: MethodsBase.REQUEST_ACCOUNTS,
});
const account = accounts?.AELF && accounts?.AELF[0];
if (account) {
setCurrentWalletAddress(account.replace(/^ELF_/, "").replace(/_AELF$/, ""));
setIsConnected(true);
}
!walletProvider && toast.success("Successfully connected");
};
Explanation:
connectFunction : This function connects the user's Portkey wallet with the dApp.- Fetch Accounts : It fetches the wallet accounts using the provider.
- Log Accounts : Logs the accounts to the console for debugging.
- Set Wallet Address : Sets the current wallet address state variable with the fetched account.
- Update Connection Status : Updates the state to indicate that the wallet is connected.
- User Notification : Displays an alert to notify the user that their wallet is successfully connected.
In this code, we fetch the Portkey wallet account using the provider and update the wallet address state variable. An alert notifies the user that their wallet is successfully connected.
With the connect wallet function defined, we're ready to write the remaining functions in the next steps.
Configure Set Admin Role
Step 1: Locate the File
- Go to the
src/pages/home/index.tsxfile. This file contains all the functionalities like initialize Contract, SetAdmin, GetAdmin etc.
Step 2: Prepare Form to set Roles
-
Find the comment
// Step F - Configure Role Form. -
Replace the form variable with this code snippet:
// Step F - Configure Role Form
const form = useForm <z.infer <typeof formSchema>>{
resolver: zodResolver(formSchema),
defaultValues: {
address: "",
},
};
Here's what the function does:
-
Initializes a new form variable with default values needed to set roles.
-
Field include:
address.
Now the form is ready for users to fill in the necessary details.
Initialize Contract & Set Default Admin
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step G - Initialize Role Contract. -
Replace the existing
initializeContractfunction with this code snippet:
// Step G - Initialize Role Contract
const initializeContract = async () => {
let loadingId;
try {
// Start Loading
loadingId = toast.loading("Contract Initializing InProgress..");
await roleContract?.callSendMethod(
"Initialize", // Function Name
currentWalletAddress as string, // User Wallet Address
{} // No Arguments
);
// Update Loading Message with Success
toast.update(loadingId, {
render: `Contract Initialize Successful`,
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
setIsContractInitialize(true);
} catch (error: any) {
// Update Loading Message with Error
toast.update(loadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
return "error";
} finally {
// Remove Loading Message
removeNotification(loadingId as Id);
return;
}
};
Set Admin Role
-
Write the function to
Set Users Role -
Find the comment
// Step H - Set Differentt Users Role. -
Replace the existing
setAuthorityfunction with this code snippet:
// Step H - Set Differentt Users Role
const setAuthority = async (values: { address: string }, type: string) => {
let loadingId;
try {
// Start Loading
loadingId = toast.loading("Set Authority InProgress..");
setFormLoading(true);
// Prepare Arguments for set Admin
const sendData = values.address;
// Call the appropriate smart contract method based on the type (Admin, Parent, or Child)
await roleContract?.callSendMethod(
type === ROLE.admin
? "SetAdmin"
: type === ROLE.parent
? "SetParent"
: "SetChild",
currentWalletAddress as string,
sendData // Pass the address as the argument
);
// Update Loading Message with Success
toast.update(loadingId, {
render: `Set ${type} Successful`,
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
// Fetch and update the role data from the contract after successful execution
getAuthorityData();
return "success";
} catch (error: any) {
// Update Loading Message with Error
toast.update(loadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
return "error";
} finally {
// Close Form Modal
handleCloseModal();
// Remove Loading Message
removeNotification(loadingId as Id);
setFormLoading(false);
}
};
What This Function Does:
- Calls Smart Contract Method : It interacts with the blockchain smart contract to set admin, parent and child using their respective wallet address.
Next, we'll Handle the submit form to set the roles function.
Submit Set Admin Role
Write the function to handle the submit form to set the users' role.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step I - Handle Submit Form. -
Replace the existing
onSubmitfunction with this code snippet:
// Step I - Handle Submit Form
const onSubmit = async (values: { address: string }) => {
// Set form loading state
setFormLoading(true);
// Check if the contract is initialized, if not, initialize it
if (!isContractInitialize) {
await initializeContract(); // Initialize the smart contract if not already done
}
// Call the setAuthority function to set the authority (Admin/Parent/Child) based on the roleType
await setAuthority(values, roleType); // Pass the form values and role type (Admin/Parent/Child)
};
Next, we'll write the Get Role Details function.
Get Role Details
-
Write the function to
Get Roles Details -
Find the comment
// Step J - Get Role Details. -
Replace the existing
getAuthorityDatafunction with this code snippet:
// Step J - Get Role Details
const getAuthorityData = async () => {
setLoading(true);
try {
// Fetch admin, parent, and child roles simultaneously using Promise.all
const [admin, parent, child] = await Promise.all([
roleContract?.callViewMethod("GetAdmin", ""),
roleContract?.callViewMethod("GetParent", ""),
roleContract?.callViewMethod("GetChild", ""),
]);
// If all roles are successfully fetched
if (admin && parent && child) {
// Set the role state with the retrieved admin, parent, and child values
setRole({
Admin: admin?.data?.value,
Parent: parent?.data?.value,
Child: child?.data?.value,
});
}
} catch (error) {
// Log any error that occurs during the process
console.log("error======", error);
} finally {
// Stop the loading indicator, whether or not the request was successful
setLoading(false);
}
};
What This Function Does:
- Calls Smart Contract Methods : It interacts with the blockchain smart contract to get the addressess of the admin, parent and child roles respectively. Once the wallet addresses based on the roles are present, FE will display different components for each user role, like Admin, Parent, and Child. Each role has specific actions they can perform:
- Admin Role : The admin can assign roles to both parent and child.
- Parent Role : The parent can assign the child role and set an allowance for the child.
- Child Role : The child can spend money, but only up to the allowance set by the parent.
Now that we've finished integrating the functionality of the RoleContract, let's move on to the functions of the AllowanceContract.
Configure Set Allowance by Parent
Step 1: Locate the File
- Go to the
src/components/parent/index.tsxfile. This file contains functionalities like initialize contract, set allowance and get allowance.
Step 2: Configure form
Write the Function of configure the set allowance form.
-
Find the comment
// Step K - Configure Set Allowance Form. -
Replace the existing code snippet:
// Step K - Configure Set Allowance Form
const form = useForm <z.infer <typeof formSchema>>{
resolver: zodResolver(formSchema),
defaultValues: {
amount: "",
},
};
Check Contract Initialize Status
Write the Function to check contract initialization status of the AllowanceContract.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// step L - Check if Allowance Contract is initialized or not. -
Replace the existing
checkIsContractInitializedfunction with this code snippet:
// step L - Check if Allowance Contract is initialized or not
const checkIsContractInitialized = async () => {
try {
const result = await allowanceContract?.callViewMethod("IfInitialized", ""); // Call the IfInitialized method which is present on Smart Contract
if (result?.data) {
setIsContractInitialize(true);
}
} catch (error) {
console.log("error", error);
}
};
What This Function Does:
- Calls Smart Contract Methods : It interacts with the allowance contract to get the initialization status of the allowance contract.
Initialize Allowance Contract
Write the function to initialize the AllowanceContract.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step M - Initialize Allowance Contract. -
Replace the existing
initializeContractfunction with this code snippet:
// Step M - Initialize Allowance Contract
const initializeContract = async () => {
let loadingId;
try {
// Start Loading
loadingId = toast.loading("Contract Initializing InProgress..");
await allowanceContract?.callSendMethod(
"Initialize", // Function Name
currentWalletAddress as string, // User Wallet Address
{} // No Arguments
);
// Update Loading Message with Success
toast.update(loadingId, {
render: `Contract Initialize Successful`,
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
setIsContractInitialize(true);
} catch (error: any) {
// Update Loading Message with Error
toast.update(loadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
return "error";
} finally {
// Remove Loading Message
removeNotification(loadingId as Id);
return;
}
};
What This Function Does:
- Calls Smart Contract Methods : It call the Initialize of the allowance contract.
Now that we've finished the initialize contract functionality. Let's move on to the set allowance functionality.
Set Allowance
Write the function for set the allowance value for child by the parent.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// step N - Set AllowanceValue. -
Replace the existing
initializeContractfunction with this code snippet:
// step N - Set AllowanceValue
const setAllowance = async (value: { amount: string }) => {
setFormLoading(true);
let loadingId;
try {
// Start Loading
loadingId = toast.loading("SetAllowance InProgress..");
await allowanceContract?.callSendMethod(
"SetAllowance", // Function Name
currentWalletAddress as string, // User Wallet Address
{ value: value.amount } // Allowance Amount
);
// fetch updated allowance value
getAllowance();
// Update Loading Message with Success
toast.update(loadingId, {
render: `SetAllowance Successful`,
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
} catch (error: any) {
console.error(error);
// Update Loading Message with Error
toast.update(loadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
return "error";
} finally {
// Close Form Modal
handleCloseModal();
// Remove Loading Message
removeNotification(loadingId as Id);
setFormLoading(false);
}
};
What This Function Does:
- Calls Smart Contract Methods : It call the initialization method of the allowance contract.
Let's handle the submit form for set allowance.
Submit Set Allowance Form (Parent)
Write the function to handle the set allowance form.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step O - Handle Set Allowance Submit Form. -
Replace the existing
onSubmitfunction with this code snippet:
// Step O - Handle Set Allowance Submit Form
const onSubmit = async (value: { amount: string }) => {
if (!isContractInitialize) {
await initializeContract();
}
setAllowance(value);
};
As we have completed the step of setting allowance value, now it's time to get that allowance value form the contract.
