Single Pool Staking dApp
Description: The Single Pool Staking dApp is a decentralized application built on the aelf blockchain that allows users to stake their tokens in a single staking pool. Users can earn rewards based on the amount and duration of their staked assets, with staking and reward distribution processes fully automated and secured by blockchain technology. The dApp offers a transparent and simple interface for users to monitor their staked assets and track reward accumulation over time.
Purpose: The Single Pool Staking dApp aims to demonstrate the seamless integration of staking mechanisms with blockchain, providing users with a secure, transparent, and efficient way to grow their holdings. It serves as an educational tool for learning about staking contracts and their role in decentralized finance (DeFi), while showcasing the potential of blockchain technology for creating decentralized financial services that offer fairness and trustless reward distribution.
Difficulty Level: Moderate
Step 1 - Setting up your development environment
- Local
- Codespaces
- Basic knowledge of terminal commands
- IDE - Install VS Code
Note for Apple Silicon users:
Ensure that Rosetta is installed, if it is not, use the following command:
softwareupdate --install-rosetta
Install Required Packages
- Install dotnet 8.0.x SDK
- Install aelf contract templates
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
dotnet new --install AElf.ContractTemplates
dotnet new install AElf.ContractTemplates
AELF.ContractTemplates contains various predefined templates for the ease of developing smart contracts on the aelf blockchain.
- Install aelf deploy tool
dotnet tool install --global aelf.deploy
aelf.deploy is a utility tool for deploying smart contracts on the aelf blockchain. Please remember to export PATH after installing aelf.deploy.
ℹ️ Note: If you have installed aelf.deploy and your terminal says that there is no such command available, please uninstall and install aelf.deploy.
Install Node.js and Yarn
Install aelf-command
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
sudo npm i -g aelf-command
npm i -g aelf-command
aelf-command is a CLI tool for interacting with the aelf blockchain, enabling tasks like creating wallets and managing transactions. Provide required permissions while installing aelf-command globally.
- Visit aelf-devcontainer-template.
- Click the
Use this templatebutton. ChooseCreate a new repository. - Enter a suitable repository name. Click
Create repository. - Within the GitHub interface of your new repository, click on
Code. SelectCodespaces. - Click on the
+sign to create a new Codespace. - After some time, your workspace will load with the contents of the repository. You can now continue your development using GitHub Codespaces.
Step 2 - Develop Smart Contract
Start Your Smart Contract Project
-
Open your
Terminal. -
Enter the following command to generate a new project:
mkdir single-pool-staking-dapp
cd single-pool-staking-dapp
dotnet new aelf -n SinglePoolStaking
Adding Your Smart Contract Code
Now that we have a template Single Pool Staking project, we can customise the template to incorporate our own contract logic. Let's start by implementing methods to handle the basic functionality like deposit tokens to the staking pool, withdraw tokens from the staking pool, withdrawing tokens before the lock(stake) period ends (forceWithdraw), get the reward amount for an address from the pool, fetch all the deposits linked to a user and retrieve the total staked amount in the contract. Single Pool Staking dApp includes the below functionalities like:
- Deposit: Allows users to stake tokens, update the total staked amount and the deposit gets linked to the user.
- Withdraw: Allows users to withdraw tokens and rewards after the lock period ends.
- ForceWithdraw: Allows users to withdraw tokens before the lock period ends without rewards.
- GetReward: Retrieves the reward amount earned from a specific deposit.
- GetDeposits: Lists all deposits linked to a user.
- GetTotalStakedAmount: Retrieves the total staked amount
- Enter this command in your
Terminal.
cd src
Defining Methods and Messages
- Rename the proto file name
hello_world_contract.protoinside folderProtobuf/contract/tosingle_pool_staking.proto:
mv Protobuf/contract/hello_world_contract.proto Protobuf/contract/single_pool_staking.proto
The .proto file defines the structure and serialization of data, ensuring consistent communication and data exchange between the contract and external systems.
- Open the project with your IDE.
The implementation of single_pool_staking.proto file inside folder src/Protobuf/contract/ is as follows:
syntax = "proto3";
import "aelf/core.proto";
import "aelf/options.proto";
import "google/protobuf/empty.proto";
import "Protobuf/reference/acs12.proto";
import "google/protobuf/wrappers.proto";
option csharp_namespace = "AElf.Contracts.StakingContract";
service StakingContract {
option (aelf.csharp_state) = "AElf.Contracts.StakingContract.StakingContractState";
option (aelf.base) = "Protobuf/reference/acs12.proto";
rpc Initialize (InitializeInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty);
rpc Deposit (DepositInput) returns (google.protobuf.StringValue);
rpc Withdraw (WithdrawInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty);
rpc ForceWithdraw (google.protobuf.StringValue) returns (google.protobuf.Empty);
rpc GetReward (google.protobuf.StringValue) returns (google.protobuf.Int64Value) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc GetDeposits (google.protobuf.StringValue) returns (DepositList) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// New functions
rpc IfInitialized (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.BoolValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc GetTotalStakedAmount (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.Int64Value) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
}
message DepositInput {
string token_symbol = 1;
int64 amount = 2;
int64 lock_time = 3;
}
message InitializeInput {
aelf.Address token_contract_address = 1;
}
message WithdrawInput {
string deposit_id = 1;
}
message TransferInput {
aelf.Address to = 1;
string symbol = 2;
int64 amount = 3;
string memo = 4; // Add this field
}
message StringList {
repeated string values = 1;
}
message Deposit {
string deposit_id = 1;
string address = 2;
string token_symbol = 3; // The specific FT token symbol
int64 amount = 4;
int64 lock_time = 5;
int64 deposit_time = 6;
}
message DepositList {
repeated Deposit deposits = 1;
}
rpcmethods define the callable functions within the contract, allowing external systems to interact with the contract's logic.messagerepresent the structured data exchanged between the contract and external systems.
Define Contract States
The implementation of the Single Pool Staking smart contract state inside file src/SinglePoolStakingState.cs is as follows:
using AElf.Sdk.CSharp.State;
using AElf.Types;
using AElf.Contracts.MultiToken;
namespace AElf.Contracts.StakingContract
{
public class StakingContractState : ContractState
{
public BoolState Initialized { get; set; }
public SingletonState<Address> Owner { get; set; }
public MappedState<string, Deposit> Deposits { get; set; } // Mapping from deposit ID to Deposit
public MappedState<Address, StringList> UserDeposits { get; set; } // User to deposit IDs
public Int32State DepositCounter { get; set; }
public Int64State TotalStakedAmount { get; set; } // New state to track total staked amount
internal TokenContractContainer.TokenContractReferenceState TokenContract { get; set; }
}
}
- The
State.csfile in the aelf blockchain smart contract holds the variables that store the contract's data, making sure this data is saved and accessible whenever the contract needs it.
Implement Single Pool Staking Smart Contract
The implementation of the Single Pool Staking smart contract inside file src/SinglePoolStaking.cs is as follows:
using Google.Protobuf.WellKnownTypes;
using AElf.Types;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using AElf.Contracts.MultiToken;
namespace AElf.Contracts.StakingContract
{
public class StakingContract : StakingContractContainer.StakingContractBase
{
private const int RewardRate = 10; // 10% reward
public override Empty Initialize(InitializeInput input)
{
if (State.Initialized.Value)
return new Empty();
State.Initialized.Value = true;
State.Owner.Value = Context.Sender;
State.DepositCounter.Value = 0;
State.TotalStakedAmount.Value = 0; // Initialize total staked amount
State.TokenContract.Value = input.TokenContractAddress;
return new Empty();
}
public override StringValue Deposit(DepositInput input)
{
var depositId = (State.DepositCounter.Value + 1).ToString();
State.DepositCounter.Value++;
var deposit = new Deposit
{
DepositId = depositId,
Address = Context.Sender.ToString(),
TokenSymbol = input.TokenSymbol,
Amount = input.Amount,
LockTime = input.LockTime,
DepositTime = Context.CurrentBlockTime.Seconds
};
State.Deposits[depositId] = deposit;
var userDeposits = State.UserDeposits[Context.Sender] ?? new StringList();
userDeposits.Values.Add(depositId);
State.UserDeposits[Context.Sender] = userDeposits;
State.TotalStakedAmount.Value += input.Amount; // Update total staked amount
return new StringValue { Value = depositId };
}
public override Empty Withdraw(WithdrawInput input)
{
var deposit = State.Deposits[input.DepositId];
Assert(deposit != null, "Deposit not found.");
Assert(deposit.Address == Context.Sender.ToString(), "Unauthorized.");
Assert(Context.CurrentBlockTime.Seconds >= deposit.DepositTime + deposit.LockTime, "Lock period not over.");
var reward = CalculateReward(deposit.Amount);
TransferFromContract(deposit.TokenSymbol, Context.Sender, deposit.Amount + reward);
State.TotalStakedAmount.Value -= deposit.Amount; // Update total staked amount
RemoveDeposit(deposit.DepositId);
return new Empty();
}
public override Empty ForceWithdraw(StringValue input)
{
var deposit = State.Deposits[input.Value];
Assert(deposit != null, "Deposit not found.");
Assert(deposit.Address == Context.Sender.ToString(), "Unauthorized.");
TransferFromContract(deposit.TokenSymbol, Context.Sender, deposit.Amount);
State.TotalStakedAmount.Value -= deposit.Amount; // Update total staked amount
RemoveDeposit(deposit.DepositId);
return new Empty();
}
public override Int64Value GetReward(StringValue input)
{
var deposit = State.Deposits[input.Value];
Assert(deposit != null, "Deposit not found.");
return new Int64Value { Value = CalculateReward(deposit.Amount) };
}
public override DepositList GetDeposits(StringValue input)
{
var deposits = State.UserDeposits[Address.FromBase58(input.Value)];
var depositList = new DepositList();
foreach (var depositId in deposits.Values)
{
var deposit = State.Deposits[depositId];
if (deposit != null)
{
depositList.Deposits.Add(deposit);
}
}
return depositList;
}
// New function to check if initialized
public override BoolValue IfInitialized(Empty input)
{
return new BoolValue { Value = State.Initialized.Value };
}
// New function to get the total staked amount
public override Int64Value GetTotalStakedAmount(Empty input)
{
return new Int64Value { Value = State.TotalStakedAmount.Value };
}
private long CalculateReward(long amount)
{
return (amount * RewardRate) / 100;
}
private void TransferFromContract(string symbol, Address to, long amount)
{
var virtualAddressHash = GetVirtualAddressHash(Context.Self, symbol);
State.TokenContract.TransferFrom.Send(
new TransferFromInput
{
Symbol = symbol,
Amount = amount,
From = Context.Self,
Memo = "Transfer from Staking Contract",
To = to
});
}
private static Hash GetVirtualAddressHash(Address contractAddress, string symbol)
{
return HashHelper.ConcatAndCompute(HashHelper.ComputeFrom(contractAddress), HashHelper.ComputeFrom(symbol));
}
private Address GetVirtualAddress(Hash virtualAddressHash)
{
return Context.ConvertVirtualAddressToContractAddress(virtualAddressHash);
}
private void RemoveDeposit(string depositId)
{
var deposit = State.Deposits[depositId];
State.Deposits.Remove(depositId);
var userDeposits = State.UserDeposits[Address.FromBase58(deposit.Address)];
userDeposits.Values.Remove(depositId);
State.UserDeposits[Address.FromBase58(deposit.Address)] = userDeposits;
}
}
}
Contract Reference State
-
Create a new file
token_contract.protoundersrc/Protobuf/reference/. -
Replace this code of implementation file of
token_contract.proto:
/**
* MultiToken contract.
*/
syntax = "proto3";
package token;
import "aelf/core.proto";
import "aelf/options.proto";
import "google/protobuf/empty.proto";
import "google/protobuf/wrappers.proto";
option csharp_namespace = "AElf.Contracts.MultiToken";
service TokenContract {
// Create a new token.
rpc Create (CreateInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// Issuing some amount of tokens to an address is the action of increasing that addresses balance
// for the given token. The total amount of issued tokens must not exceed the total supply of the token
// and only the issuer (creator) of the token can issue tokens.
// Issuing tokens effectively increases the circulating supply.
rpc Issue (IssueInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// Transferring tokens simply is the action of transferring a given amount of tokens from one address to another.
// The origin or source address is the signer of the transaction.
// The balance of the sender must be higher than the amount that is transferred.
rpc Transfer (TransferInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// The TransferFrom action will transfer a specified amount of tokens from one address to another.
// For this operation to succeed the from address needs to have approved (see allowances) enough tokens
// to Sender of this transaction. If successful the amount will be removed from the allowance.
rpc TransferFrom (TransferFromInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// The approve action increases the allowance from the Sender to the Spender address,
// enabling the Spender to call TransferFrom.
rpc Approve (ApproveInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc BatchApprove (BatchApproveInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// This is the reverse operation for Approve, it will decrease the allowance.
rpc UnApprove (UnApproveInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// This method can be used to lock tokens.
rpc Lock (LockInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// This is the reverse operation of locking, it un-locks some previously locked tokens.
rpc Unlock (UnlockInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// This action will burn the specified amount of tokens, removing them from the token’s Supply.
rpc Burn (BurnInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// Set the primary token of side chain.
rpc SetPrimaryTokenSymbol (SetPrimaryTokenSymbolInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// This interface is used for cross-chain transfer.
rpc CrossChainTransfer (CrossChainTransferInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// This method is used to receive cross-chain transfers.
rpc CrossChainReceiveToken (CrossChainReceiveTokenInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// The side chain creates tokens.
rpc CrossChainCreateToken(CrossChainCreateTokenInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// When the side chain is started, the side chain is initialized with the parent chain information.
rpc InitializeFromParentChain (InitializeFromParentChainInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// Handle the transaction fees charged by ChargeTransactionFees.
rpc ClaimTransactionFees (TotalTransactionFeesMap) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// Used to collect transaction fees.
rpc ChargeTransactionFees (ChargeTransactionFeesInput) returns (ChargeTransactionFeesOutput) {
}
rpc ChargeUserContractTransactionFees(ChargeTransactionFeesInput) returns(ChargeTransactionFeesOutput){
}
// Check the token threshold.
rpc CheckThreshold (CheckThresholdInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// Initialize coefficients of every type of tokens supporting charging fee.
rpc InitialCoefficients (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.Empty){
}
// Processing resource token received.
rpc DonateResourceToken (TotalResourceTokensMaps) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// A transaction resource fee is charged to implement the ACS8 standards.
rpc ChargeResourceToken (ChargeResourceTokenInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// Verify that the resource token are sufficient.
rpc CheckResourceToken (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// Set the list of tokens to pay transaction fees.
rpc SetSymbolsToPayTxSizeFee (SymbolListToPayTxSizeFee) returns (google.protobuf.Empty){
}
// Update the coefficient of the transaction fee calculation formula.
rpc UpdateCoefficientsForSender (UpdateCoefficientsInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// Update the coefficient of the transaction fee calculation formula.