Get Allowance Value
Write the function for get the allowance value.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// step P - Get AllowanceValue. -
Replace the existing
getAllowancefunction with this code snippet:
// step P - Get AllowanceValue
const getAllowance = async () => {
try {
// Call the smart contract method "GetAllowance" for the child role
const result = await allowanceContract?.callViewMethod(
"GetAllowance",
role.Child
);
// If the result contains a valid allowance value, set it in the state
if (result?.data?.value) {
setAllowanceValue(result?.data?.value);
} else {
// If no valid allowance is returned, set the allowance value to null
setAllowanceValue(null);
}
} catch (error) {
// Log any errors that occur during the process
console.log("error", error);
}
};
At this point, we have completed all the functionalities for the parent role and now it's time to prepare functionalities for the child role.
Configure Spend Allowance Form
Step 1: Locate the File
- Go to the
src/components/child/index.tsxfile. This file contains functionalities like spend allowance and get allowance value.
Step 2: Prepare Form for Spend Allowance
-
Find the comment
// Step Q - Configure Spend Allowance Form. -
Replace the form variable with this code snippet:
// Step Q - Configure Spend Allowance Form
const form =useForm <z.infer <typeof formSchema>>{
resolver: zodResolver(formSchema),
defaultValues: {
amount: "0",
},
};
Ge Allowance Value (Child)
Write the function for get the allowance value.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// step R - Get AllowanceValue. -
Replace the existing
getAllowancefunction with this code snippet:
// step R - Get AllowanceValue
const getAllowance = async () => {
try {
// Call the smart contract method "GetAllowance" for the child role
const result = await allowanceContract?.callViewMethod(
"GetAllowance",
currentWalletAddress
);
// If the result contains a valid allowance value, set it in the state
if (result?.data?.value) {
setAllowanceValue(result?.data?.value);
}
} catch (error) {
// Log any errors that occur during the process
console.log("error", error);
}
};
Spend Funds
Write the function to spend the funds by the child.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// step S - Spend Allowance. -
Replace the existing
spendFundsfunction with this code snippet:
// step S - Spend Funds
const spendFunds = async (value: { amount: string }) => {
if(value.amount === "0"){
return
}
let loadingId;
try {
if (Number(allowanceValue) < Number(value.amount)) {
toast.info("Amount should be less then or equal to Allowance value");
return;
}
setFormLoading(true);
// Start Loading
loadingId = toast.loading("Spending Funds InProgress..");
await allowanceContract?.callSendMethod(
"useFunds", // Function Name
currentWalletAddress as string, // User Wallet Address
{ value: value.amount } // Allowance Amount
);
form.reset();
getAllowance();
// Update Loading Message with Success
toast.update(loadingId, {
render: `Funds Spent Successful`,
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
} catch (error: any) {
console.error(error);
// Update Loading Message with Error
toast.update(loadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
return "error";
} finally {
// Remove Loading Message
removeNotification(loadingId as Id);
setFormLoading(false);
}
};
What This Function Does:
- Calls Smart Contract Methods : It calls the useFunds smart contract method to spend the allowance value.
Let's handle the submit form to spend allowance.
Submit Spend Funds Form (Child)
Write the function for handle the spend Funds form.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step T - Handle Spend Funds Submit Form. -
Replace the existing
onSubmitfunction with this code snippet:
// Step T - Handle Spend Funds Submit Form
const onSubmit = (values: { amount: string }) => {
spendFunds(values);
};
Now that we've written all the necessary frontend functions and components, we're ready to run the Allowance dApp application in the next step.
Run Application
In this step, we will run the Allowance dApp application.
- To begin, run the following command on your terminal.
npm run dev
Note: Ensure that you are running this command under the allowance/2-dapp folder.
-
You should observe the following as shown below.
-
Upon clicking on the localhost URL, you should be directed to the Allowance dApp landing page as shown below.
If you are developing and testing this with github codespace, you can use port forward to test the web server that is running in codespace, here is the link on how to use port forward for codespace https://docs.github.com/en/codespaces/developing-in-a-codespace/forwarding-ports-in-your-codespace
-
Usually codespace will automatically forward port, you should see a pop-up message at the bottom right of your codespace browser window as shown in the diagram below:
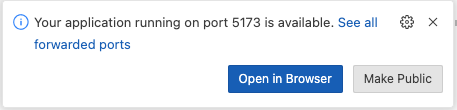
-
Click the link to open the Allowance dApp in the browser.
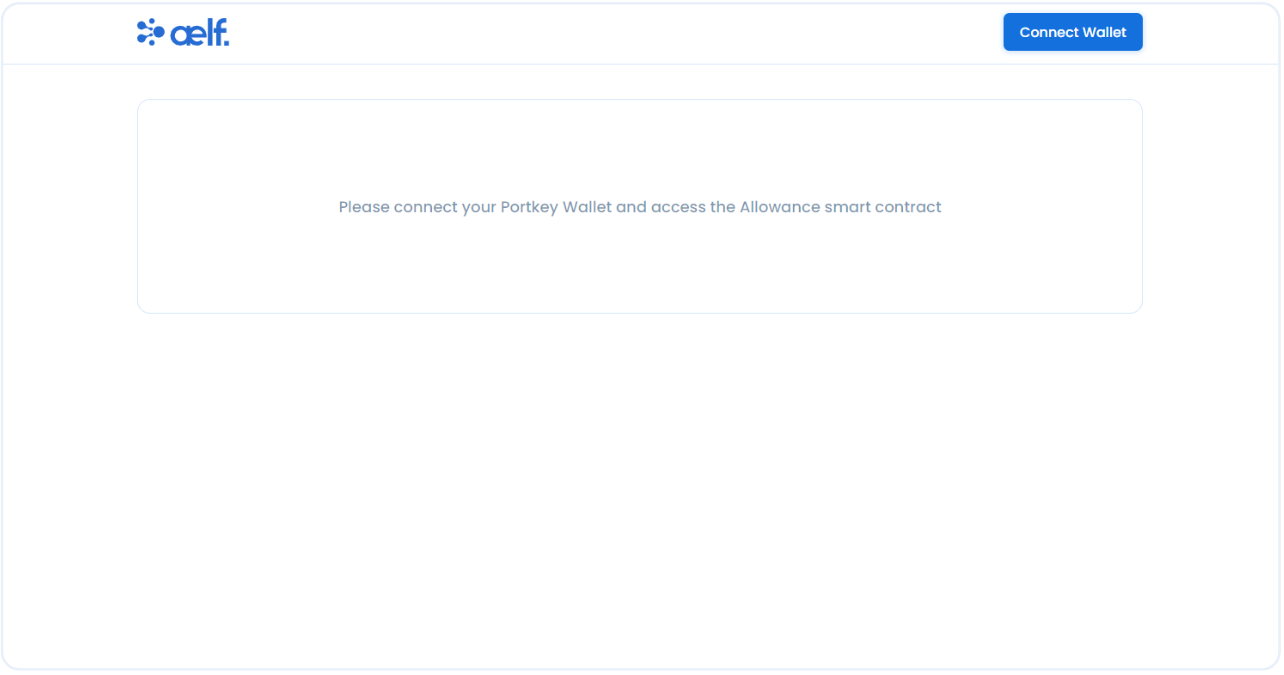
Create Portkey Wallet
Portkey is the first AA wallet from aelf's ecosystem, migrating users, developers and projects from Web2 to Web3 with DID solution.
Users can swiftly log into Portkey via their Web2 social info with no private keys or mnemonics required. Underpinned by social recovery and decentralized guardian design, Portkey safeguards users' assets from centralized control and theft. Portkey has a unique payment delegation mechanism which enables interested parties to function as delegatees to pay for user activities on users' behalf. This means that users can create accounts for free and fees for other usages may also be covered in Portkey.
Portkey also provides crypto on/off-ramp services, allowing users to exchange fiat with crypto freely. It supports the storage and management of various digital assets such as tokens, NFTs, etc. The compatibility with multi-chains and seamless connection to all kinds of DApps makes Portkey a great way to enter the world of Web3.
With DID solution as its core, Portkey provides both Portkey Wallet and Portkey SDKs.
For more information, you may visit the official documentation for Portkey at https://doc.portkey.finance/.
- Download the Chrome extension for Portkey from https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/portkey-wallet/iglbgmakmggfkoidiagnhknlndljlolb.
The Portkey extension supports Chrome browser only (for now). Please ensure that you are using Chrome browser. You may download Chrome from https://www.google.com/intl/en_sg/chrome/.
-
Once you have downloaded the extension, you should see the following on your browser as shown below.

-
Click on
Get Startand you should see the following interface as shown below.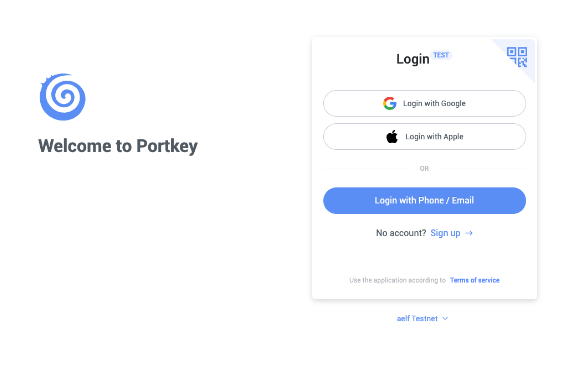
Sign up
-
Switch to aelf Testnet network by selecting it:
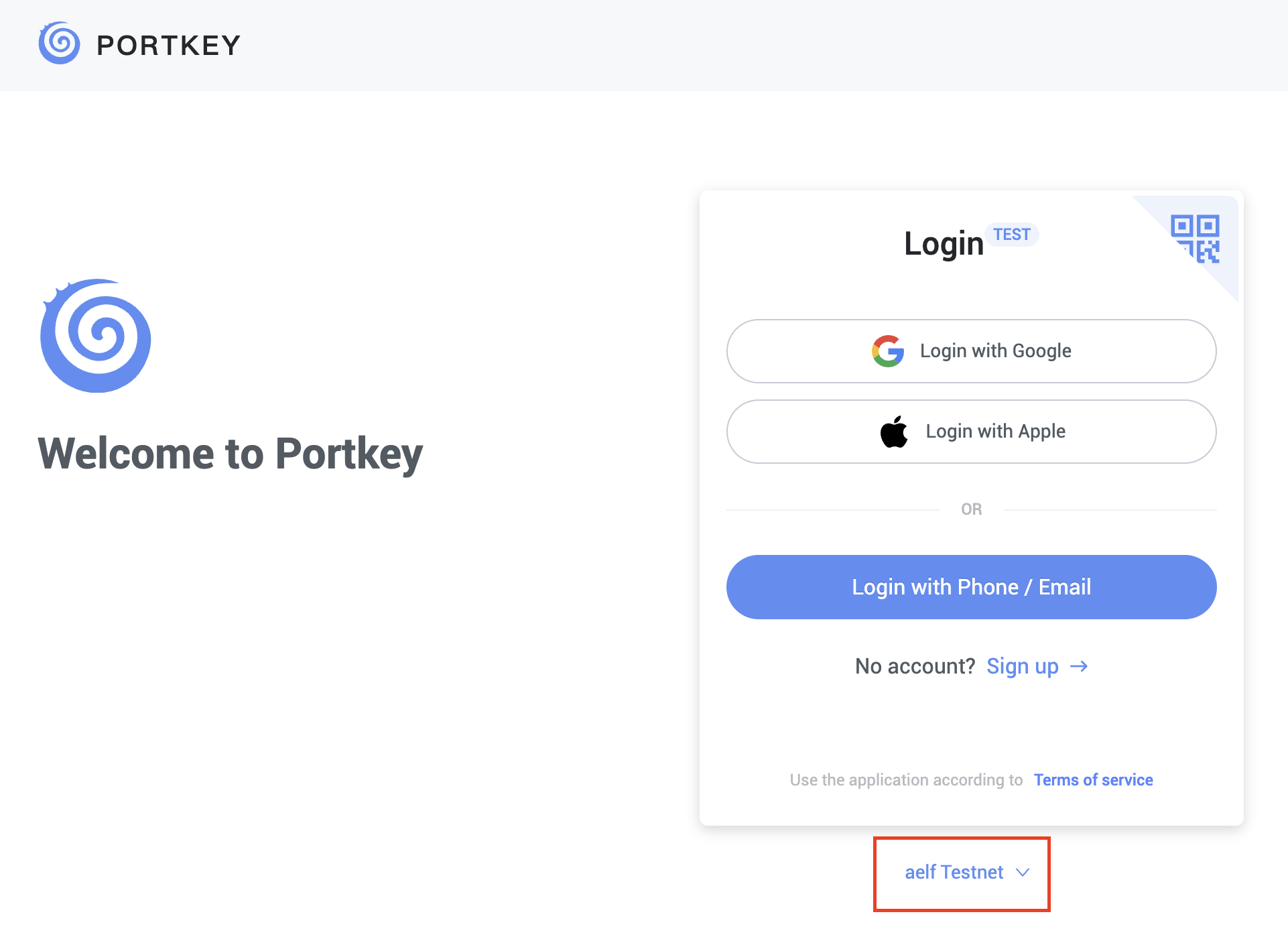
Please make sure you are using aelf Testnet in order to be able to receive your testnet tokens from the Faucet.
-
Proceed to sign up with a Google Account or your preferred login method and complete the necessary accounts creation prompts and you should observe the following interface once you have signed up.
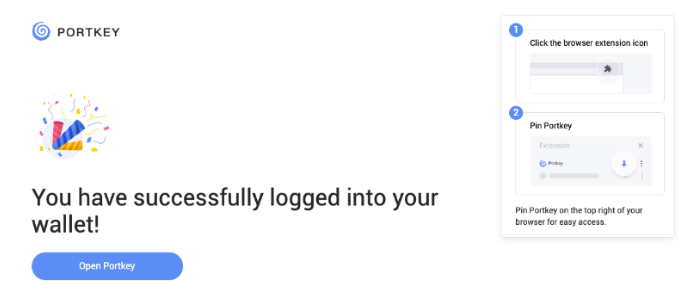
With that, you have successfully created your very first Portkey wallet within seconds. How easy was that?
It is highly recommended to pin the Portkey wallet extension for easier access and navigation to your Portkey wallet!
-
Next, click on ‘Open Portkey’ and you should now observe the following as shown below.
Connect Portkey Wallet
-
Click on "Connect Wallet" to connect your Portkey wallet.
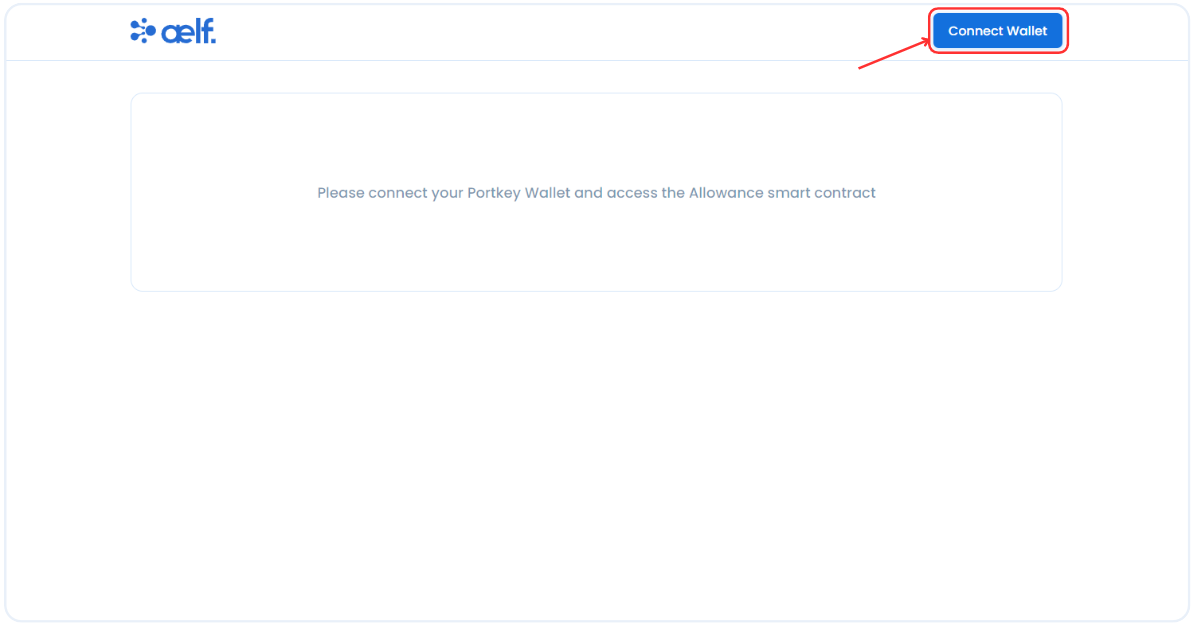
-
The button will change to "Your Wallet Address" when the connection is successful.
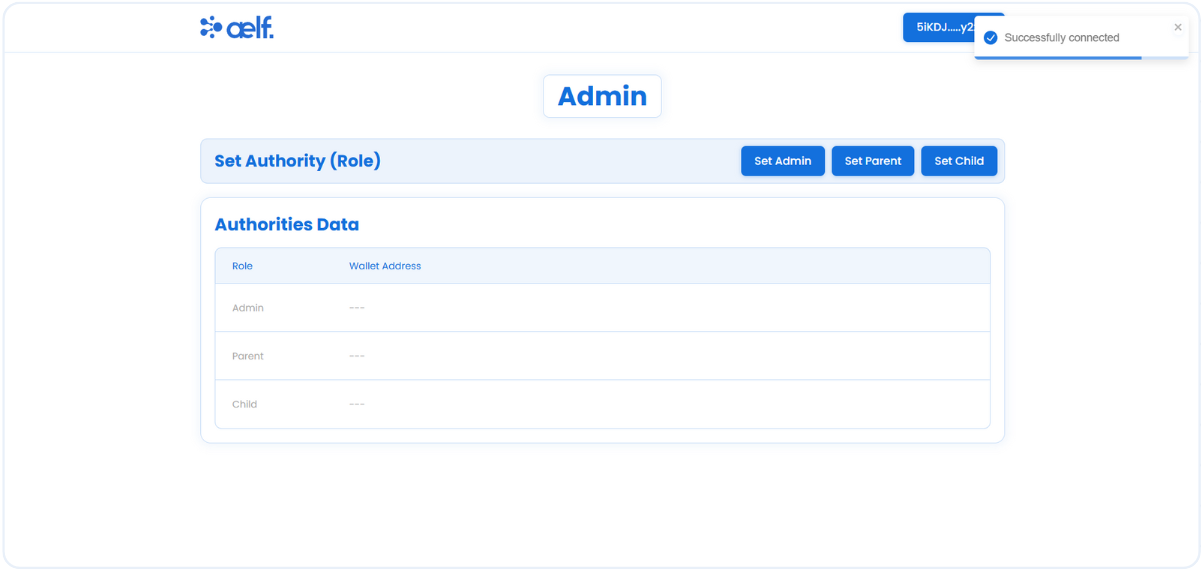 Now we have successfully connected our portkey wallet with Allowance dApp so let's move into set Roles functionality throgh Admin wallet.
Now we have successfully connected our portkey wallet with Allowance dApp so let's move into set Roles functionality throgh Admin wallet.
Set Roles
-
Click on "Set Admin" button to assign the admin role.