rpc UpdateCoefficientsForContract (UpdateCoefficientsInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
// This method is used to initialize the governance organization for some functions,
// including: the coefficient of the user transaction fee calculation formula,
// the coefficient of the contract developer resource fee calculation formula, and the side chain rental fee.
rpc InitializeAuthorizedController (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.Empty){
}
rpc AddAddressToCreateTokenWhiteList (aelf.Address) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc RemoveAddressFromCreateTokenWhiteList (aelf.Address) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc SetTransactionFeeDelegations (SetTransactionFeeDelegationsInput) returns (SetTransactionFeeDelegationsOutput){
}
rpc RemoveTransactionFeeDelegator (RemoveTransactionFeeDelegatorInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty){
}
rpc RemoveTransactionFeeDelegatee (RemoveTransactionFeeDelegateeInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty){
}
rpc SetSymbolAlias (SetSymbolAliasInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty){
}
// Get all delegatees' address of delegator from input
rpc GetTransactionFeeDelegatees (GetTransactionFeeDelegateesInput) returns (GetTransactionFeeDelegateesOutput) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query token information.
rpc GetTokenInfo (GetTokenInfoInput) returns (TokenInfo) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query native token information.
rpc GetNativeTokenInfo (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (TokenInfo) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query resource token information.
rpc GetResourceTokenInfo (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (TokenInfoList) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query the balance at the specified address.
rpc GetBalance (GetBalanceInput) returns (GetBalanceOutput) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query the account's allowance for other addresses
rpc GetAllowance (GetAllowanceInput) returns (GetAllowanceOutput) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query the account's available allowance for other addresses
rpc GetAvailableAllowance (GetAllowanceInput) returns (GetAllowanceOutput) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Check whether the token is in the whitelist of an address,
// which can be called TransferFrom to transfer the token under the condition of not being credited.
rpc IsInWhiteList (IsInWhiteListInput) returns (google.protobuf.BoolValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query the information for a lock.
rpc GetLockedAmount (GetLockedAmountInput) returns (GetLockedAmountOutput) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query the address of receiving token in cross-chain transfer.
rpc GetCrossChainTransferTokenContractAddress (GetCrossChainTransferTokenContractAddressInput) returns (aelf.Address) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query the name of the primary Token.
rpc GetPrimaryTokenSymbol (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.StringValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query the coefficient of the transaction fee calculation formula.
rpc GetCalculateFeeCoefficientsForContract (google.protobuf.Int32Value) returns (CalculateFeeCoefficients) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query the coefficient of the transaction fee calculation formula.
rpc GetCalculateFeeCoefficientsForSender (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (CalculateFeeCoefficients) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query tokens that can pay transaction fees.
rpc GetSymbolsToPayTxSizeFee (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (SymbolListToPayTxSizeFee){
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query the hash of the last input of ClaimTransactionFees.
rpc GetLatestTotalTransactionFeesMapHash (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (aelf.Hash){
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
// Query the hash of the last input of DonateResourceToken.
rpc GetLatestTotalResourceTokensMapsHash (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (aelf.Hash){
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc IsTokenAvailableForMethodFee (google.protobuf.StringValue) returns (google.protobuf.BoolValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc GetReservedExternalInfoKeyList (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (StringList) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc GetTransactionFeeDelegationsOfADelegatee(GetTransactionFeeDelegationsOfADelegateeInput) returns(TransactionFeeDelegations){
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc GetTokenAlias (google.protobuf.StringValue) returns (google.protobuf.StringValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc GetSymbolByAlias (google.protobuf.StringValue) returns (google.protobuf.StringValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
}
message TokenInfo {
// The symbol of the token.f
string symbol = 1;
// The full name of the token.
string token_name = 2;
// The current supply of the token.
int64 supply = 3;
// The total supply of the token.
int64 total_supply = 4;
// The precision of the token.
int32 decimals = 5;
// The address that has permission to issue the token.
aelf.Address issuer = 6;
// A flag indicating if this token is burnable.
bool is_burnable = 7;
// The chain id of the token.
int32 issue_chain_id = 8;
// The amount of issued tokens.
int64 issued = 9;
// The external information of the token.
ExternalInfo external_info = 10;
// The address that owns the token.
aelf.Address owner = 11;
}
message ExternalInfo {
map<string, string> value = 1;
}
message CreateInput {
// The symbol of the token.
string symbol = 1;
// The full name of the token.
string token_name = 2;
// The total supply of the token.
int64 total_supply = 3;
// The precision of the token
int32 decimals = 4;
// The address that has permission to issue the token.
aelf.Address issuer = 5;
// A flag indicating if this token is burnable.
bool is_burnable = 6;
// A whitelist address list used to lock tokens.
repeated aelf.Address lock_white_list = 7;
// The chain id of the token.
int32 issue_chain_id = 8;
// The external information of the token.
ExternalInfo external_info = 9;
// The address that owns the token.
aelf.Address owner = 10;
}
message SetPrimaryTokenSymbolInput {
// The symbol of the token.
string symbol = 1;
}
message IssueInput {
// The token symbol to issue.
string symbol = 1;
// The token amount to issue.
int64 amount = 2;
// The memo.
string memo = 3;
// The target address to issue.
aelf.Address to = 4;
}
message TransferInput {
// The receiver of the token.
aelf.Address to = 1;
// The token symbol to transfer.
string symbol = 2;
// The amount to to transfer.
int64 amount = 3;
// The memo.
string memo = 4;
}
message LockInput {
// The one want to lock his token.
aelf.Address address = 1;
// Id of the lock.
aelf.Hash lock_id = 2;
// The symbol of the token to lock.
string symbol = 3;
// a memo.
string usage = 4;
// The amount of tokens to lock.
int64 amount = 5;
}
message UnlockInput {
// The one want to un-lock his token.
aelf.Address address = 1;
// Id of the lock.
aelf.Hash lock_id = 2;
// The symbol of the token to un-lock.
string symbol = 3;
// a memo.
string usage = 4;
// The amount of tokens to un-lock.
int64 amount = 5;
}
message TransferFromInput {
// The source address of the token.
aelf.Address from = 1;
// The destination address of the token.
aelf.Address to = 2;
// The symbol of the token to transfer.
string symbol = 3;
// The amount to transfer.
int64 amount = 4;
// The memo.
string memo = 5;
}
message ApproveInput {
// The address that allowance will be increased.
aelf.Address spender = 1;
// The symbol of token to approve.
string symbol = 2;
// The amount of token to approve.
int64 amount = 3;
}
message BatchApproveInput {
repeated ApproveInput value = 1;
}
message UnApproveInput {
// The address that allowance will be decreased.
aelf.Address spender = 1;
// The symbol of token to un-approve.
string symbol = 2;
// The amount of token to un-approve.
int64 amount = 3;
}
message BurnInput {
// The symbol of token to burn.
string symbol = 1;
// The amount of token to burn.
int64 amount = 2;
}
message ChargeResourceTokenInput {
// Collection of charge resource token, Symbol->Amount.
map<string, int64> cost_dic = 1;
// The sender of the transaction.
aelf.Address caller = 2;
}
message TransactionFeeBill {
// The transaction fee dictionary, Symbol->fee.
map<string, int64> fees_map = 1;
}
message TransactionFreeFeeAllowanceBill {
// The transaction free fee allowance dictionary, Symbol->fee.
map<string, int64> free_fee_allowances_map = 1;
}
message CheckThresholdInput {
// The sender of the transaction.
aelf.Address sender = 1;
// The threshold to set, Symbol->Threshold.
map<string, int64> symbol_to_threshold = 2;
// Whether to check the allowance.
bool is_check_allowance = 3;
}
message GetTokenInfoInput {
// The symbol of token.
string symbol = 1;
}
message GetBalanceInput {
// The symbol of token.
string symbol = 1;
// The target address of the query.
aelf.Address owner = 2;
}
message GetBalanceOutput {
// The symbol of token.
string symbol = 1;
// The target address of the query.
aelf.Address owner = 2;
// The balance of the owner.
int64 balance = 3;
}
message GetAllowanceInput {
// The symbol of token.
string symbol = 1;
// The address of the token owner.
aelf.Address owner = 2;
// The address of the spender.
aelf.Address spender = 3;
}
message GetAllowanceOutput {
// The symbol of token.
string symbol = 1;
// The address of the token owner.
aelf.Address owner = 2;
// The address of the spender.
aelf.Address spender = 3;
// The amount of allowance.
int64 allowance = 4;
}
message CrossChainTransferInput {
// The receiver of transfer.
aelf.Address to = 1;
// The symbol of token.
string symbol = 2;
// The amount of token to transfer.
int64 amount = 3;
// The memo.
string memo = 4;
// The destination chain id.
int32 to_chain_id = 5;
// The chain id of the token.
int32 issue_chain_id = 6;
}
message CrossChainReceiveTokenInput {
// The source chain id.
int32 from_chain_id = 1;
// The height of the transfer transaction.
int64 parent_chain_height = 2;
// The raw bytes of the transfer transaction.
bytes transfer_transaction_bytes = 3;
// The merkle path created from the transfer transaction.
aelf.MerklePath merkle_path = 4;
}
message IsInWhiteListInput {
// The symbol of token.
string symbol = 1;
// The address to check.
aelf.Address address = 2;
}
message SymbolToPayTxSizeFee{
// The symbol of token.
string token_symbol = 1;
// The charge weight of primary token.
int32 base_token_weight = 2;
// The new added token charge weight. For example, the charge weight of primary Token is set to 1.
// The newly added token charge weight is set to 10. If the transaction requires 1 unit of primary token,
// the user can also pay for 10 newly added tokens.
int32 added_token_weight = 3;
}
message SymbolListToPayTxSizeFee{
// Transaction fee token information.
repeated SymbolToPayTxSizeFee symbols_to_pay_tx_size_fee = 1;
}
message ChargeTransactionFeesInput {
// The method name of transaction.
string method_name = 1;
// The contract address of transaction.
aelf.Address contract_address = 2;
// The amount of transaction size fee.
int64 transaction_size_fee = 3;
// Transaction fee token information.
repeated SymbolToPayTxSizeFee symbols_to_pay_tx_size_fee = 4;
}
message ChargeTransactionFeesOutput {
// Whether the charge was successful.
bool success = 1;
// The charging information.
string charging_information = 2;
}
message CallbackInfo {
aelf.Address contract_address = 1;
string method_name = 2;
}
message ExtraTokenListModified {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// Transaction fee token information.
SymbolListToPayTxSizeFee symbol_list_to_pay_tx_size_fee = 1;
}
message GetLockedAmountInput {
// The address of the lock.
aelf.Address address = 1;
// The token symbol.
string symbol = 2;
// The id of the lock.
aelf.Hash lock_id = 3;
}
message GetLockedAmountOutput {
// The address of the lock.
aelf.Address address = 1;
// The token symbol.
string symbol = 2;
// The id of the lock.
aelf.Hash lock_id = 3;
// The locked amount.
int64 amount = 4;
}
message TokenInfoList {
// List of token information.
repeated TokenInfo value = 1;
}
message GetCrossChainTransferTokenContractAddressInput {
// The chain id.
int32 chainId = 1;
}
message CrossChainCreateTokenInput {
// The chain id of the chain on which the token was created.
int32 from_chain_id = 1;
// The height of the transaction that created the token.
int64 parent_chain_height = 2;
// The transaction that created the token.
bytes transaction_bytes = 3;
// The merkle path created from the transaction that created the transaction.
aelf.MerklePath merkle_path = 4;
}
message InitializeFromParentChainInput {
// The amount of resource.
map<string, int32> resource_amount = 1;
// The token contract addresses.
map<int32, aelf.Address> registered_other_token_contract_addresses = 2;
// The creator the side chain.
aelf.Address creator = 3;
}
message UpdateCoefficientsInput {
// The specify pieces gonna update.
repeated int32 piece_numbers = 1;
// Coefficients of one single type.
CalculateFeeCoefficients coefficients = 2;
}
enum FeeTypeEnum {
READ = 0;
STORAGE = 1;
WRITE = 2;
TRAFFIC = 3;
TX = 4;
}
message CalculateFeePieceCoefficients {
// Coefficients of one single piece.
// The first char is its type: liner / power.
// The second char is its piece upper bound.
repeated int32 value = 1;
}
message CalculateFeeCoefficients {
// The resource fee type, like READ, WRITE, etc.
int32 fee_token_type = 1;
// Coefficients of one single piece.
repeated CalculateFeePieceCoefficients piece_coefficients_list = 2;
}
message AllCalculateFeeCoefficients {
// The coefficients of fee Calculation.
repeated CalculateFeeCoefficients value = 1;
}
message TotalTransactionFeesMap
{
// Token dictionary that charge transaction fee, Symbol->Amount.
map<string, int64> value = 1;
// The hash of the block processing the transaction.
aelf.Hash block_hash = 2;
// The height of the block processing the transaction.
int64 block_height = 3;
}
message TotalResourceTokensMaps {
// Resource tokens to charge.
repeated ContractTotalResourceTokens value = 1;
// The hash of the block processing the transaction.
aelf.Hash block_hash = 2;
// The height of the block processing the transaction.
int64 block_height = 3;
}
message ContractTotalResourceTokens {
// The contract address.
aelf.Address contract_address = 1;
// Resource tokens to charge.
TotalResourceTokensMap tokens_map = 2;
}
message TotalResourceTokensMap
{
// Resource token dictionary, Symbol->Amount.
map<string, int64> value = 1;
}
message StringList {
repeated string value = 1;
}
message TransactionFeeDelegations{
// delegation, symbols and its' amount
map<string, int64> delegations = 1;
// height when added
int64 block_height = 2;
//Whether to pay transaction fee continuously
bool isUnlimitedDelegate = 3;
}
message TransactionFeeDelegatees{
map<string,TransactionFeeDelegations> delegatees = 1;
}
message SetTransactionFeeDelegationsInput {
// the delegator address
aelf.Address delegator_address = 1;
// delegation, symbols and its' amount
map<string, int64> delegations = 2;
}
message SetTransactionFeeDelegationsOutput {
bool success = 1;
}
message RemoveTransactionFeeDelegatorInput{
// the delegator address
aelf.Address delegator_address = 1;
}
message RemoveTransactionFeeDelegateeInput {
// the delegatee address
aelf.Address delegatee_address = 1;
}
message GetTransactionFeeDelegationsOfADelegateeInput {
aelf.Address delegatee_address = 1;
aelf.Address delegator_address = 2;
}
message GetTransactionFeeDelegateesInput {
aelf.Address delegator_address = 1;
}
message GetTransactionFeeDelegateesOutput {
repeated aelf.Address delegatee_addresses = 1;
}
message SetSymbolAliasInput {
string symbol = 1;
string alias = 2;
}
// Events
message Transferred {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// The source address of the transferred token.
aelf.Address from = 1 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
// The destination address of the transferred token.
aelf.Address to = 2 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
// The symbol of the transferred token.
string symbol = 3 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
// The amount of the transferred token.
int64 amount = 4;
// The memo.
string memo = 5;
}
message Approved {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// The address of the token owner.
aelf.Address owner = 1 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
// The address that allowance be increased.
aelf.Address spender = 2 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
// The symbol of approved token.
string symbol = 3 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
// The amount of approved token.
int64 amount = 4;
}
message UnApproved {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// The address of the token owner.
aelf.Address owner = 1 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
// The address that allowance be decreased.
aelf.Address spender = 2 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
// The symbol of un-approved token.
string symbol = 3 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
// The amount of un-approved token.
int64 amount = 4;
}
message Burned
{
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// The address who wants to burn token.
aelf.Address burner = 1 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
// The symbol of burned token.
string symbol = 2 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
// The amount of burned token.
int64 amount = 3;
}
message ChainPrimaryTokenSymbolSet {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// The symbol of token.
string token_symbol = 1;
}
message CalculateFeeAlgorithmUpdated {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// All calculate fee coefficients after modification.