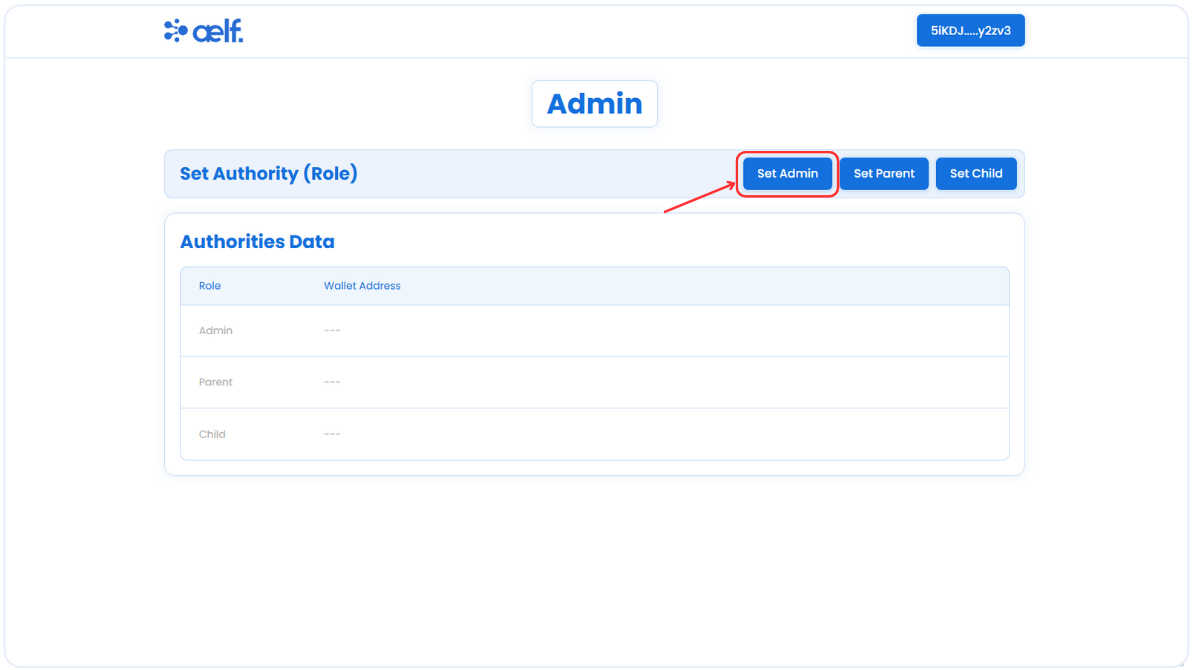
-
A pop-up form will appear to set the admin role. Please enter the wallet address you want to assign as admin address. You can then use this wallet to perform other admin functions.
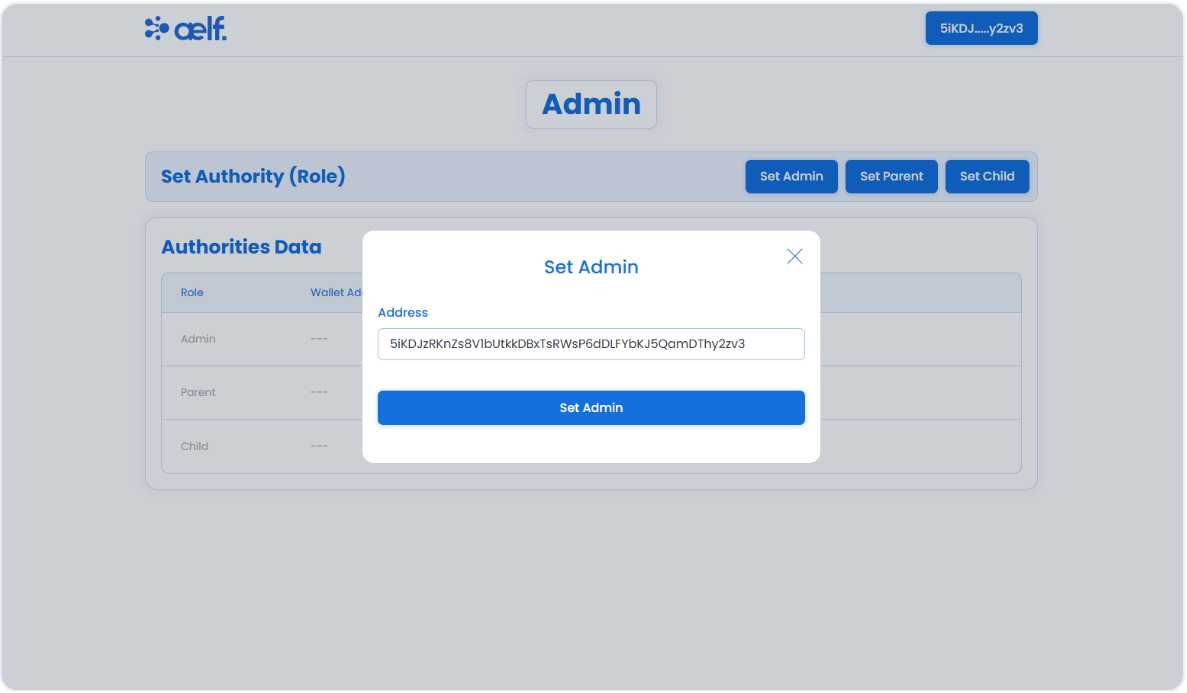
-
Click on the Set Admin button.
-
You will now receive two transaction requests in your Portkey wallet to sign. The first request is to initialize the role contract, and the second is to set the admin role.
-
Click on Sign for both the transaction.
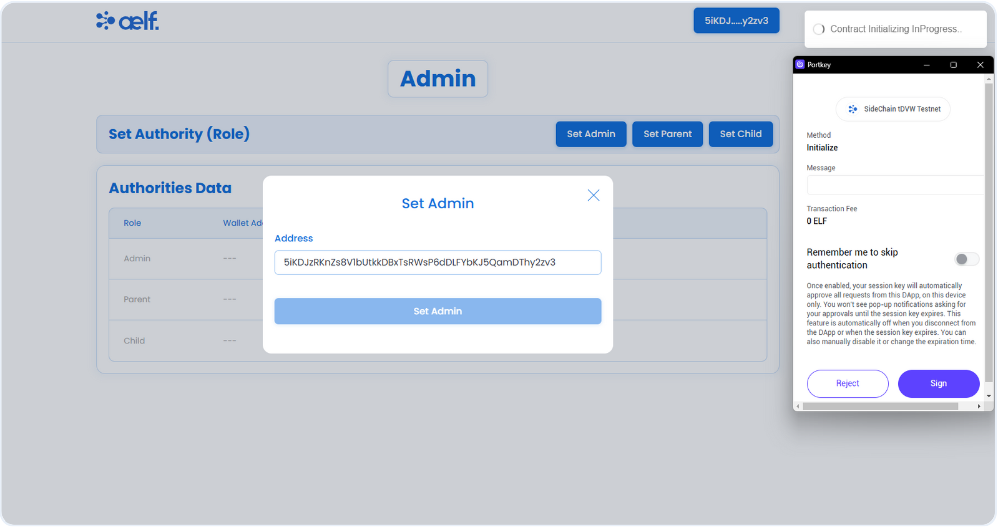
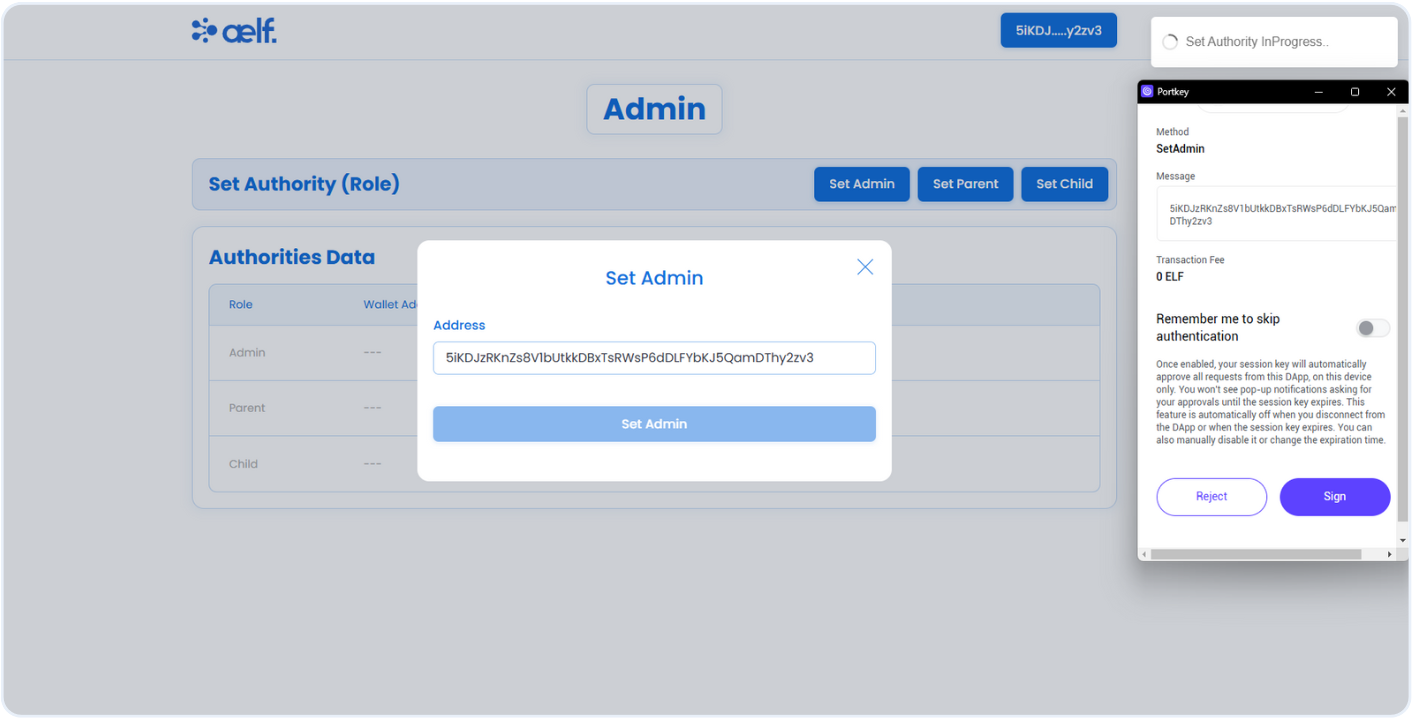
-
After the transaction is successfully processed, you will be able to see the wallet address of the Admin role.