AllCalculateFeeCoefficients all_type_fee_coefficients = 1;
}
message RentalCharged {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// The symbol of rental fee charged.
string symbol = 1;
// The amount of rental fee charged.
int64 amount = 2;
// The payer of rental fee.
aelf.Address payer = 3;
// The receiver of rental fee.
aelf.Address receiver = 4;
}
message RentalAccountBalanceInsufficient {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// The symbol of insufficient rental account balance.
string symbol = 1;
// The balance of the account.
int64 amount = 2;
}
message TokenCreated {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// The symbol of the token.
string symbol = 1;
// The full name of the token.
string token_name = 2;
// The total supply of the token.
int64 total_supply = 3;
// The precision of the token.
int32 decimals = 4;
// The address that has permission to issue the token.
aelf.Address issuer = 5;
// A flag indicating if this token is burnable.
bool is_burnable = 6;
// The chain id of the token.
int32 issue_chain_id = 7;
// The external information of the token.
ExternalInfo external_info = 8;
// The address that owns the token.
aelf.Address owner = 9;
}
message Issued {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// The symbol of issued token.
string symbol = 1;
// The amount of issued token.
int64 amount = 2;
// The memo.
string memo = 3;
// The issued target address.
aelf.Address to = 4;
}
message CrossChainTransferred {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// The source address of the transferred token.
aelf.Address from = 1;
// The destination address of the transferred token.
aelf.Address to = 2;
// The symbol of the transferred token.
string symbol = 3;
// The amount of the transferred token.
int64 amount = 4;
// The memo.
string memo = 5;
// The destination chain id.
int32 to_chain_id = 6;
// The chain id of the token.
int32 issue_chain_id = 7;
}
message CrossChainReceived {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
// The source address of the transferred token.
aelf.Address from = 1;
// The destination address of the transferred token.
aelf.Address to = 2;
// The symbol of the received token.
string symbol = 3;
// The amount of the received token.
int64 amount = 4;
// The memo.
string memo = 5;
// The destination chain id.
int32 from_chain_id = 6;
// The chain id of the token.
int32 issue_chain_id = 7;
// The parent chain height of the transfer transaction.
int64 parent_chain_height = 8;
// The id of transfer transaction.
aelf.Hash transfer_transaction_id =9;
}
message TransactionFeeDelegationAdded {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
aelf.Address delegator = 1 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
aelf.Address delegatee = 2 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
aelf.Address caller = 3 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
}
message TransactionFeeDelegationCancelled {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
aelf.Address delegator = 1 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
aelf.Address delegatee = 2 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
aelf.Address caller = 3 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
}
message SymbolAliasAdded {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
string symbol = 1 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
string alias = 2 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
}
message SymbolAliasDeleted {
option (aelf.is_event) = true;
string symbol = 1 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
string alias = 2 [(aelf.is_indexed) = true];
}
Building Smart Contract
- Build the smart contract code with the following command inside
srcfolder:
dotnet build
You should see SinglePoolStaking.dll.patched in the directory SinglePoolStaking/src/bin/Debug/net.8.0
Step 3 - Deploy Smart Contract
Create A Wallet
To send transactions on the aelf blockchain, you must have a wallet.
- Run this command to create aelf wallet.
aelf-command create

- You will be prompted to save your account, please do save your account as shown below:
? Save account info into a file? (Y/n) Y
Make sure to choose Y to save your account information.
ℹ️ Note: If you do not save your account information (by selecting n or N), do not export the wallet password. Only proceed to the next step if you have saved your account information.
- Next, enter and confirm your password. Then export your wallet password as shown below:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export WALLET_PASSWORD="YOUR_WALLET_PASSWORD"
$env:WALLET_PASSWORD = "YOUR_WALLET_PASSWORD"
Acquire Testnet Tokens (Faucet) for Development
To deploy smart contracts or execute on-chain transactions on aelf, you'll require testnet ELF tokens.
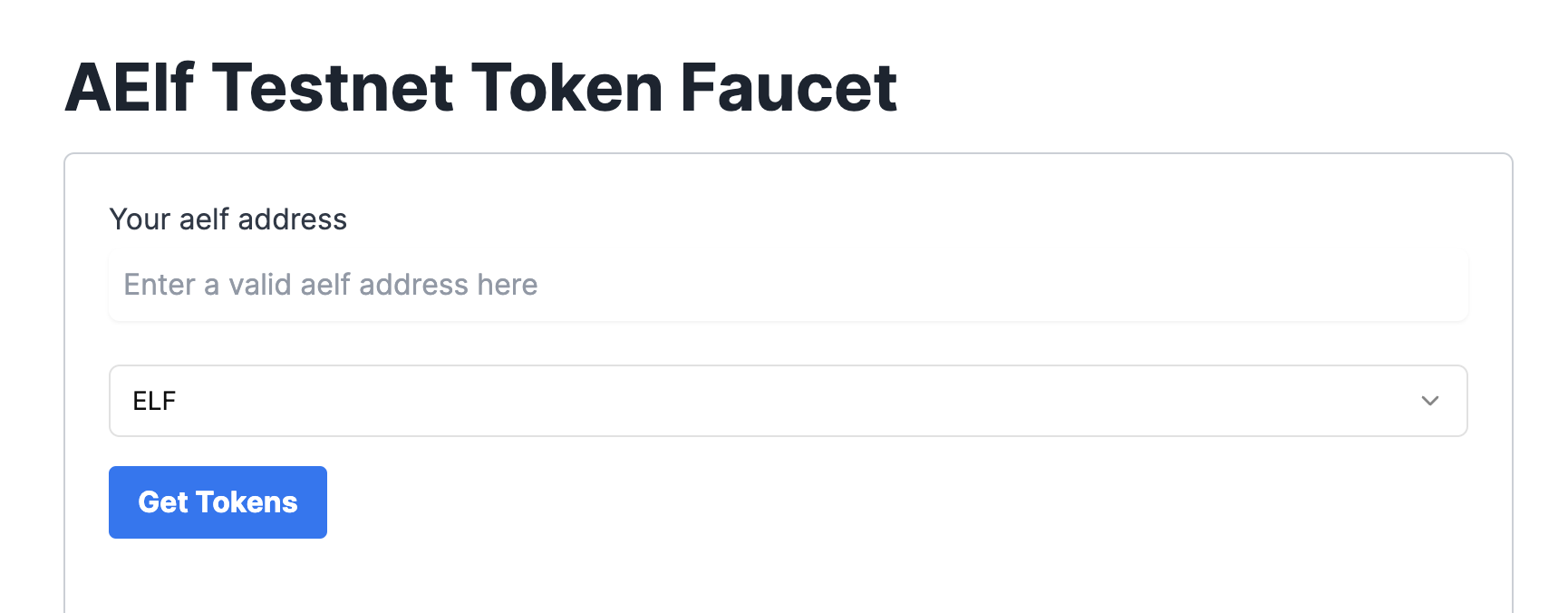
Get ELF Tokens
Go to https://faucet-ui.aelf.dev Enter your address and click Get Tokens.
Deploy Smart Contract:
The smart contract needs to be deployed on the chain before users can interact with it.
Run the following command to deploy a contract. Remember to export the path of SinglePoolStaking.dll.patched to CONTRACT_PATH.
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export CONTRACT_PATH=$(find ~+ . -path "*patched*" | head -n 1)
aelf-deploy -a $WALLET_ADDRESS -p $WALLET_PASSWORD -c $CONTRACT_PATH -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io/
$CONTRACT_PATH = Get-ChildItem -Recurse -Filter "*patched*" | Select-Object -First 1 -ExpandProperty FullName
$env:CONTRACT_PATH = $CONTRACT_PATH
aelf-deploy -a $env:WALLET_ADDRESS -p $env:WALLET_PASSWORD -c $env:CONTRACT_PATH -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io/
-
Please wait for approximately 1 to 2 minutes. If the deployment is successful, it will provide you with the contract address.
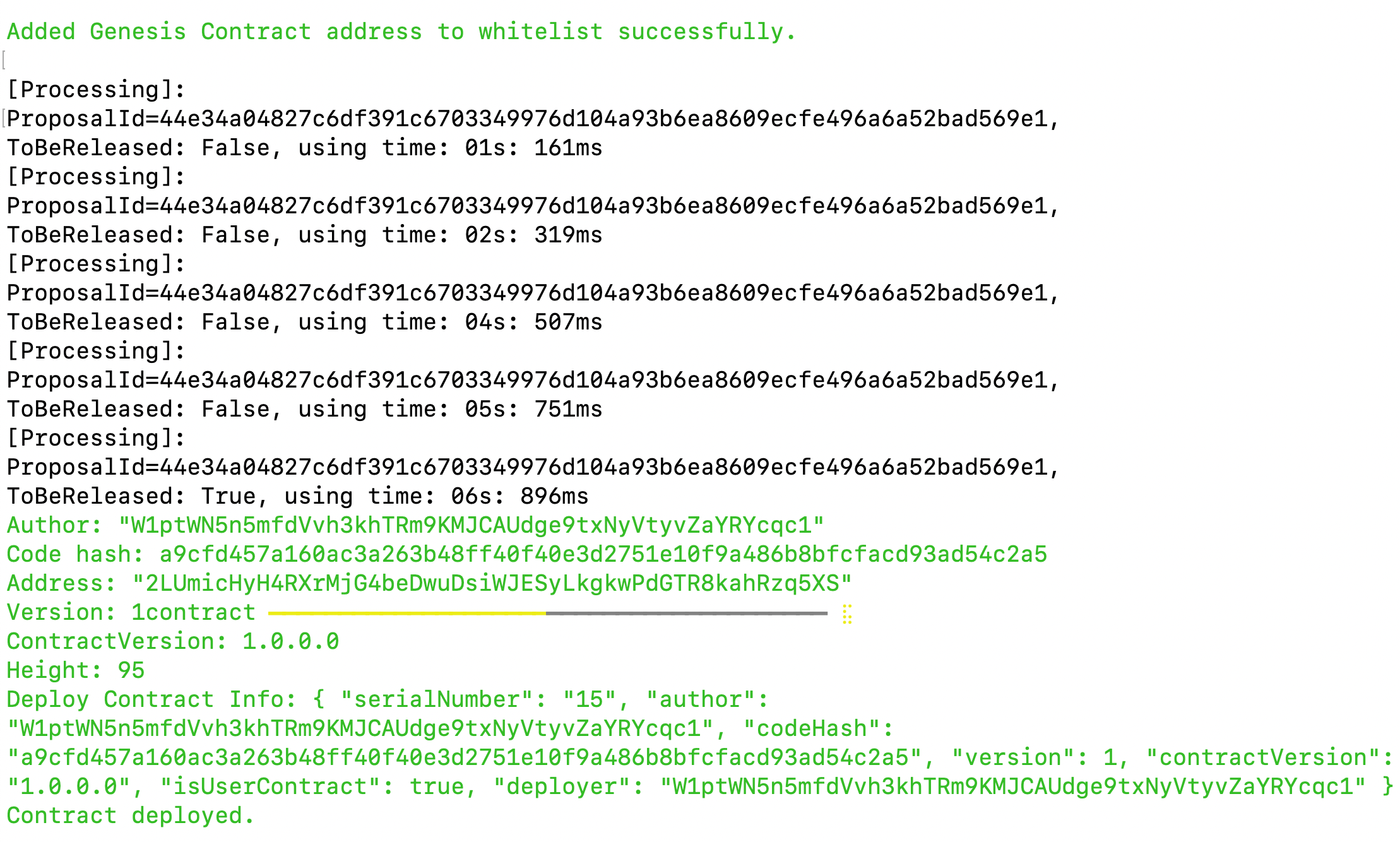
-
Copy the smart contract address from the
addressfield
-
Export your smart contract address:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export CONTRACT_ADDRESS="YOUR_SMART_CONTRACT_ADDRESS e.g. 2LUmicHyH4RXrMjG4beDwuDsiWJESyLkgkwPdGTR8kahRzq5XS"
$env:CONTRACT_ADDRESS="YOUR_SMART_CONTRACT_ADDRESS e.g. 2LUmicHyH4RXrMjG4beDwuDsiWJESyLkgkwPdGTR8kahRzq5XS"
ℹ️ Note: You are to copy the smart contract address as we will be referencing it in the next steps!
🎉 You have successfully deployed your Single Pool Staking dApp smart contract on the aelf testnet! In the next steps, we will be building the frontend components that allow us to interact with our deployed smart contract!
Step 4 - Getting TOKEN Seed
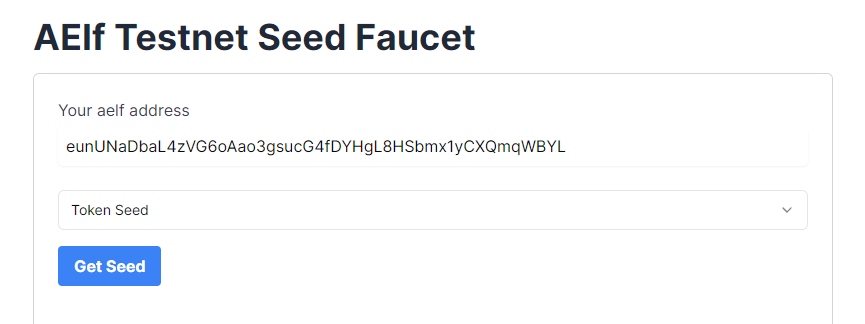
In order to create a fungible token on the aelf blockchain, the deployer wallet must have a TOKEN SEED.
- Visit TOKEN Faucet to get your TOKEN SEED.
- After the request is successfully processed, the requestor wallet will receive the SEED.
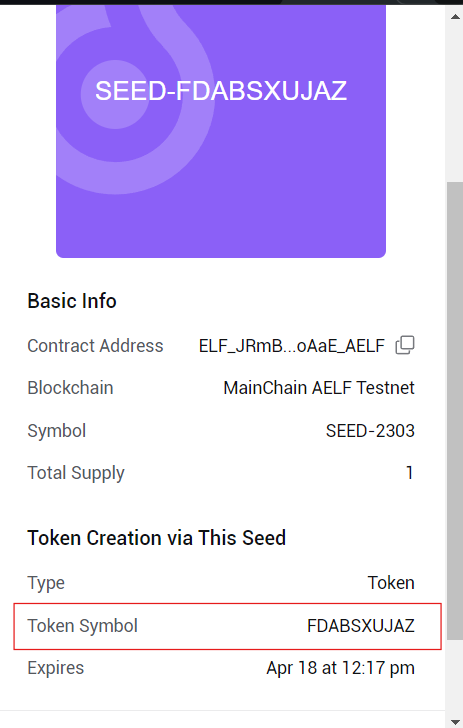
- Please note this SEED symbol value separately as it will be needed while creating the fungible token and staking integration. This will become our Token Symbol.