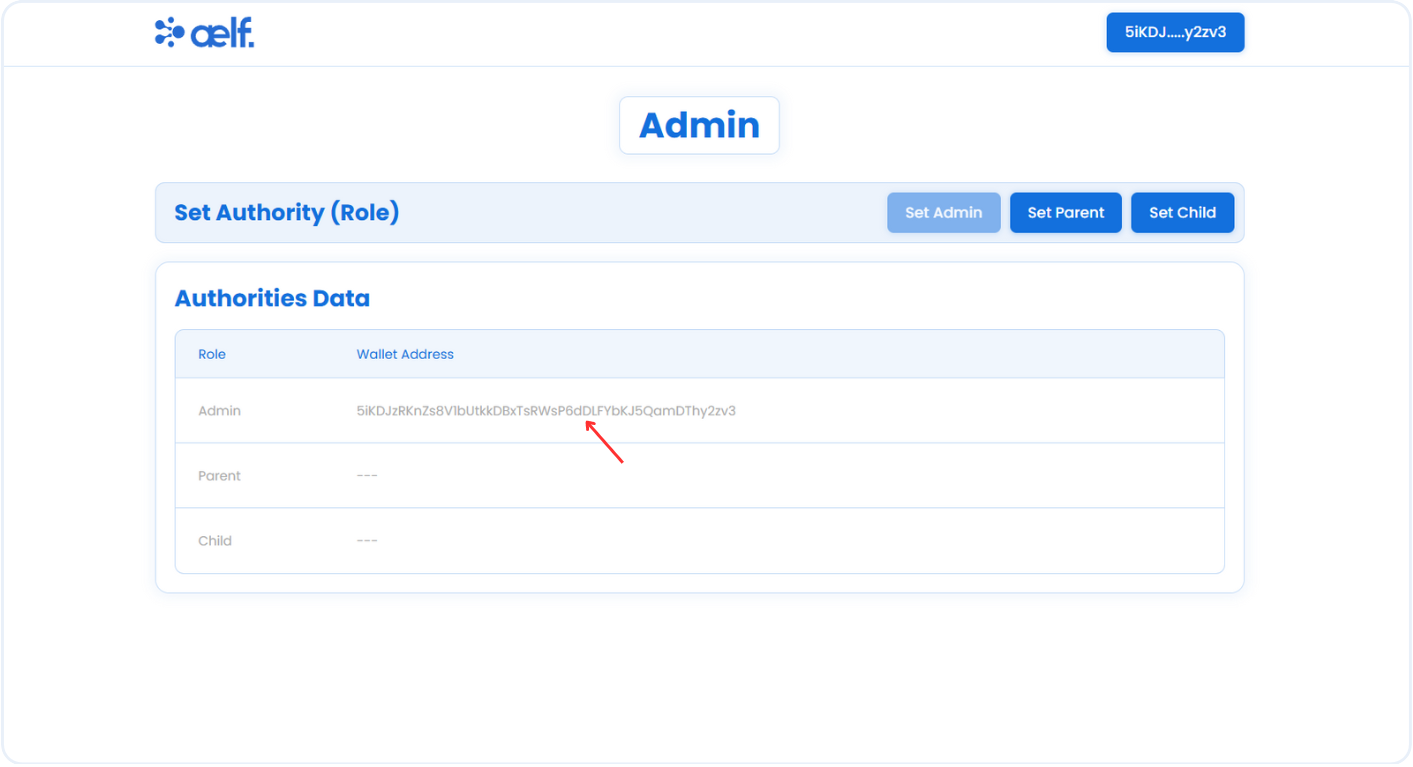
-
As Admin role has been assigned, Please follow same steps to assign the Parent and Child roles.
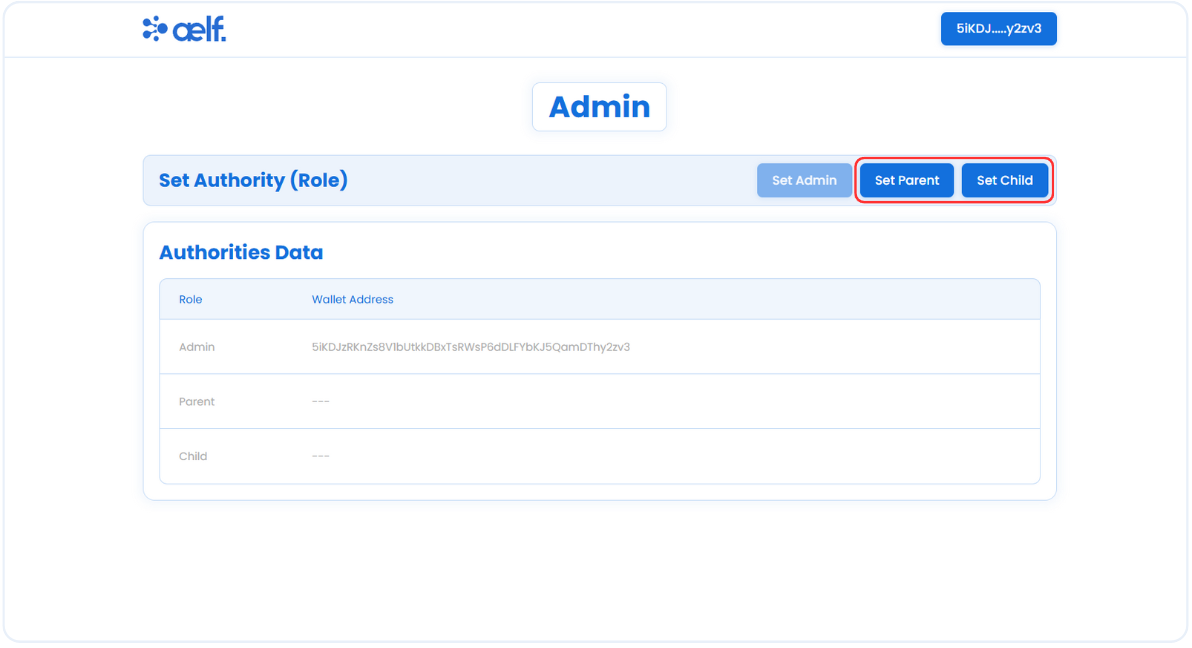
-
After assigning the Parent and Child roles, you will be able to see the wallet addresses for each of the roles.
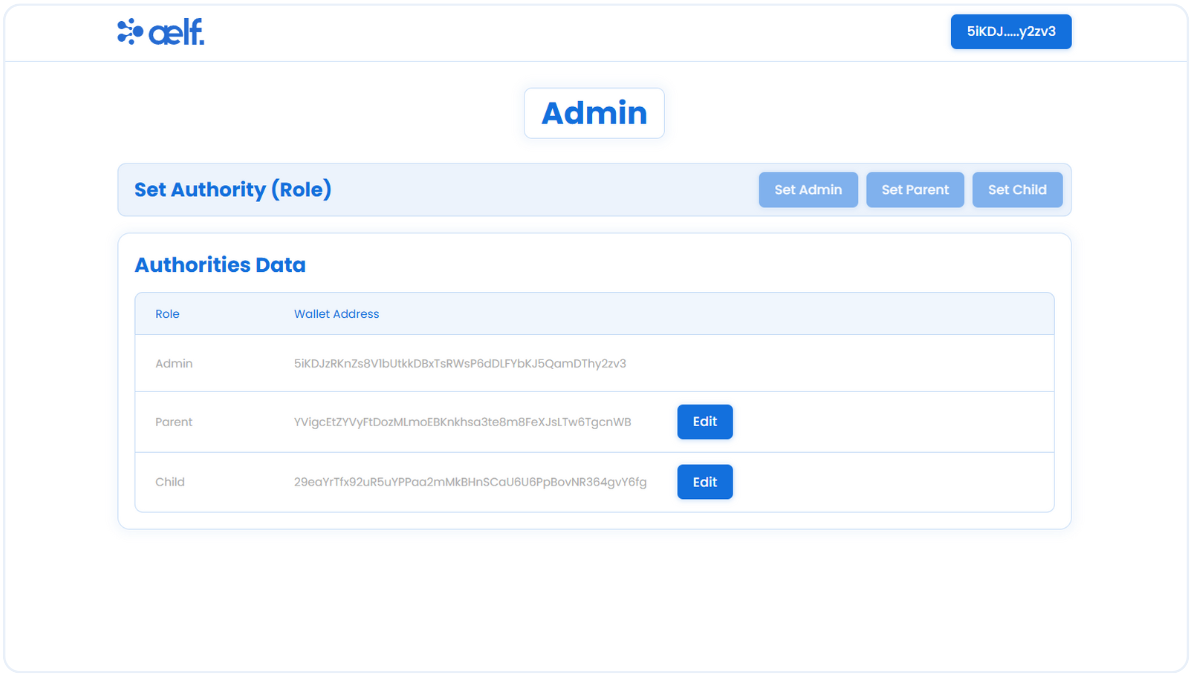
We have now assigned the role using the role contract, and as an Admin, you can update all the roles. Next, we need to work with the allowance contract. To access the parent front end components, connect the Parent address portkey wallet, and you will automatically switch to the Parent role.