Step 5 - Interact with Your Deployed Smart Contracts
Project Setup
Let's start by cloning the frontend project repository from github.
- Run the following command in your Terminal:
git clone https://github.com/AElfProject/aelf-samples.git
- Next, navigate to the staking frontend project directory with this command:
cd aelf-samples/staking/2-dapp
- Once you're inside the
2-dappdirectory, open the project with your preferred IDE (e.g., VSCode). You should see the project structure as shown below.
Install necessary packages and libraries
- Run this command in the terminal to install all necessary packages and libraries.
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
sudo npm install
npm install
We are now ready to build the frontend components of our Staking dApp.
Configure Portkey Provider & Write Contract Hooks Function
We'll set up our Portkey provider to allow users to connect their Portkey wallets to the dApp and interact with the aelf smart contracts. We'll be interacting with the Stakinng contract and the Multi-token contract.
Write Functions for MainChain and dAppChain Contracts
Step 1. Locate the File:
- Go to the
src/hooks/useSmartContract.tsfile.
Step 2. Fetch the Smart Contract:
-
Find the comment
//Step A - Function to fetch a smart contract based on the chain symbol and the contract address -
Replace the existing
fetchContractfunction with the below code:
//Step A - Function to fetch a smart contract based on the chain symbol and the contract address
const fetchContract = async (
symbol: "AELF" | "tDVW",
contractAddress: string
) => {
try {
// If no provider is available, return null
if (!provider) return null;
// Fetch the chain information using the provider
const chain = await provider.getChain(symbol);
if (!chain) throw new Error("Chain not found");
// Get the smart contract instance from the chain
const contract = chain.getContract(contractAddress);
// Return the smart contract instance
return contract;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error in fetchContract", { symbol, contractAddress, error });
}
};
Explanation:
-
fetchContractFunction: This function fetches a smart contract based on the given chain symbol (e.g., "AELF" or "tDVW") and the contract address.- Check Provider : If no provider is available, the function returns null.
- Fetch Chain : This function fetches chain information using the provider.
- Get Contract : It retrieves the smart contract instance from the chain.
Step 3. Initialize and Fetch the Smart Contracts:
-
Find the comment
// Step B - Effect hook to initialize and fetch the smart contracts when the provider changes. -
Replace the existing
useEffecthook with this updated code:
// Step B - Effect hook to initialize and fetch the smart contracts when the provider changes
useEffect(() => {
(async () => {
// Fetch the MainChain Testnet Contract
const mainChainContract = await fetchContract(
"AELF",
"JRmBduh4nXWi1aXgdUsj5gJrzeZb2LxmrAbf7W99faZSvoAaE"
);
setMainChainSmartContract(mainChainContract as IContract);
// Fetch the dAppChain Testnet Contract
const sideChainContract = await fetchContract(
"tDVW",
"ASh2Wt7nSEmYqnGxPPzp4pnVDU4uhj1XW9Se5VeZcX2UDdyjx"
);
setSideChainSmartContract(sideChainContract as IContract);
})();
}, [provider]); // Dependency array ensures this runs when the provider changes
Explanation:
-
useEffectHook : This hook initializes and fetches the smart contracts when the provider changes.- Check Provider : If no provider is available, the function returns null.
- Fetch Contracts : It fetches and sets the smart contracts for the main chain, side chain.
- MainChain Contract : Fetches the mainchain testnet contract and sets it in the state.
- dAppChain Contract : Fetches the dAppChain testnet contract and sets it in the state.
Write Functions for Staking Contract
Step 4. Locate the File:
- Go to the
src/hooks/useStakingContract.tsfile.
Step 5. Fetch the Smart Contract:
-
Find the comment
//Step C - Function to fetch a smart contract based on the chain symbol and the contract address -
Replace the existing
fetchContractfunction with this updated code:
//Step C - Function to fetch a smart contract based on the chain symbol and the contract address
const fetchContract = async (
symbol: "AELF" | "tDVW",
contractAddress: string
) => {
try {
// If no provider is available, return null
if (!provider) return null;
// Fetch the chain information using the provider
const chain = await provider.getChain(symbol);
if (!chain) throw new Error("Chain not found");
// Get the smart contract instance from the chain
const contract = chain.getContract(contractAddress);
// Return the smart contract instance
return contract;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error in fetchContract", { symbol, contractAddress, error });
}
};
Explanation:
-
fetchContractFunction: This function fetches a smart contract based on the given chain symbol (e.g., "AELF" or "tDVW") and the contract address.- Check Provider : If no provider is available, the function returns null.
- Fetch Chain : The function fetches chain information using the provider.
- Get Contract : It retrieves the smart contract instance from the chain.
Step 6. Initialize and Fetch the Smart Contracts:
-
Find the comment
// Step D - Effect hook to initialize and fetch the smart contracts when the provider changes -
Replace the existing
useEffecthook with this updated code:
// Step D - Effect hook to initialize and fetch the smart contracts when the provider changes
useEffect(() => {
(async () => {
// Fetch the Staking Testnet Contract
const stakingContract = await fetchContract(
"tDVW",
stakingContractAddress
);
setStakingSmartContract(stakingContract as IContract);
})();
}, [provider]); // Dependency array ensures this runs when the provider changes
Explanation:
-
useEffectHook : This hook initializes and fetches the staking smart contract when the provider changes.- Check Provider : If no provider is available, the function returns null.
- Fetch Contracts : It fetches and sets the smart contract for the staking.
By following these steps, we'll configure the Portkey provider to connect users' wallets to the dApp and interact with the multi-token and staking smart contract including interaction with the fungible token and the staking functionalities. This setup will enable our frontend components to perform actions like create tokens, transfer tokens, and stake tokens, withdraw tokens, emergency withdraw tokens, etc.
Configure Connect Wallet Function
Step 1: Locate the File
- Go to the
src/components/layout/header/index.tsxfile.
Step 2: Write the Connect Wallet Function
-
The
header/index.tsxfile is the header of our Staking dApp. It allows users to connect their Portkey wallet with the staking dApp. -
Before users can interact with the smart contract, we need to write the
Connect Walletfunction. -
Find the comment
// Step E - Connect Portkey Wallet. -
Replace the existing connect function with this code snippet:
// Step E - Connect Portkey Wallet
const connect = async (walletProvider?: IPortkeyProvider) => {
const accounts = await (walletProvider ? walletProvider : provider)?.request({
method: MethodsBase.REQUEST_ACCOUNTS,
});
const account = accounts?.AELF && accounts?.AELF[0];
if (account) {
setCurrentWalletAddress(account.replace(/^ELF_/, "").replace(/_AELF$/, ""));
setIsConnected(true);
}
!walletProvider && toast.success("Successfully connected");
};
Explanation:
-
connectFunction : This function connects the user's Portkey wallet with the dApp.- Fetch Accounts : It fetches the wallet accounts using the provider.
- Log Accounts : Logs the accounts to the console for debugging.
- Set Wallet Address : Sets the current wallet address state variable with the fetched account.
- Update Connection Status : Updates the state to indicate that the wallet is connected.
In this code, we fetch the Portkey wallet account using the provider and update the wallet address state variable. An alert notifies the user that their wallet is successfully connected.
With the ConnectWallet function defined, we're ready to write the remaining functions in the next steps.
Configure Create TOKEN Form
Step 1: Locate the File
- Go to the
src/components/create-token-modal/index.tsxfile. This file is the Create Fungible TOKEN popup modal where users can create a new TOKEN by submitting the details liketokenName,symbolandtotalSupply.
Step 2: Prepare Form to Create TOKEN
-
Find the comment
// Step F - Configure TOKEN Create Form. -
Replace the form variable with this code snippet:
// Step F - Configure TOKEN Create Form
const form = useForm<z.infer<typeof formSchema>>({
resolver: zodResolver(formSchema),
defaultValues: {
tokenName: "$TOKEN",
symbol: "",
totalSupply: "",
},
});
Here's what the function does:
-
Initializes a new form variable with default values needed to create a token.
-
Fields include:
tokenName,symbolandtotalSupply.
Now the form is ready for users to fill in the necessary details for their token related function interaction.
Get CrossChain Contract
Let's write the helper function to Get CrossChain Contract to fetch the parent chain height later.
Write the function to Get CrossChain Contract
-
The
create-token-modal/index.tsxfile includes the code to create a fungible token. -
Find the comment
// Step G - Get CrossChain Contract. -
Replace the existing
getCrossChainContractfunction with this code snippet:
// Step G - Get CrossChain Contract
const getCrossChainContract = async (aelf: any, wallet: any) => {
const crossChainContractName = "AElf.ContractNames.CrossChain";
// get chain status
const chainStatus = await aelf.chain.getChainStatus();
// get genesis contract address
const GenesisContractAddress = chainStatus.GenesisContractAddress;
// get genesis contract instance
const zeroContract = await aelf.chain.contractAt(
GenesisContractAddress,
wallet
);
// Get contract address by the read only method `GetContractAddressByName` of genesis contract
const crossChainContractAddress = await zeroContract.GetContractAddressByName.call(AElf.utils.sha256(crossChainContractName));
return await aelf.chain.contractAt(crossChainContractAddress, wallet);
};
What This Function Does:
-
Get chainStatus : It gets chainStatus from getChainStatus function which is there in aelf.
-
Get GenesisContractAddress : It gets GenesisContractAddress from chainStatus.
-
fetch zeroContract : It fetches zeroContract using GenesisContractAddress and wallet.
-
fetch crossChainContractAddress : It fetch crossChainContractAddress by calling GetContractAddressByName method from zeroContract.
Next, we'll write the Get the parent chain height function.
Get the parent chain height
Write the function to get the parent chain height
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step H - Get the parent chain height. -
Replace the existing
GetParentChainHeightfunction with the following code snippet:
// Step H - Get the parent chain height
// This function fetches the current height of the parent blockchain.
const GetParentChainHeight = async () => {
try {
const tdvwCrossChainContract = await getCrossChainContract(tdvw, wallet);
// Call the smart contract method to get the parent chain height.
const result = await tdvwCrossChainContract.GetParentChainHeight.call();
// Return the parent chain height if it exists, otherwise return an empty string.
return result ? (result.value as string) : "";
} catch (error: any) {
// If there's an error, log it and return an error status.
console.error(error, "=====error in GetParentChainHeight");
return "error";
}
};
What This Function Does:
-
Calls Smart Contract Method : It interacts with the side chain smart contract method to fetch the current height of the parent blockchain.
-
Returns Parent Chain's Height : It returns the parent chain's height if it exists.
Next, we'll write the Fetch the Merkle path function.
Fetch the Merkle path
Write the fetch the merkle path function
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step I - Fetch the merkle path by transaction Id. -
Replace the existing
getMerklePathByTxIdfunction with this code snippet:
// Step I - Fetch the merkle path by transaction Id
const getMerklePathByTxId = async (aelf: any, txId: string) => {
try {
const { MerklePathNodes } = await aelf.chain.getMerklePathByTxId(txId);
const formattedMerklePathNodes = MerklePathNodes.map(
({
Hash,
IsLeftChildNode,
}: {
Hash: string;
IsLeftChildNode: boolean;
}) => ({
hash: Hash,
isLeftChildNode: IsLeftChildNode,
})
)
return { merklePathNodes: formattedMerklePathNodes };
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error fetching Merkle path:", error);
throw new Error("Failed to get Merkle path by transaction ID.");
}
};
What This Function Does:
-
Fetches Merkle Path : It sends a request to fetch the merkle path using the transaction ID.
-
Parses Response : It parses the response from the server as JSON.
-
Returns Merkle Path Nodes : It extracts and returns the merkle path of the nodes from the JSON response.
Get Token Contract
Write the Get Token Contract function
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step J - Get Token Contract. -
Replace the existing
getTokenContractfunction with this code snippet:
// Step J - Get Token Contract
const getTokenContract = async (aelf: any, wallet: any) => {
const tokenContractName = "AElf.ContractNames.Token";
// get chain status
const chainStatus = await aelf.chain.getChainStatus();
// get genesis contract address
const GenesisContractAddress = chainStatus.GenesisContractAddress;
// get genesis contract instance
const zeroContract = await aelf.chain.contractAt(
GenesisContractAddress,
wallet
);
// Get contract address by the read only method `GetContractAddressByName` of genesis contract
const tokenContractAddress =
await zeroContract.GetContractAddressByName.call(
AElf.utils.sha256(tokenContractName)
);
return await aelf.chain.contractAt(tokenContractAddress, wallet);
};
What This Function Does:
-
Get chainStatus : It gets chainStatus from getChainStatus function.
-
Get GenesisContractAddress : It gets GenesisContractAddress from chainStatus.
-
fetch zeroContract : It fetches zeroContract using GenesisContractAddress and wallet.
-
fetch tokenContractAddress : It fetches tokenContractAddress by calling GetContractAddressByName method from zeroContract.
Create Fungible Token on the MainChain
Write a function to Create a new Fungible Token on the MainChain
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step K - Create Token on MainChain. -
Replace the existing
createTokenOnMainChainfunction with this code snippet:
// Step K - Create Token on MainChain
const createTokenOnMainChain = async (values: {
tokenName: string;
symbol: string;
totalSupply: string;
}) => {
setFormLoading(true);
let createMainChainTokenLoadingId;
try {
createMainChainTokenLoadingId = toast.loading(
"Creating $TOKEN on MainChain..."
);
// Preparing Parameter for Create Function
const createTokenMainChainInput = {
tokenName: values.tokenName,
symbol: values.symbol,
totalSupply: Number(values.totalSupply) + Number(extraRewardAmount),
issuer: currentWalletAddress,
isBurnable: true,
issueChainId: sidechain_from_chain_id,
owner: currentWalletAddress,
externalInfo: {},
};
const resultMainchain = await mainChainSmartContract?.callSendMethod(
"Create",
currentWalletAddress as string,
createTokenMainChainInput
);
console.log(
"========= result of create New $TOKEN =========",
resultMainchain
);
toast.update(createMainChainTokenLoadingId, {
render: "$TOKEN Created Successfully on MainChain",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
return "success";
} catch (error: any) {
if (!createMainChainTokenLoadingId) {
return "error";
}
handleCloseModal();
toast.update(createMainChainTokenLoadingId, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
return "error";
} finally {
removeNotification(createMainChainTokenLoadingId as Id, 5000);
}
};
ℹ️ Note: You need to get symbol from the Portkey wallet.
-
Follow Steps to get TOKEN symbol from Portkey Wallet:
- Open Portkey Wallet.
- Go to the NFTs tab.
- You will find the SEED that you already got from the above seed generation step.
- Click on the SEED to see details.
- You will find the Token Symbol inside the Token Creation via This Seed section.
- Copy and use that value of the token symbol.
What this function does:
-
Prepares Parameters : Constructs input parameters for creating the token, including token details and the issuer's information.
-
Calls Smart Contract : Sends a request to the mainchain smart contract to create the token using the prepared parameters.
-
Return Status : Returns
"success"if the token is created successfully; otherwise, returns"error".
Write the Function to Validate Token Info
Now, let's write the Validate TOKEN Info function.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step L - Validate Mainchain Token Create's Transaction. -
Replace the existing
validateTokenfunction with this code snippet:
// Step L - Validate Mainchain Token Create's Transaction
const validateToken = async (values: ITokenParams) => {
let validateTOKENLoadingId;
try {
setFormLoading(true);
// Start Loading before initiate the transaction
validateTOKENLoadingId = toast.loading(
<CustomToast
title="Transaction is getting validated on aelf blockchain. Please wait!"
message="Validation means transaction runs through a consensus algorithm to be selected or rejected. Once the status changes process will complete. It usually takes some time in distributed systems."
/>
);
// Create an object with the necessary information for token validation.
const validateInput = {
symbol: values.symbol,
tokenName: values.tokenName,
totalSupply: Number(values.totalSupply) + Number(extraRewardAmount),
issuer: currentWalletAddress,
isBurnable: true,
issueChainId: sidechain_from_chain_id,
owner: currentWalletAddress,
externalInfo: {},
};
// get mainnet contract
const aelfTokenContract = await getTokenContract(aelf, wallet);
// prepare Sign the transaction using contract method (ValidateTokenInfoExists Function)
const signedTx =
aelfTokenContract.ValidateTokenInfoExists.getSignedTx(validateInput);
// send the transaction using signed Transaction
const { TransactionId: VALIDATE_TXID } = await aelf.chain.sendTransaction(
signedTx
);
await delay(3000);
// get Validate Result
let VALIDATE_TXRESULT = await aelf.chain.getTxResult(VALIDATE_TXID);
await delay(3000);
// if dAppChain index has a MainChain height greater than validateTokenInfoExist's
let heightDone = false;
while (!heightDone) {
// get latest index Hight
const sideIndexMainHeight = await GetParentChainHeight();
if (
// check the latest index Hight is grater than or equal
Number(sideIndexMainHeight) >=
Number(VALIDATE_TXRESULT.Transaction.RefBlockNumber)
) {
VALIDATE_TXRESULT = await aelf.chain.getTxResult(VALIDATE_TXID);
heightDone = true;
}
}
console.log(VALIDATE_TXRESULT, "VALIDATE_TXRESULT=====2");
const merklePath = await getMerklePathByTxId(aelf, VALIDATE_TXID);
toast.update(validateTOKENLoadingId, {
render: "Validating $TOKEN Successfully Executed",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
// return necessary values
return {
parentChainHeight: VALIDATE_TXRESULT.BlockNumber,
signedTx: signedTx,
merklePath: merklePath,
};
} catch (error: any) {
toast.update(validateTOKENLoadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
handleCloseModal();
return "error";
} finally {
removeNotification(validateTOKENLoadingId as Id);
}
};
Here's what the function does:
-
Prepares Validation Input: Constructs the input parameters needed for validating the token.
-
Gets Token Contract: Retrieves the token contract instance from the MainChain.
-
Signs and Sends Transaction: Signs the transaction to validate the token info and sends it to the blockchain.
-
Polls for Transaction Result: Waits for the transaction result and ensures that the transaction has reached the required block height.
-
Fetches Merkle Path: Retrieves the Merkle path for the validated transaction.
Create Fungible Token on dAppChain
Write a Function to Create Token on the dAppChain
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step M - Create a Token on the dAppChain.. -
Replace the existing
createTokenOnSideChainfunction with this code snippet:
// Step M - Create a Token on the dAppChain.
const createTokenOnSideChain = async (values: ITokenValidateResult) => {
let createSideChainTokenLoadingId;
try {
createSideChainTokenLoadingId = toast.loading(
"Creating $TOKEN on SideChain..."
);
// Prepare create Token Parameters
const CREATE_TOKEN_PARAMS = {
fromChainId: mainchain_from_chain_id,
parentChainHeight: values.parentChainHeight,
transactionBytes: Buffer.from(values.signedTx, "hex").toString(
"base64"
),
merklePath: values.merklePath,
};
// Calling CrossChainCreateToken function on dAppChain
await sideChainSmartContract?.callSendMethod(
"CrossChainCreateToken",
currentWalletAddress as string,
CREATE_TOKEN_PARAMS
);
toast.update(createSideChainTokenLoadingId, {
render: "$TOKEN Created Successfully On SideChain",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
return "success";
} catch (error) {
toast.update(createSideChainTokenLoadingId as Id, {
render: "$TOKEN Created Successfully On SideChain",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
console.log("error====", error);
return "error";
} finally {
removeNotification(createSideChainTokenLoadingId as Id);
}
};
Here's what the function does:
-
Prepares Parameters: Constructs the parameters needed for creating the token on the dAppChain, including chain IDs & block height, transaction data, and Merkle path.
-
Calls Smart Contract Method: Sends the transaction to the dAppChain smart contract to create the token.
Issue the created token on the dAppChain
Write a Function to Issue Token which has been Created on the dAppChain.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step N - Issue Token on dAppChain. -
Replace the existing
issueTokenOnSideChainfunction with this code snippet:
// Step N - Issue Token on dAppChain
const issueTokenOnSideChain = async (values: {
symbol: string;
amount: string | number;
memo: string;
}) => {
let issueTokenLoadingId;
try {
setFormLoading(true);
issueTokenLoadingId = toast.loading("Issuing $TOKEN on SideChain...");
// prepate parameters
const issueTokenInput = {
symbol: values.symbol,
amount: values.amount,
memo: values.memo,
to: currentWalletAddress,
};
// call Issue function on dAppChain smart contract
const result = await sideChainSmartContract?.callSendMethod(
"Issue",
currentWalletAddress as string,
issueTokenInput
);
console.log(
"========= result of issue Token Transaction =========",
result
);
toast.update(issueTokenLoadingId, {
render: "$TOKEN Issue Successfully Executed",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
toast.success(
"You will get $TOKEN on your Wallet! It can take sometimes to get into your wallet"
);
return result;
} catch (error: any) {
handleCloseModal();
toast.update(issueTokenLoadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
return "error";
} finally {
removeNotification(issueTokenLoadingId as Id);
}
};
Here's what the function does:
-
Prepares Issuance Input: Constructs the input parameters for issuing the token including symbol, amount, memo, and recipient address.
-
Calls Smart Contract Method: Sends the transaction to the dAppChain smart contract to issue the token.
-
Handles Success: Updates the notification to show successful issuance and notifies the user that the token will appear in their wallet.
Transfer Token to Staking Contract
Create a Function to Transfer Token to the Staking Contract for Reward Balance
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step O - Transfer TOKEN to Staking Contract. -
Replace the existing
transferTokenToStakingContractfunction with this code snippet:
// Step O - Transfer TOKEN to Staking Contract
const transferTokenToStakingContract = async (
amount: string,
symbol: string
) => {
let transferTokenLoadingId = toast.loading(
"Transferring $TOKEN to Staking Contract for Reward Balance"
);
// prepare parameters
try {
const transferNtfInput = {
to: stakingContractAddress,
symbol: symbol,
amount: amount,
memo: "Transfering Amount to Staking Contract for Reward Balance",
};
// call Transfer function on dAppChain contract
await sideChainSmartContract?.callSendMethod(
"Transfer",
currentWalletAddress as string,
transferNtfInput
);
toast.update(transferTokenLoadingId, {
render: "$TOKEN Transfer Successfully!",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
return "success";
} catch (error: any) {
toast.update(transferTokenLoadingId, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
return "error";
} finally {
removeNotification(transferTokenLoadingId as Id);
}
};
Here's what the function does:
-
Prepares Transfer Input: Constructs the input parameters to transfer the token including to address, symbol, amount & memo.
-
Calls Smart Contract Method: Sends the transaction to the dAppChain smart contract to transfer the token.
Initialize the staking contract
Create a Function to Initialize the Staking Contract using Token Address
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step P - Initializing the staking contract. -
Replace the existing
initializedContractfunction with this code snippet:
// Step P - Initializing the staking contract
const initializedContract = async (tokenContractAddress: string) => {
let initializeLoadingId: any;
try {
initializeLoadingId = toast.loading("Staking Contract is Initialising...");
// call Initialize function on Staking contract using token contract
const result = await stakingContract?.callSendMethod(
"Initialize",
currentWalletAddress as string,
{ tokenContractAddress }
);
toast.update(initializeLoadingId, {
render: "Staking Contract Initialised Successful",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
return "true";
} catch (error: any) {
toast.update(initializeLoadingId, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
return "error";
} finally {
removeNotification(initializeLoadingId as Id);
}
};
Here's what the function does:
- Calls Smart Contract Method: Sends the transaction to the staking smart contract to initialize the contract using the token address.
Configure Submit Form
Create a Function to Handle Submit of Create form
Now, let's write the create token function.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step Q - handle Submit of Create Token. -
Replace the existing
onSubmitfunction with this code snippet:
// Step Q - handle Submit of Create Token
const onSubmit = async (values: {
tokenName: string;
symbol: string;
totalSupply: string;
}) => {
try {
// creating TOKEN on mainchain
const mainChainResult = await createTokenOnMainChain(values);
if (mainChainResult === "error") {
setFormLoading(false);
return;
}
await delay(3000);
// Validating Transaction of Create Token on mainchain
const validateTokenData: ITokenValidateResult | "error" = await validateToken(values);
if (validateTokenData === "error") {
setFormLoading(false);
return;
}
// creating TOKEN on side chain once Transaction validate
const sideChainResult = await createTokenOnSideChain(validateTokenData);
if (sideChainResult === "error") {
setFormLoading(false);
return;
}
// Issuing TOKEN on side chain once it's created succefully
const issueTokenResult: any = await issueTokenOnSideChain({
symbol: values.symbol,
amount: Number(values.totalSupply) + Number(extraRewardAmount),
memo: "We are issuing Token",
});
if (issueTokenResult === "error") {
setFormLoading(false);
return;
}
// get TokenContractDetails from transactio logs on issues Token
const tokenLog = issueTokenResult.data.Logs.find(({Name}:{Name:string})=>Name === "Issued")
if(!tokenLog){
toast.error("Error in Token Address");
return
}
// Transferring Reward Amount on Staking Contract
await transferTokenToStakingContract(extraRewardAmount, values.symbol);
// Initializing Staking smart contract using Token Address
await initializedContract(tokenLog.Address);
} catch (error: any) {
toast.error(error);
} finally {
setFormLoading(false);
handleCloseModal();
}
};
Here's what the function does:
-
Creates Token on the MainChain: Calls
createTokenOnMainChainto create the token on the mainchain. If it fails, it updates the transaction status and exits. -
Validates Create Token Transaction: Waits for 3 seconds, then calls
validateTokento validate the token. If validation fails, it updates the transaction status and exits. -
Creates Token on the dAppChain: Calls
createTokenOnSideChainto create the token on the dAppChain using the validated data. If it fails, it updates the transaction status and exits. -
Issues Token on the dAppChain: Calls
issueTokenOnSideChainto issue the token. Updates the transaction status to false after completion. -
Transferring Reward Amount to the Staking Contract : Calls
transferTokenToStakingContractto transfer the reward amount to the staking contract. -
Initializing Staking smart contract: Calls
initializedContractto initialize the staking smart contract using the token address.
Fetch Token Data
Let's write the function to fetch the token data from user's wallet using graphql API.
Step 1: Locate the File
- go to the
/src/pages/home/index.tsxfile.
Step 2: Write Function to fetch the fungible token data
-
Find the comment
// Step R - fetch Fungible Token data. -
Replace the existing
fetchTokenDatafunction with this code snippet:
// Step R - fetch Fungible Token data
const fetchTokenData = async () => {
if (!currentWalletAddress) {
return;
}
try {
// Your GraphQL query and variables from the curl command
const query = `
query ExampleQuery($dto: GetCAHolderTokenBalanceDto) {
caHolderTokenBalanceInfo(dto: $dto) {
data {
balance
tokenInfo {
symbol
}
}
}
}
`;
const variables = {
dto: {
chainId: "tDVW", // AELF or tDVW
skipCount: 0,
maxResultCount: 100,
caAddressInfos: [
{
caAddress: currentWalletAddress,
},
],
},
};
// Axios POST request to the GraphQL endpoint
const response = await axios.post(
"https://dapp-aa-portkey-test.portkey.finance/Portkey_V2_DID/PortKeyIndexerCASchema/graphql",
{
query: query,
variables: variables,
},
{
headers: {
"content-type": "application/json",
},
}
);
// Handle the response
const tokensData = response.data.data.caHolderTokenBalanceInfo.data;
// find token detilas from API data
if (tokensData && tokensData.length > 0) {
const filterTokenInfo = tokensData.find(
(data: ITokenInfo) => data.tokenInfo.symbol.length === 10,
[]
);
if (filterTokenInfo) {
setTokenInfo(filterTokenInfo);
}
}
} catch (err) {
console.log("error", err);
}
};
Here's what the function does:
-
Fetch Token balance: Fetches token balance using graphql api.
-
Filter Token Details: It finds the token details from the API response.
Now, it's time to start the implementation of the staking functionality.
Deposit Stake Amount on the Staking Contract
As we have completed Create Token and Fetch Token balance functionality, it's time to acheive Stake Token functionality using the staking smart contract.
Now, let's prepare the Deposit Stake Amount related functions.