Set Allowance (Parent)
As a Parent, you can manage child role functions, such as set a child address, edit the child's address, and set an allowance for the child.
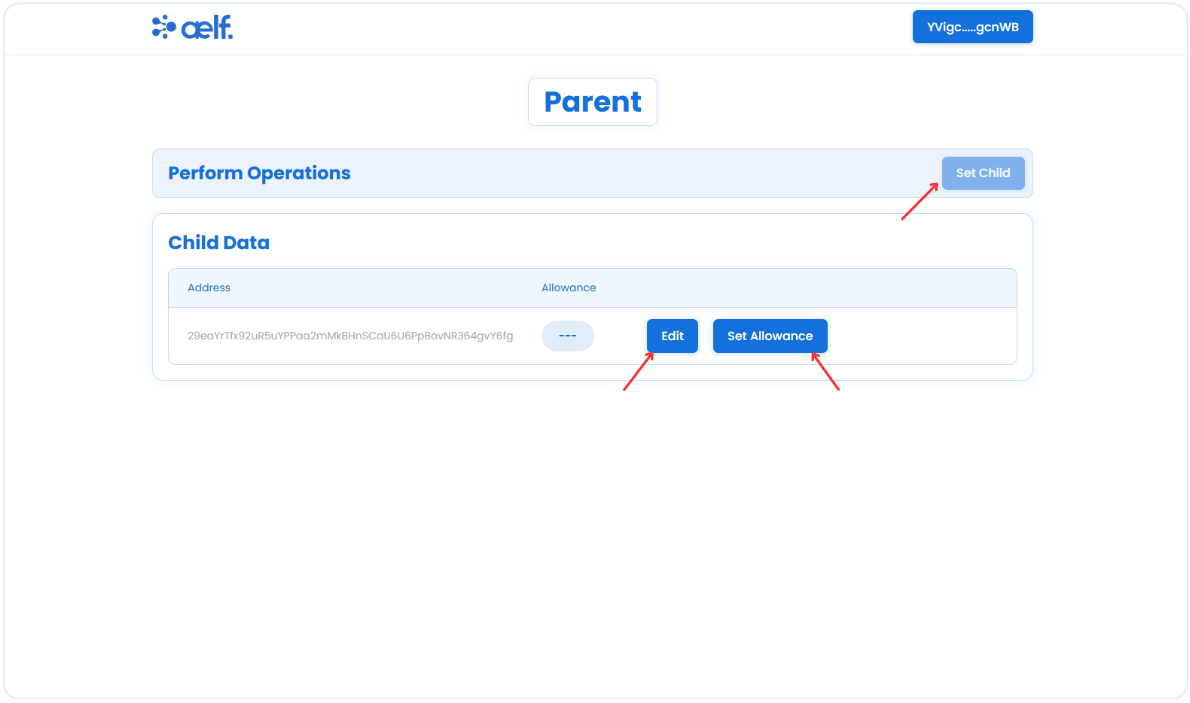
-
Click on Set Allowance button to set the allowance for child.
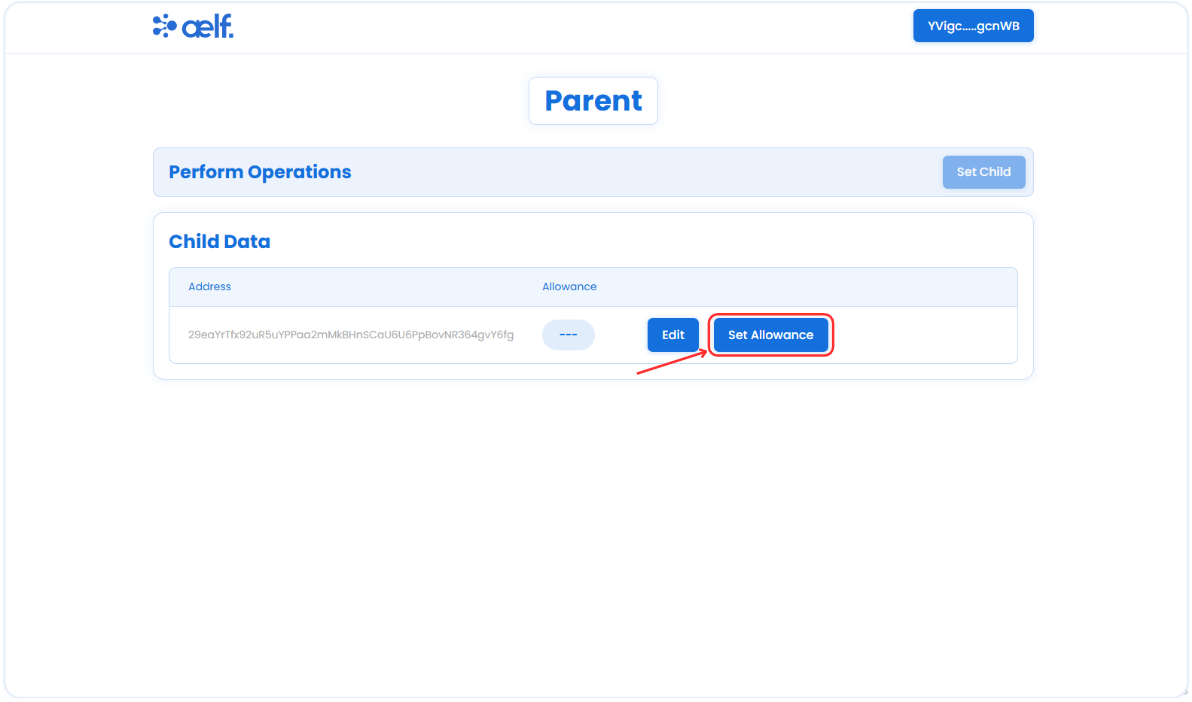
-
A pop-up form will appear to set the allowance. Please enter the amount you want to set as an allowance and click on the Set Allowance button.
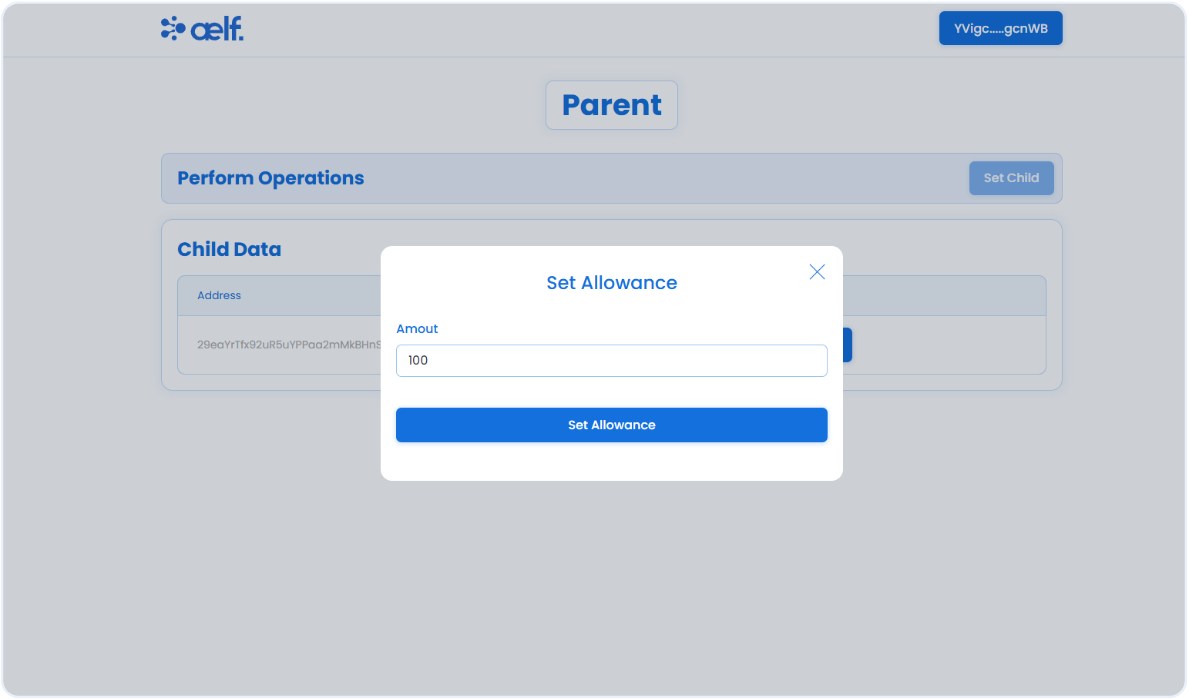
-
You will now receive two transaction requests in your Portkey wallet to sign . The first request is to initialize the allowance contract, and the second is to set the allowance.
-
Click on Sign for both the transaction.