Transfer Tokens to the Staking Contract
First, we need to transfer stake amount to the staking contract address using dAppChain contract and then we can call the GetDeposits function on the staking contract.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step S - Function to transfer tokens to the staking contract. -
Replace the existing
transferTokenToStakingContractfunction with this code snippet:
// Step S - Function to transfer tokens to the staking contract
const transferTokenToStakingContract = async (amount: string) => {
// Show a loading toast notification while the transfer is in progress
let transferTokenLoadingId = toast.loading("$TOKEN Deposit Transaction Executing");
try {
// Prepare the transfer input with required parameters
const transferNtfInput = {
to: stakingContractAddress, // Address of the staking contract
symbol: tokenInfo?.tokenInfo.symbol, // Symbol of the token being transferred
amount: amount, // Amount to be transferred
memo: "Transferring Amount to Staking Contract for Deposit Token", // Description or memo for the transaction
};
// Call the transfer method on the side chain smart contract
await sideChainSmartContract?.callSendMethod(
"Transfer",
currentWalletAddress as string, // Address of the current wallet initiating the transfer
transferNtfInput
);
// Update the toast notification on successful transfer
toast.update(transferTokenLoadingId, {
render: "$TOKEN Deposit Successfully!",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
removeNotification(transferTokenLoadingId); // Remove the notification
return "success"; // Return success status
} catch (error: any) {
// Handle any error during the token transfer and update the toast notification
toast.update(transferTokenLoadingId, {
render: error.message, // Display the error message
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
removeNotification(transferTokenLoadingId); // Remove the notification
return "error"; // Return error status
}
};
Create Handle Staking function
Now, let's create the function to handle staking, as we have already completed transferTokenToStakingContract function.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// Step T - Function to handle staking of the tokens. -
Replace the existing
handleStakingfunction with this code snippet:
// Step T - Function to handle staking of the tokens
const handleStaking = async () => {
// Validate the amount and handle any errors
const isError = handleAmountError(amount);
if (isError) {
return; // Exit if there is an error with the amount
}
let stakingLoadingId: any; // Variable to store the loading toast ID
try {
// Transfer the token to the staking contract before proceeding with staking
const result: "success" | "error" = await transferTokenToStakingContract(amount);
// Exit if the transfer encountered an error
if (result === "error") {
return;
}
// Show a loading toast notification for the staking process
stakingLoadingId = toast.loading("Staking $TOKEN on Smart Contract...");
// Prepare the deposit parameters
const DEPOSIT_PARAMS = {
tokenSymbol: tokenInfo?.tokenInfo.symbol, // Symbol of the token being staked
amount: amount, // Amount being staked
lockTime: 300, // Time for which the tokens are locked
};
// Call the deposit method on the staking contract
await stakingContract?.callSendMethod(
"Deposit",
currentWalletAddress as string, // Address of the current wallet
DEPOSIT_PARAMS
);
// Fetch the updated deposit data and total staked amount after staking
fetchDepositData();
fetchTotalStakedAmount();
// Reset the edited status and clear the amount field
setIsEdited(false);
setAmount("");
// Update the toast notification for successful staking
toast.update(stakingLoadingId, {
render: "$TOKEN Staked Successfully",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
removeNotification(stakingLoadingId); // Remove the notification
} catch (error: any) {
// Handle any error during staking and update the toast notification
setAmount(""); // Clear the amount field in case of an error
toast.update(stakingLoadingId, {
render: error.message, // Display the error message
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
removeNotification(stakingLoadingId); // Remove the notification
return "error"; // Return error status
}
};
Fetch Deposited (Staked) Tokens
-
Find the comment
// Step U - Function to fetch deposited (staked) tokens for the connected wallet address. -
Replace the existing
fetchDepositDatafunction with this code snippet:
// Step U - Function to fetch deposit data for the current wallet address
const fetchDepositData = async () => {
try {
// Call the "GetDeposits" method on the staking contract to get deposits for the wallet address
const deposite: any = await stakingContract?.callViewMethod("GetDeposits",{value: currentWalletAddress as string});
// Check if there are any deposits in the returned data
if (deposite.data && deposite.data.deposits.length > 0) {
setDepositData(deposite.data.deposits); // Update state with the deposit data
} else {
setDepositData([]); // If no deposits, set the data to an empty array
}
} catch (error) {
// Log and handle any errors during the fetch
console.log("error", error);
return "error";
}
};
Fetch Total Staked Amount
-
Find the comment
// Step V - Function to fetch the total staked amount from the staking contract. -
Replace the existing
fetchTotalStakedAmountfunction with this code snippet:
// Step V - Function to fetch the total staked amount from the staking contract
const fetchTotalStakedAmount = async () => {
try {
// Call the "GetTotalStakedAmount" method to get the total staked amount
const amount: any = await stakingContract?.callViewMethod("GetTotalStakedAmount","");
// Check if there is valid data for the total staked amount
if (amount?.data) {
setTotalStakedAmount(amount.data.value); // Update state with the total staked amount
} else {
setTotalStakedAmount("0"); // If no data, set the total staked amount to "0"
}
} catch (error) {
// Log and handle any errors during the fetch
console.log("error", error);
return "error";
}
};
Withdraw Staked Tokens
Users can withdraw the staked amount after the staking period is over for a specific deposit.
-
Find the comment
// Step W - Function to withdraw staked tokens based on a deposit ID. -
Replace the existing
withdrawStakefunction with this code snippet:
// Step W - Function to withdraw staked tokens based on a deposit ID
const withdrawStake = async (depositId: string) => {
let withdrawLoadingId: any; // Variable to store the loading toast ID
setIsWithdrawing(true); // Set the withdrawing state to true
try {
// Show a loading toast notification while the withdrawal is in progress
withdrawLoadingId = toast.loading("$TOKEN Withdrawal in Progress...");
// Call the "Withdraw" method on the staking contract to withdraw based on deposit ID
await stakingContract?.callSendMethod(
"Withdraw",
currentWalletAddress as string, // Pass the current wallet address
{ depositId } // Pass the deposit ID to withdraw
);
// Update the toast notification on successful withdrawal
toast.update(withdrawLoadingId, {
render: "$TOKEN Withdraw Successful",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
removeNotification(withdrawLoadingId); // Remove the loading notification
} catch (error: any) {
// Handle any errors during withdrawal and update the toast notification
toast.update(withdrawLoadingId, {
render: error.message, // Display the error message
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
removeNotification(withdrawLoadingId); // Remove the loading notification
return "error"; // Return error status
} finally {
// After withdrawal, fetch updated deposit data and total staked amount
fetchDepositData();
fetchTotalStakedAmount();
setIsWithdrawing(false); // Set the withdrawing state to false
}
};
Emergency Withdraw Staked Tokens
Users can withdraw their staked amount at any time through the emergency withdrawal function before the staking period gets over.
-
Find the comment
// Step X - Function to perform an emergency withdrawal of staked tokens based on a deposit ID. -
Replace the existing
emergencyWithdrawStakefunction with this code snippet:
// Step X - Function to perform an emergency withdrawal of staked tokens based on a deposit ID
const emergencyWithdrawStake = async (depositId: string) => {
let withdrawLoadingId: any; // Variable to store the loading toast ID
setIsWithdrawing(true); // Set the withdrawing state to true
try {
// Show a loading toast notification while the emergency withdrawal is in progress
withdrawLoadingId = toast.loading("Emergency $TOKEN Withdrawal in Progress...");
// Call the "ForceWithdraw" method on the staking contract to forcefully withdraw the deposit
await stakingContract?.callSendMethod(
"ForceWithdraw",
currentWalletAddress as string, // Pass the current wallet address
{ value: depositId } // Pass the deposit ID for the emergency withdrawal
);
// Update the toast notification on successful emergency withdrawal
toast.update(withdrawLoadingId, {
render: "$TOKEN Withdraw Successful",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
removeNotification(withdrawLoadingId); // Remove the loading notification
} catch (error: any) {
// Handle any errors during emergency withdrawal and update the toast notification
toast.update(withdrawLoadingId, {
render: error.message, // Display the error message
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
removeNotification(withdrawLoadingId); // Remove the loading notification
return "error"; // Return error status
} finally {
// After the emergency withdrawal, fetch updated deposit data
fetchDepositData();
setIsWithdrawing(false); // Set the withdrawing state to false
}
};
Set Staking Contract Address
You need to set your deployed Staking contract Address in utils file so let's set it now.
Step 1: Locate the File
- Go to the
/src/lib/utils.tsxfile.
Step 2: Set Deployed Staking Contract Address
-
Find the comment
// Step Y - Staking contract addresson below of page. -
Replace your deployed staking contract with value of stakingContractAddress (
your_deployed_stakinng_contract).
// Step Y - Staking contract address
export const stakingContractAddress = "your_deployed_staking_contract_address"
As we've written all the necessary frontend functions and components, we're ready to run the Staking dApp application in the next step.
Run Application
In this step, we will run the Staking dApp application.
- To begin, run the following command on your terminal.
npm run dev
ℹ️ Note: Ensure that you are running this command under the staking/2-dapp folder.
-
You should observe the following as shown below.
-
Upon clicking on the localhost URL, you should be directed to the Staking dApp landing page as shown below.
If you are developing and testing this with GitHub codespace, you can use Port Forward to test the web server that is running in codespace, here is the link on how to use Port forward for codespace https://docs.github.com/en/codespaces/developing-in-a-codespace/forwarding-ports-in-your-codespace
-
Usually codespace will automatically forward port, you should see a pop-up message at the bottom right of your codespace browser window as shown in the diagram below:
-
Click the link to open the Staking dApp in the browser.
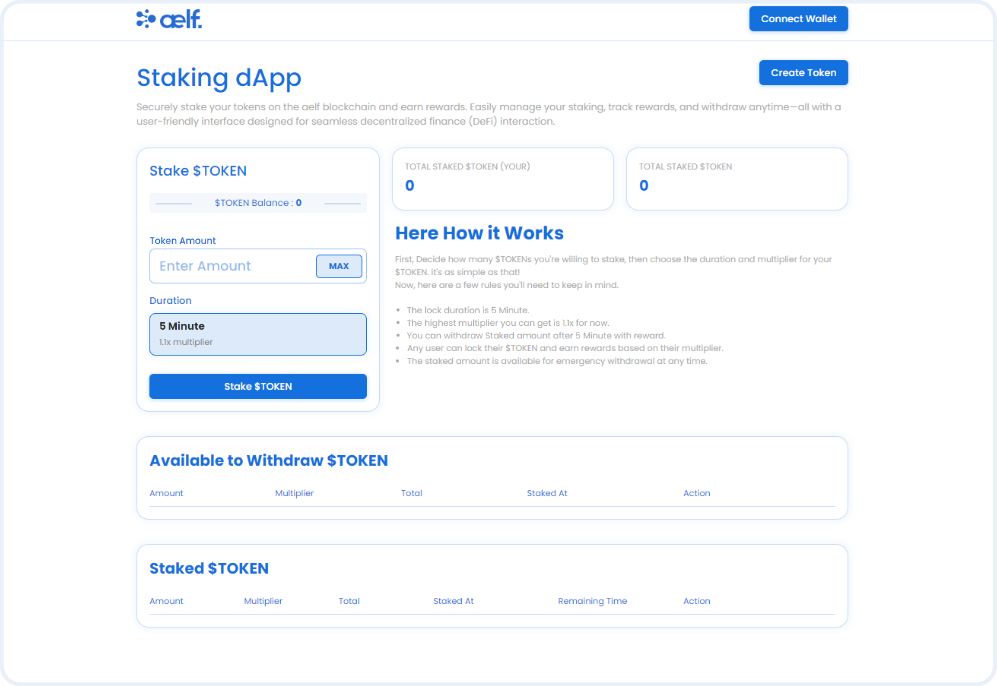
Create Portkey Wallet
Portkey is the first AA wallet from aelf's ecosystem, migrating users, developers and projects from Web2 to Web3 with DID solution.
Users can swiftly log into Portkey via their Web2 social info with no private keys or mnemonics required. Underpinned by social recovery and decentralized guardian design, Portkey safeguards users' assets from centralized control and theft. Portkey has a unique payment delegation mechanism which enables interested parties to function as delegates to pay for user activities on users' behalf. This means that users can create accounts for free and fees for other usages may also be covered in Portkey.
Portkey also provides crypto on/off-ramp services, allowing users to exchange fiat with crypto freely. It supports the storage and management of various digital assets such as tokens, NFTs, etc. The compatibility with multi-chains and seamless connection to all kinds of dApps makes Portkey a great way to enter the world of Web3.
With DID solution as its core, Portkey provides both Portkey Wallet and Portkey SDKs.
For more information, you may visit the official documentation for Portkey at https://doc.portkey.finance/.
- Download the Chrome extension for Portkey from https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/portkey-wallet/iglbgmakmggfkoidiagnhknlndljlolb.
The Portkey extension supports Chrome browser only (for now). Please ensure that you are using Chrome browser. You may download Chrome from https://www.google.com/intl/en_sg/chrome/.
-
Once you have downloaded the extension, you should see the following on your browser as shown below.

-
Click on
Get Startand you should see the following interface as shown below.
Sign up
-
Switch to aelf Testnet network by selecting it:
Please make sure you are using aelf Testnet in order to be able to receive your testnet tokens from the Faucet.
-
Proceed to sign up with a Google Account or your preferred login method and complete the necessary accounts creation prompts and you should observe the following interface once you have signed up.
With that, you have successfully created your very first Portkey wallet within seconds. How easy was that?
It is highly recommended to pin the Portkey wallet extension for easier access and navigation to your Portkey wallet!
-
Next, click on ‘Open Portkey’ and you should now observe the following as shown below.
Connect Portkey Wallet
-
Click on "Connect Wallet" to connect your Portkey wallet.
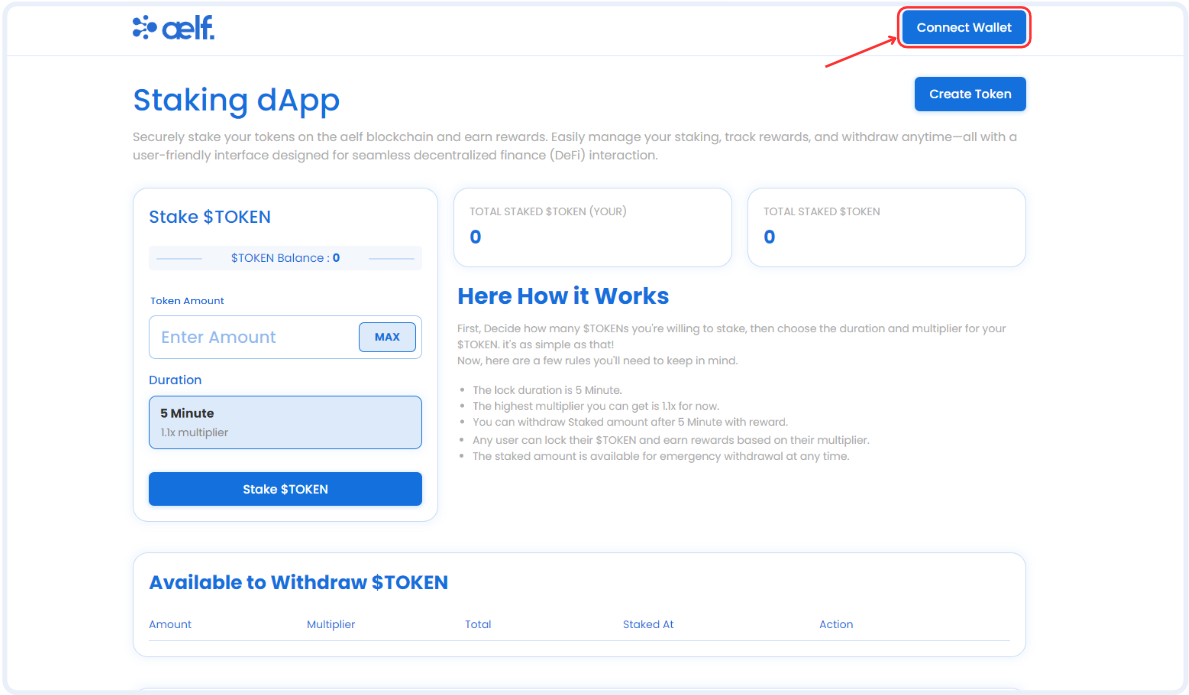
-
You will get a connection request on Portkey wallet as you can see in the below image.
-
Click on Approve button.
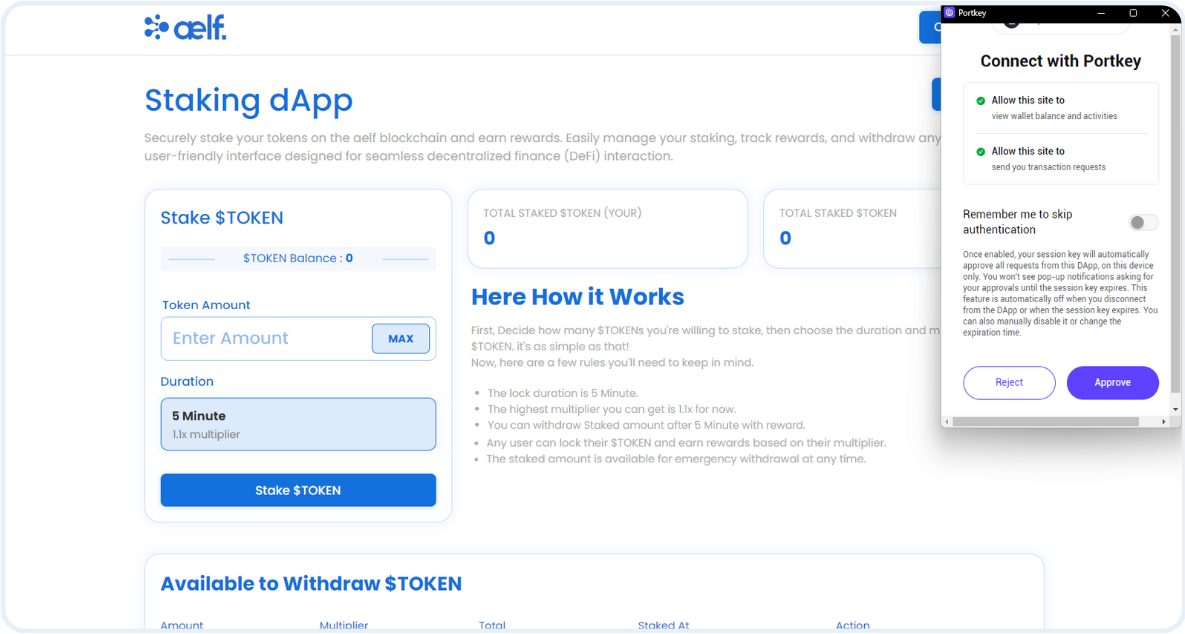
-
The button will change to "Your Wallet Address" when the connection is successful.
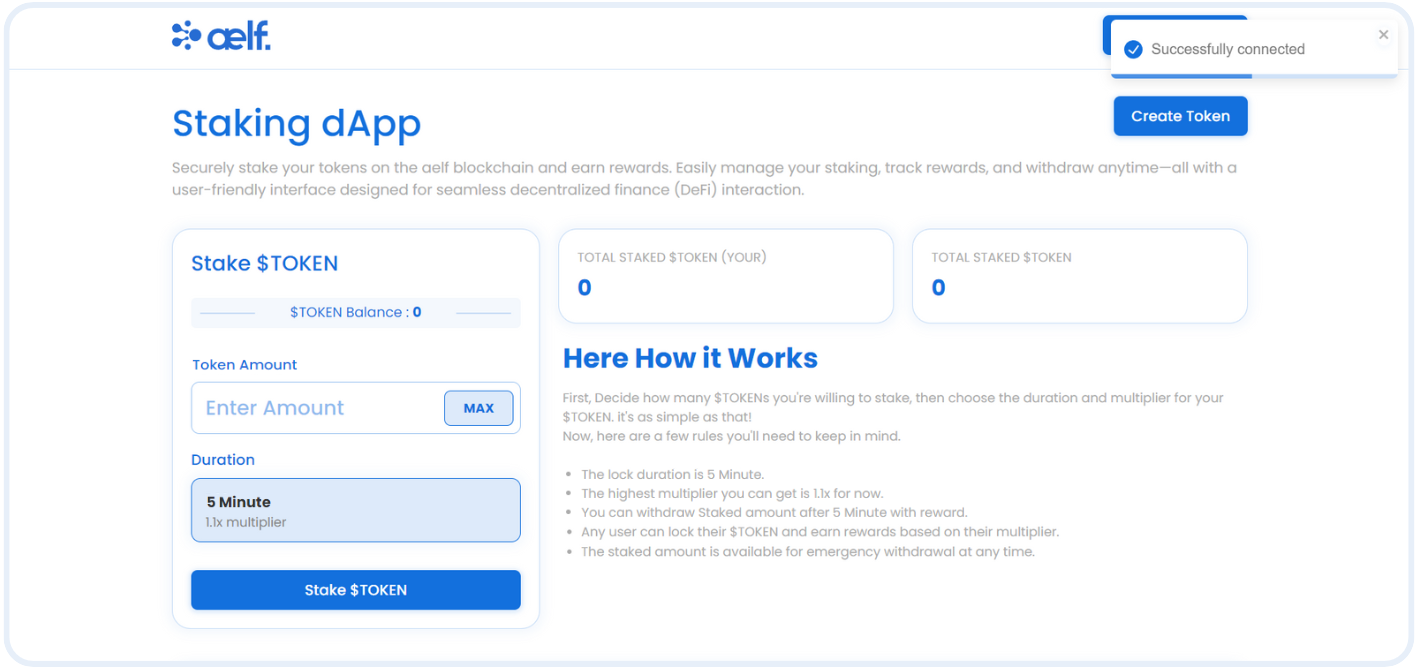
Create Fungible Token
-
Click on "Create Token" button to create new Fungible Token.
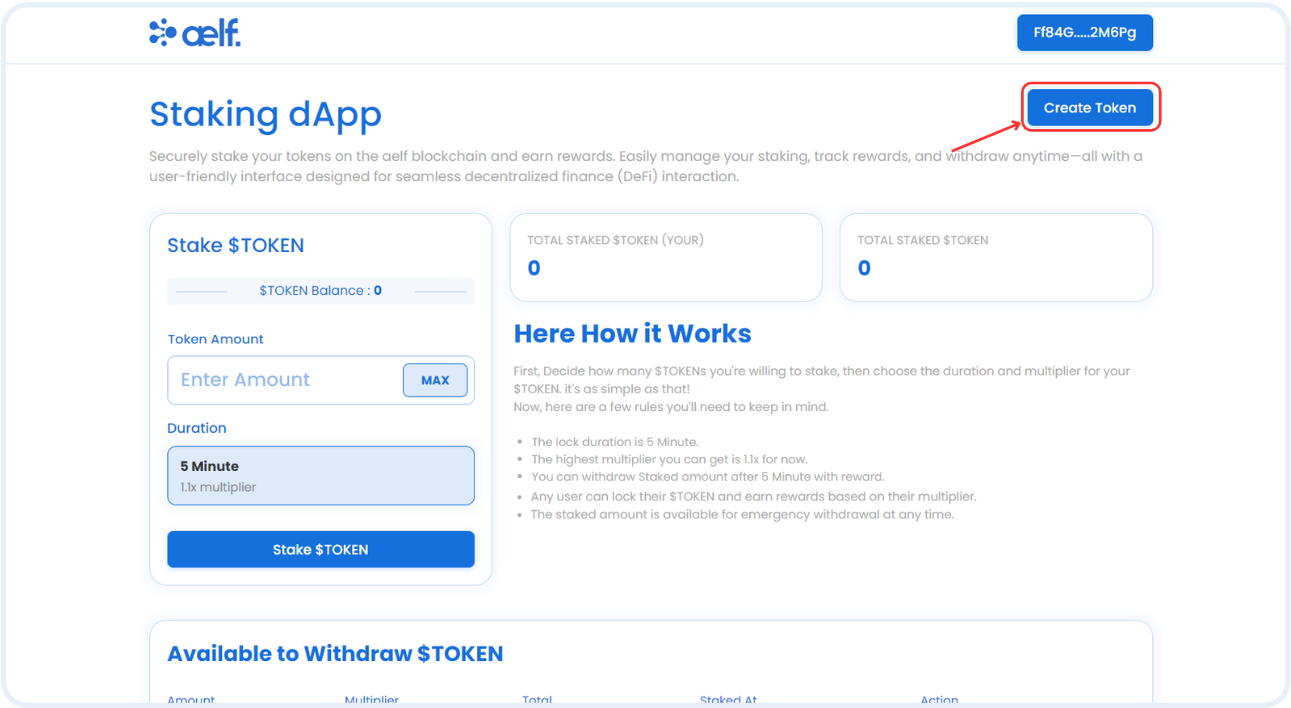
-
The
Create TokenPopup modal will appear with prefilled token name. (You can modify the token name)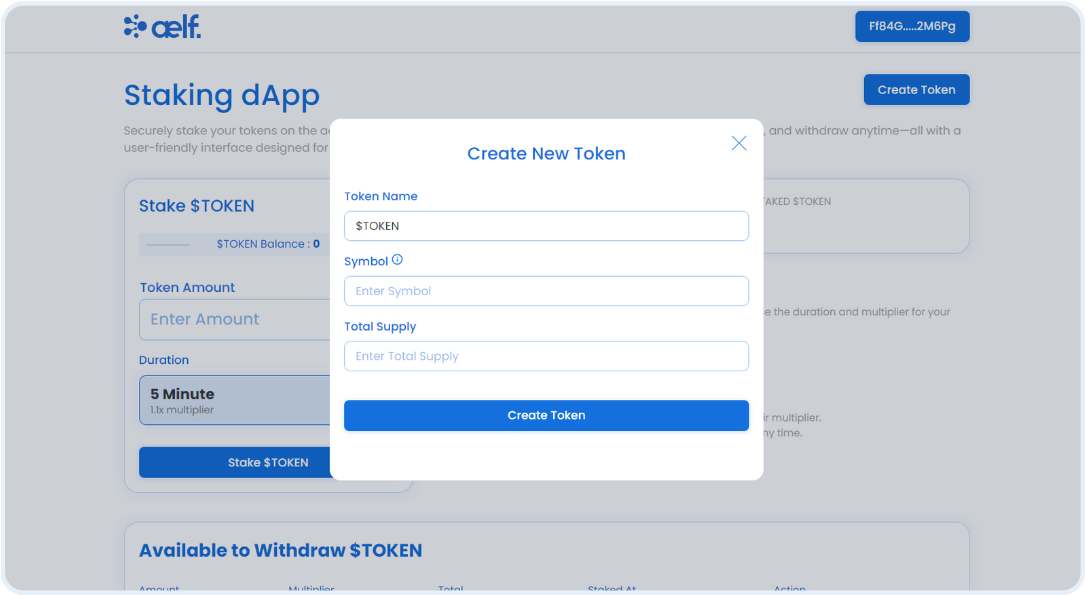
-
Now, you need Token Seed to create the new token.
-
If you don't have Token Seed then please follow this steps to get it.
-
Open your Portkey Wallet and you will find the TOKEN Symbol on the NFT Tab.
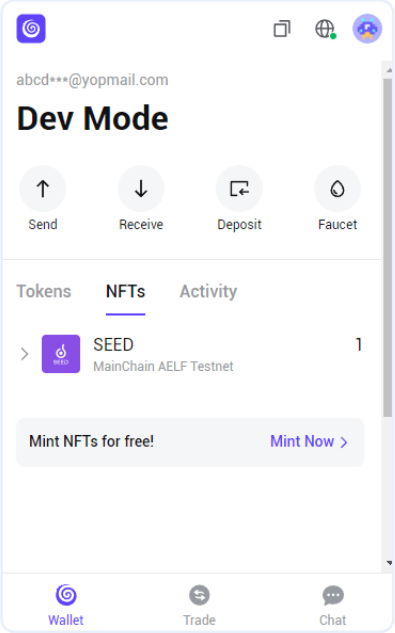
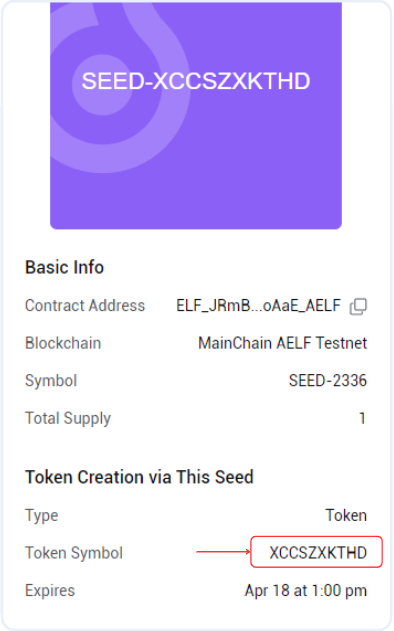
-
Copy the Token Symbol and use it inside the
Symbolfield of the token creation form. -
Fill other necessary details like
Total Supply.
-
Click on the Create Token Button.
-
You will get a transaction request on your Portkey wallet. Proceed to Sign the transaction.
-
After transaction is succesfully signed, you will get a successful/failed transaction notification.
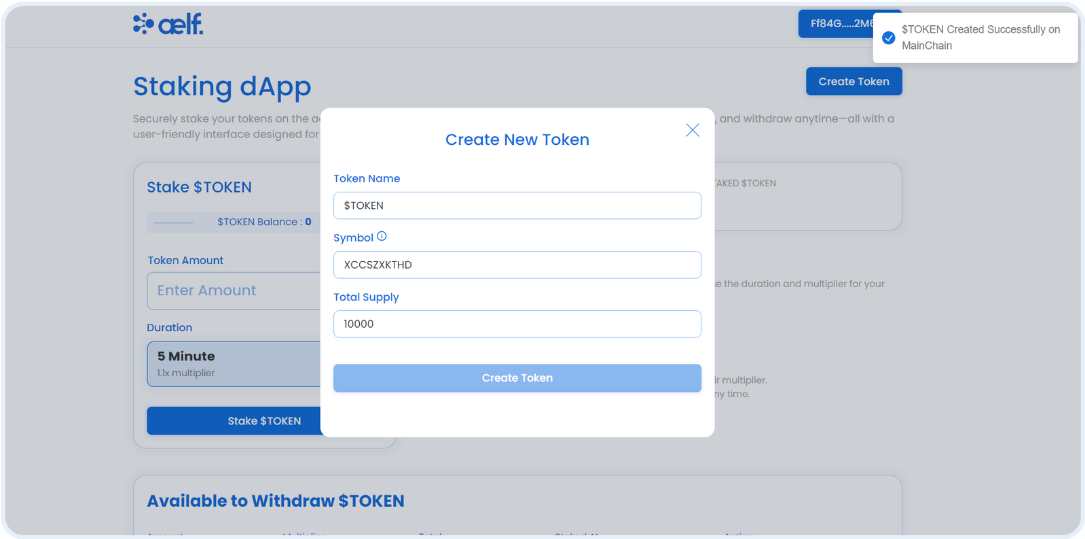
-
Now, the transaction will be validated on the aelf blockchain. Let's wait till the transaction gets validated.