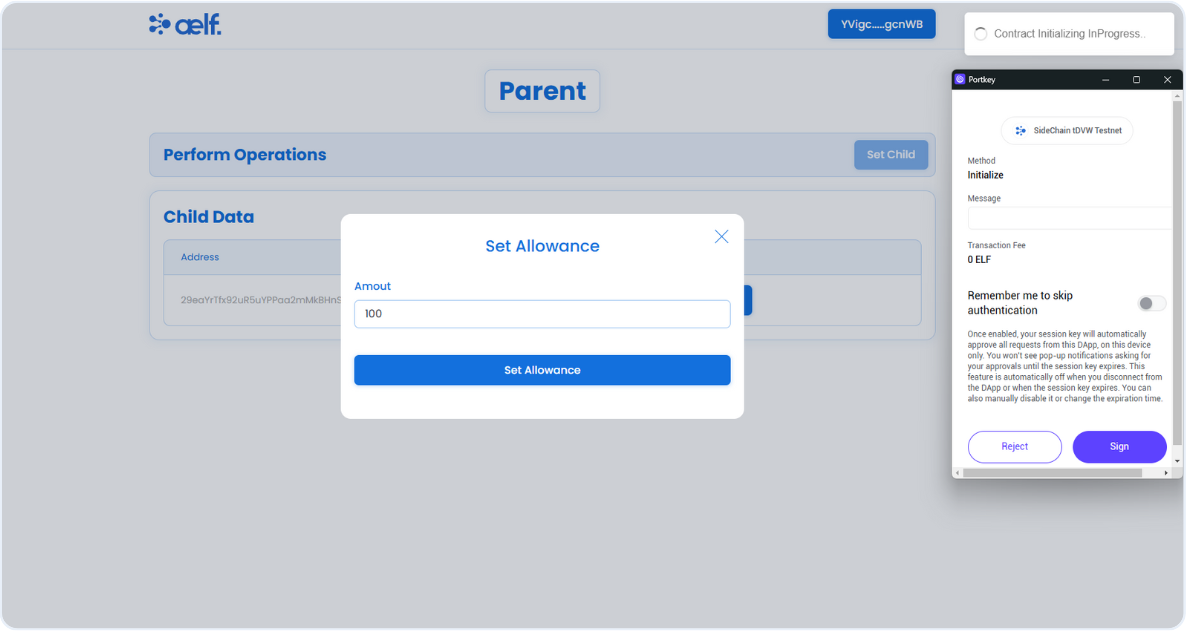
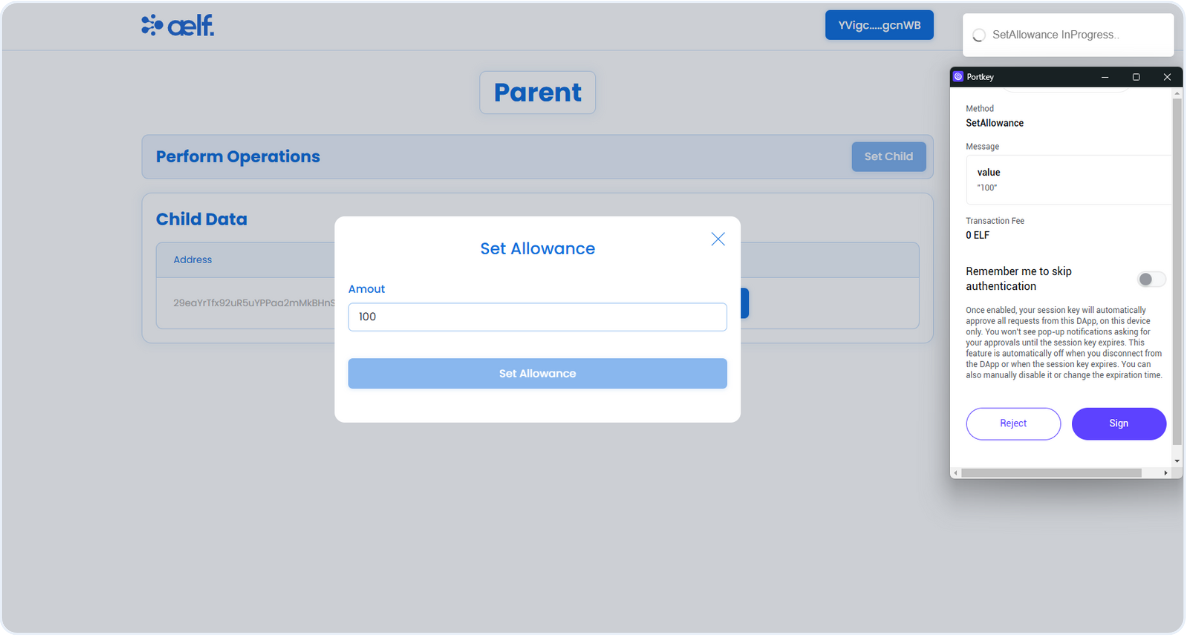
-
After the transaction is successfully processed, allowance value will be appear as shown below.
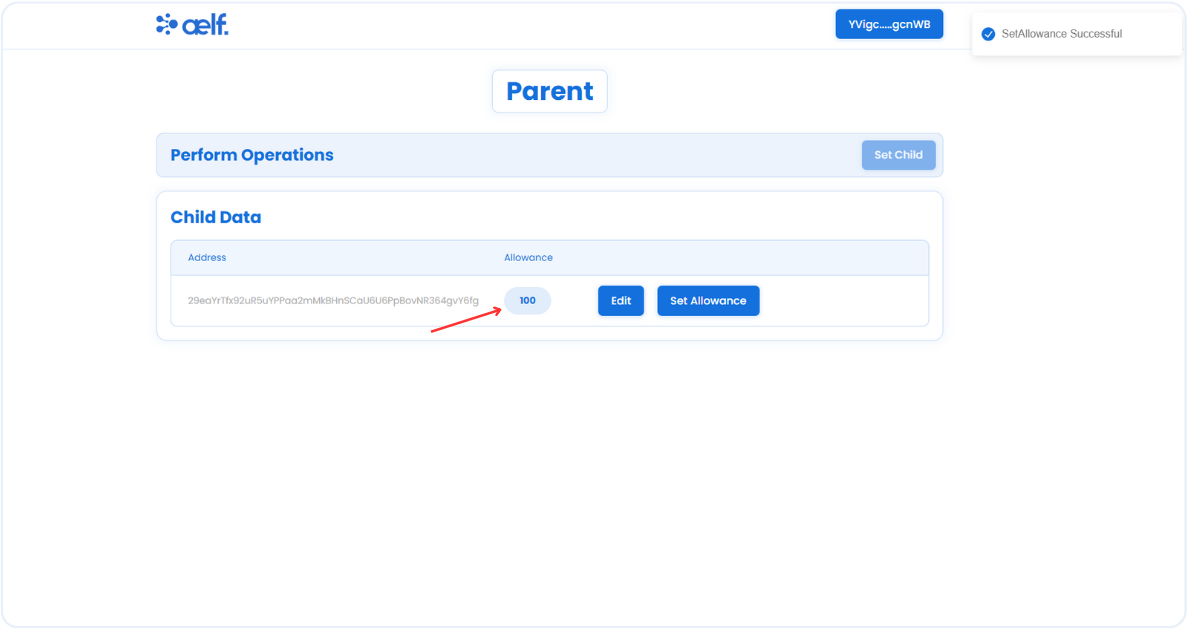
As we hav completed Set Allowance functionality successfully. Let's move to the other functionalities for the child role. To access the child role's front end components, connect the assigned child's Portkey wallet, and you will automatically switch to the child role.
Spend Funds
As a Child, the allowance amount will be visible and the child can spend funds within the assigned allowance limit.
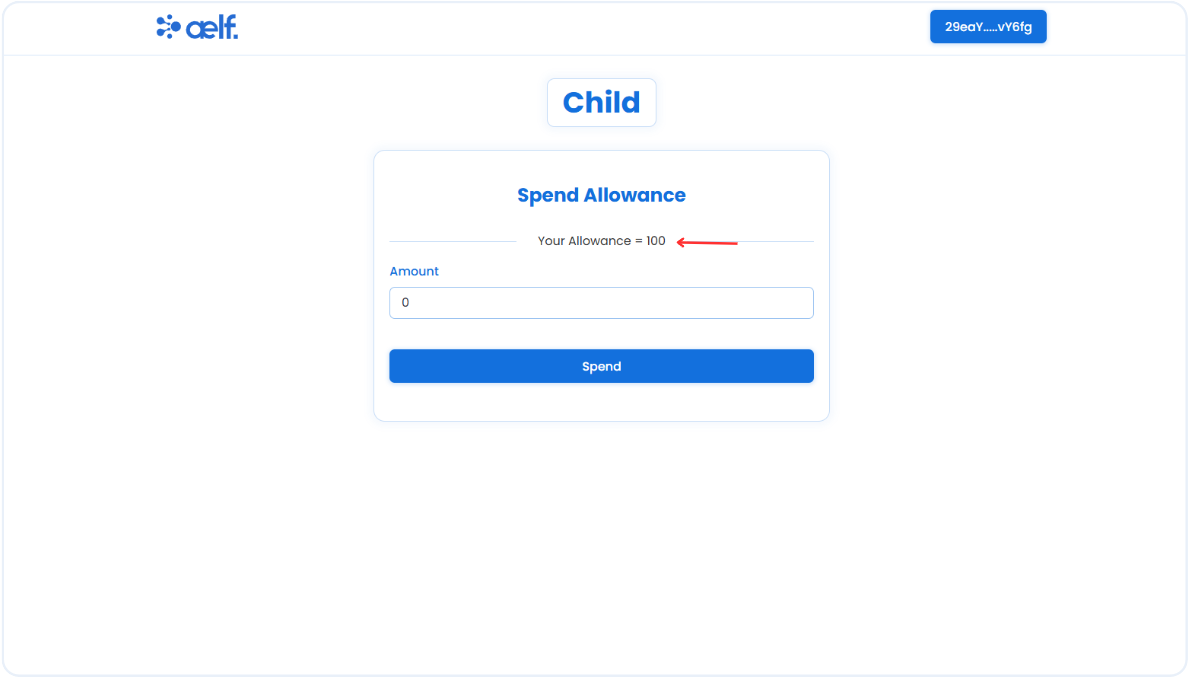
-
Enter the amount you want to spend and click on the Spend button.
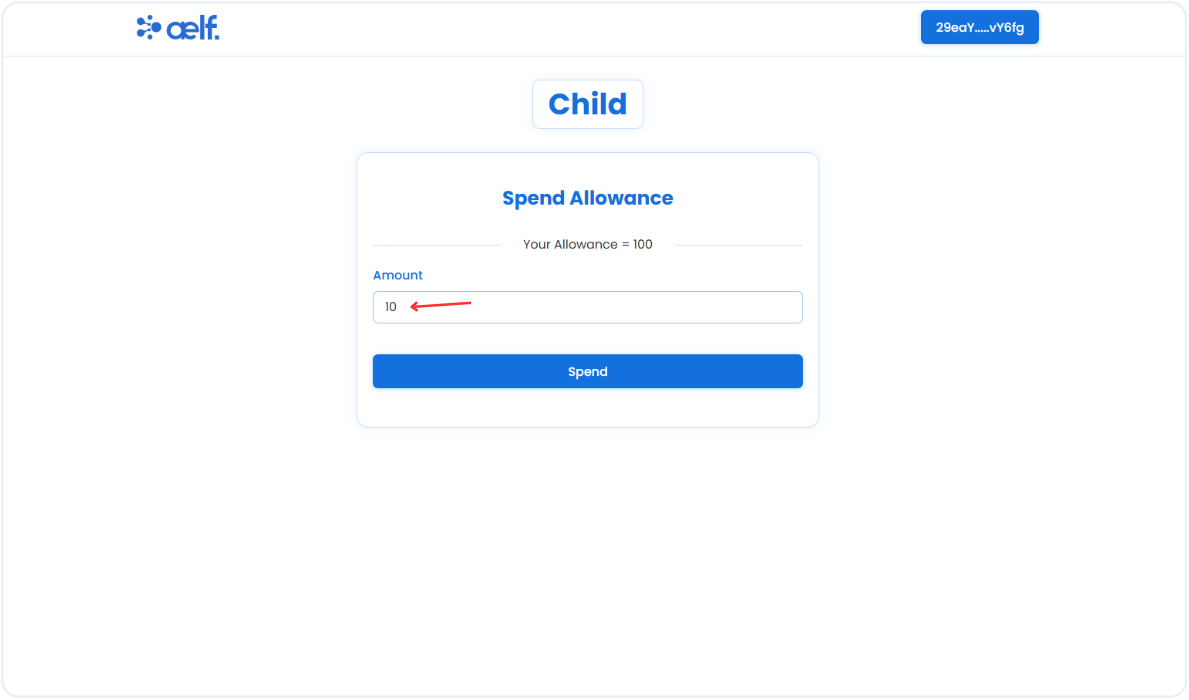
-
Now, You will receive a transaction request on your portkey wallet to Sign the transaction.
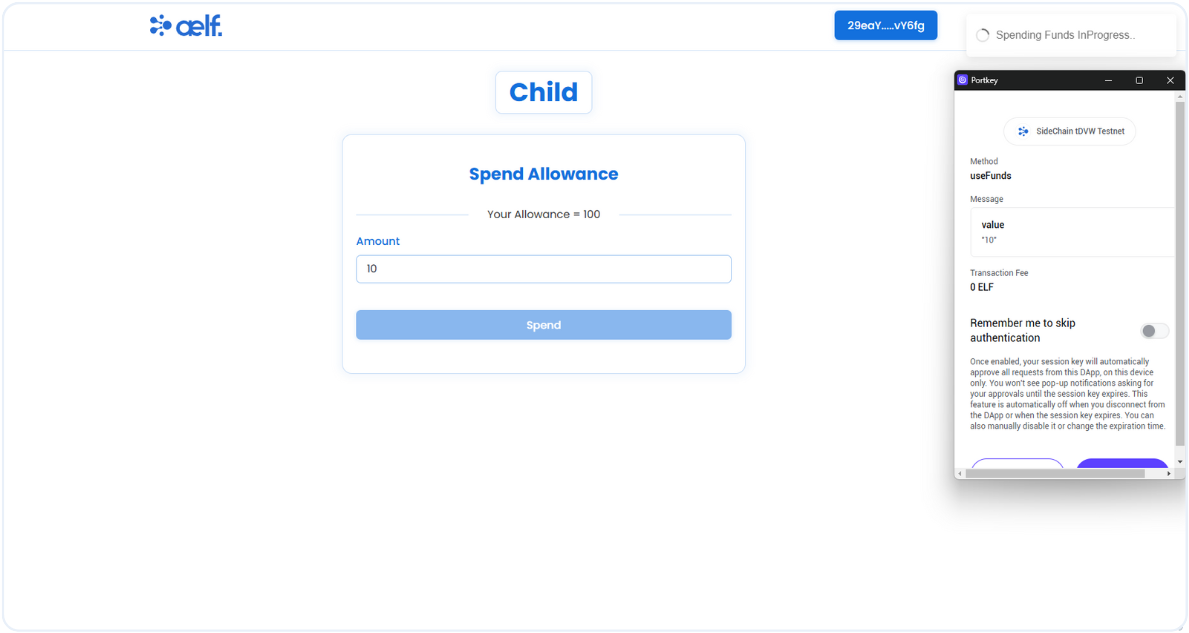
-
Click on Sign the transaction.
-
After the transaction is successfully processed, your allowance value will be updated.
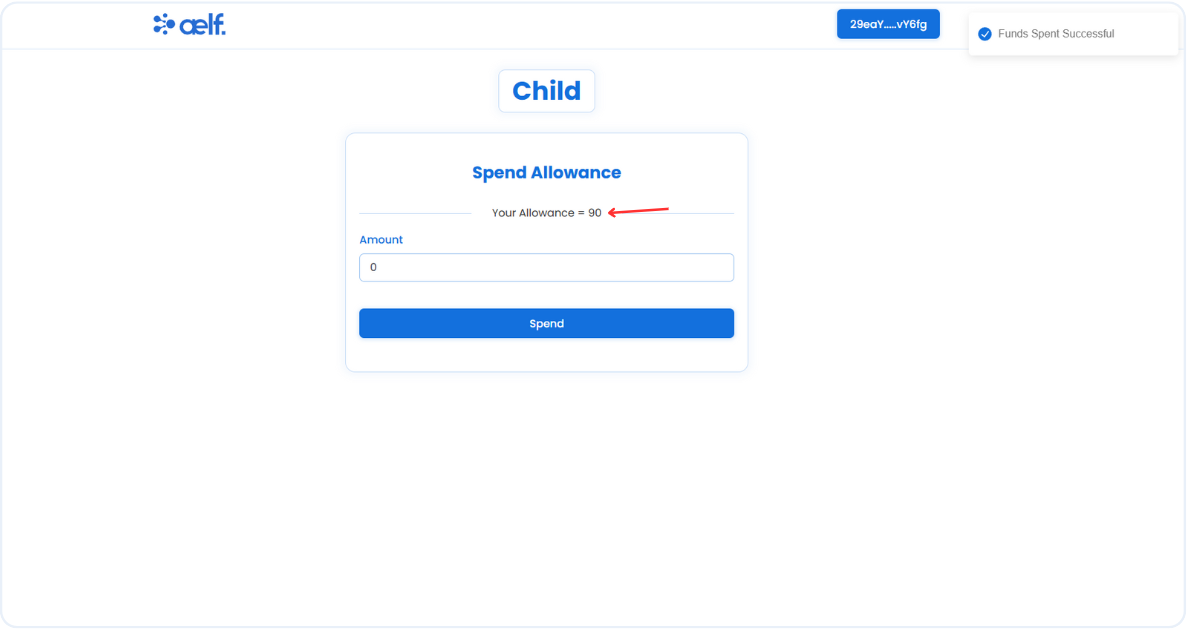
🎉 Congratulations Learners! You have successfully built your Allowance dApp.
🎯 Conclusion
🎉 Congratulations on completing the Allowance dApp tutorial! 🎉 You’ve taken significant steps in setting up your development environment, building and deploying two smart contracts, and creating a fully functional Allowance dApp on the aelf blockchain. 🌟
📚 What You've Learned
Throughout this tutorial, you've mastered:
-
🛠️ Setting Up Your Development Environment: You prepared your workspace by installing and configuring all the necessary tools to kickstart your smart contract project.
-
💻 Developing the Role Smart Contract: You created a Role contract that defines roles and permissions, including Admin, Parent, and Child roles, which allow users to interact according to assigned roles.
-
💻 Developing the Allowance Smart Contract: You built the Allowance contract to enable Parents to set spending limits for Children, creating the foundation of a decentralized allowance management system.
-
🚀 Deploying Both Smart Contracts: You deployed both contracts to the aelf blockchain, enabling your dApp to use the features in a live environment.
-
🔧 Interacting with Your Deployed Smart Contract: You connected the dApp frontend to the blockchain, integrated Portkey for wallet connectivity, and set up functions for managing roles and allowances directly through the dApp interface.
🔍 Final Output
By now, you should have:
-
📜 Two deployed smart contracts — one for managing user roles (Admin, Parent, and Child) and another for setting and managing allowances within the dApp.
-
💻 A fully functional Allowance dApp — allowing users to assign roles, set allowances, and spend funds within set limits, all through a secure and intuitive interface.
➡️ What's Next?
With the foundation in place, consider exploring advanced topics:
-
📈 Enhancing Smart Contract Logic: Add new features, such as notifications for spending limits, allowance resets, or reports on spending habits.
-
🔒 Improving Security: Ensure your dApp and smart contract are secure by implementing best practices and security measures.
-
🌍 Exploring Cross-Chain Features: Expand your dApp’s reach by exploring aelf’s cross-chain interoperability, enabling interactions with other blockchain networks
You’ve now acquired the tools to take your Allowance dApp to the next level! Keep building, innovating, and exploring with aelf. 🚀
Happy coding and growing your Allowance dApp! 😊