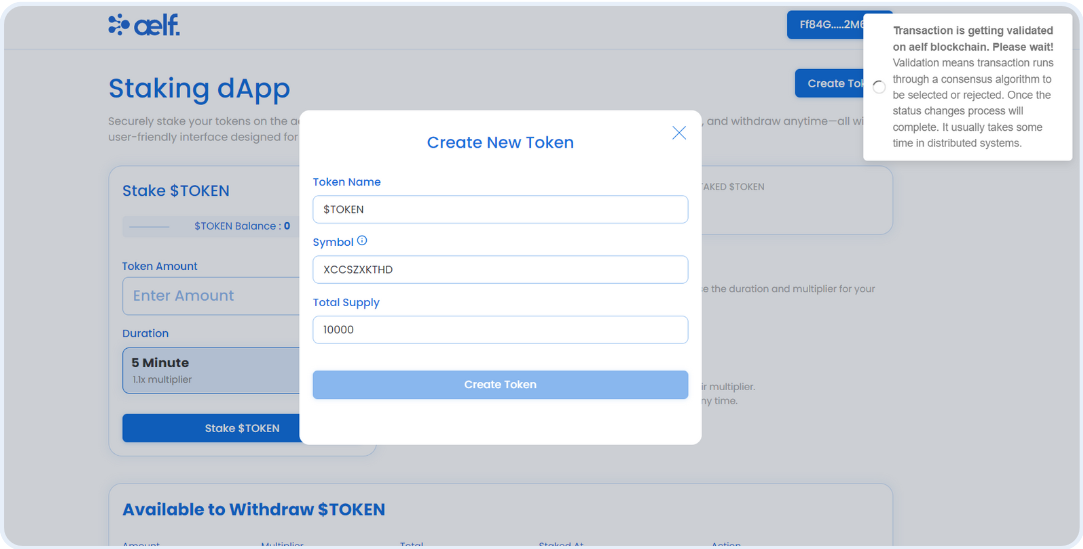
-
Once the transaction is successfully validated, a new Sign transaction request will pop-up on Portkey to Create Token on the dAppChain.
-
Click on the Approve button and wait for the transaction to complete.
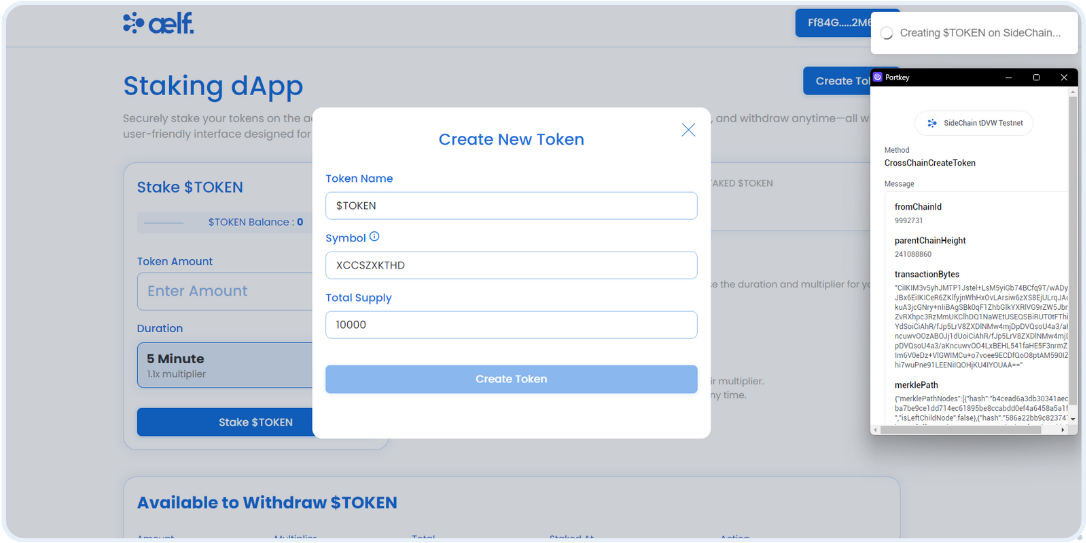
-
After the successful creation of the token on the dAppChain, a new Sign transaction request will pop-up on Portkey to Issue Tokens On the dAppChain.
-
Click on the Approve button and wait for the transaction to complete.
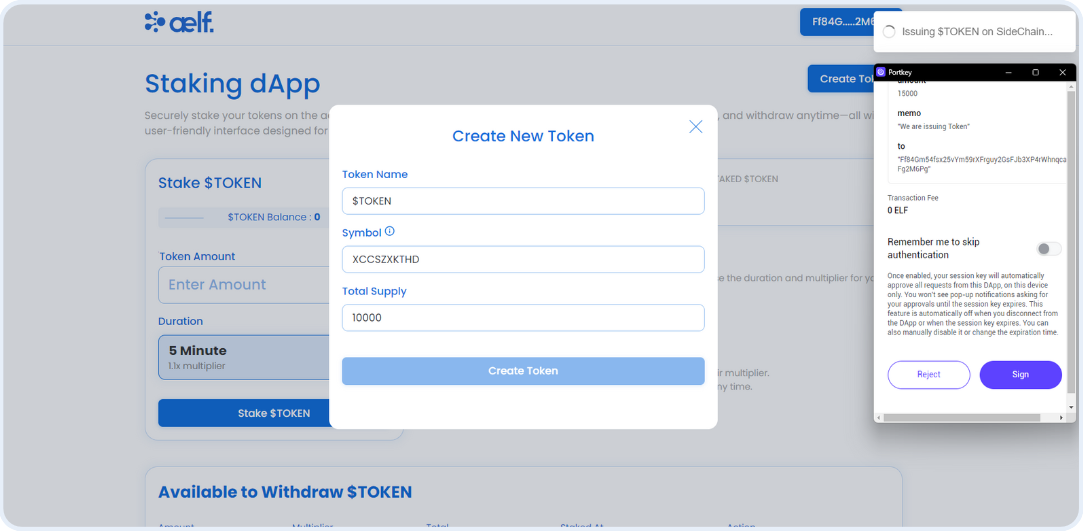
-
Once tokens are issued successfully on the dAppChain, a new Sign transaction request will pop-up on Portkey to Transfer Tokens to the Staking Contract to distribute future staking rewards.
-
Click on the Approve button and wait for the transaction to complete.
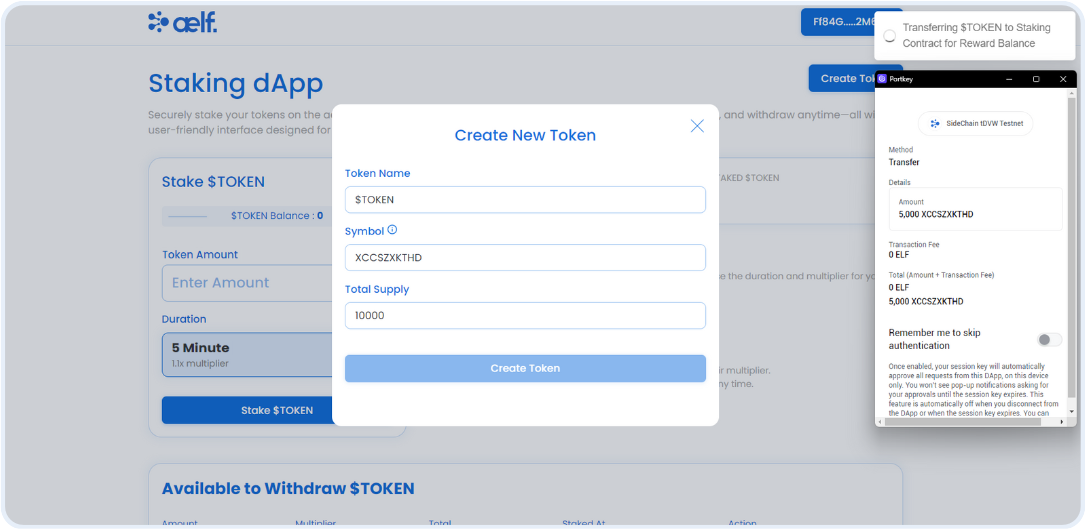
-
Once the reward tokens are transferred successfully, a new Sign transaction request will pop-up on Portkey to Initialize the Staking Contract.
-
Click on the Approve button and wait for the transaction to complete.
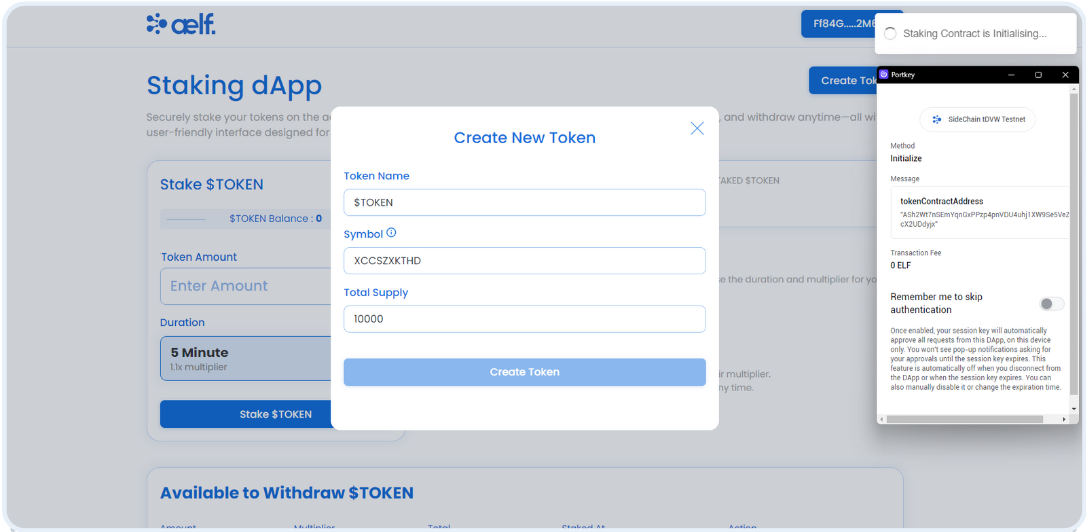
-
Once the transaction is suceessfully completed, a notification will pop-up and the Token balance will be visible on the staking widget like below.
Stake Tokens
-
Enter the amount to stake the tokens and click on the Stake $TOKEN Button.
-
A new Sign transaction request will pop-up on Portkey to Transfer $TOKEN amount to the staking contract. Click on the Sign Button.
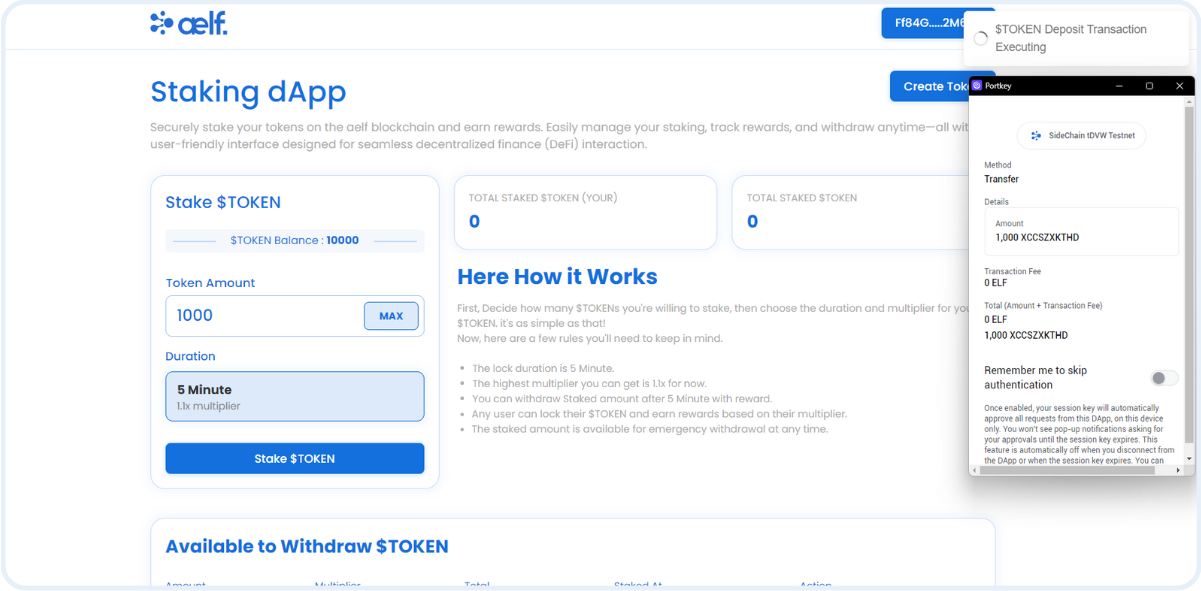
-
Now You will get another transaction request to Deposit $TOKEN on the staking contract on the Portkey Wallet. Click on the Sign Button.
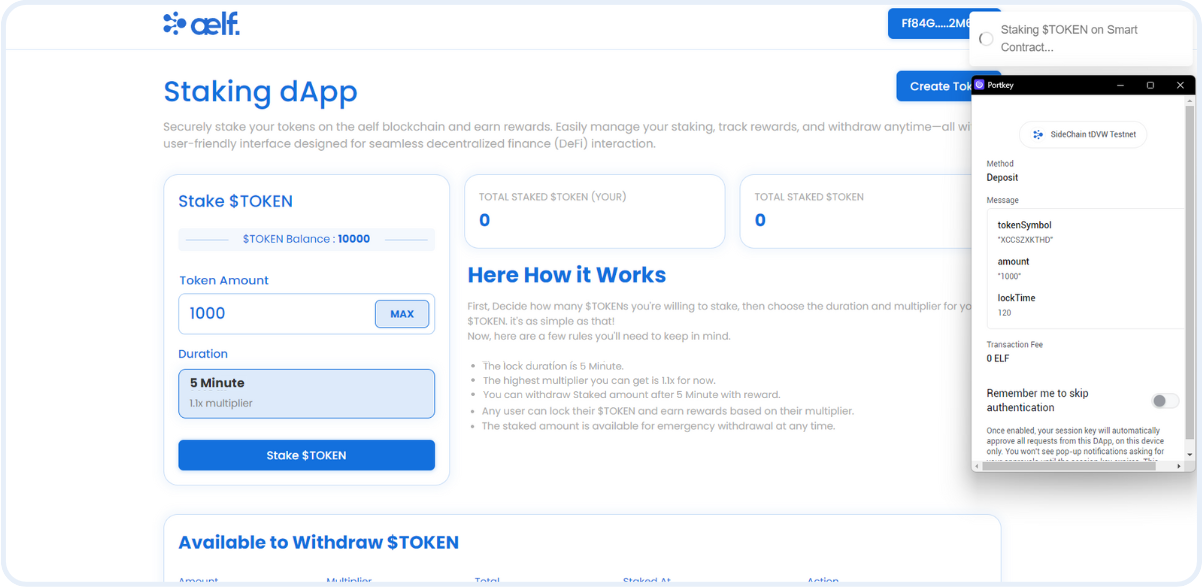
-
A notification will pop-up that the $TOKEN are Staked Succesfully. The Token balance will be updated.
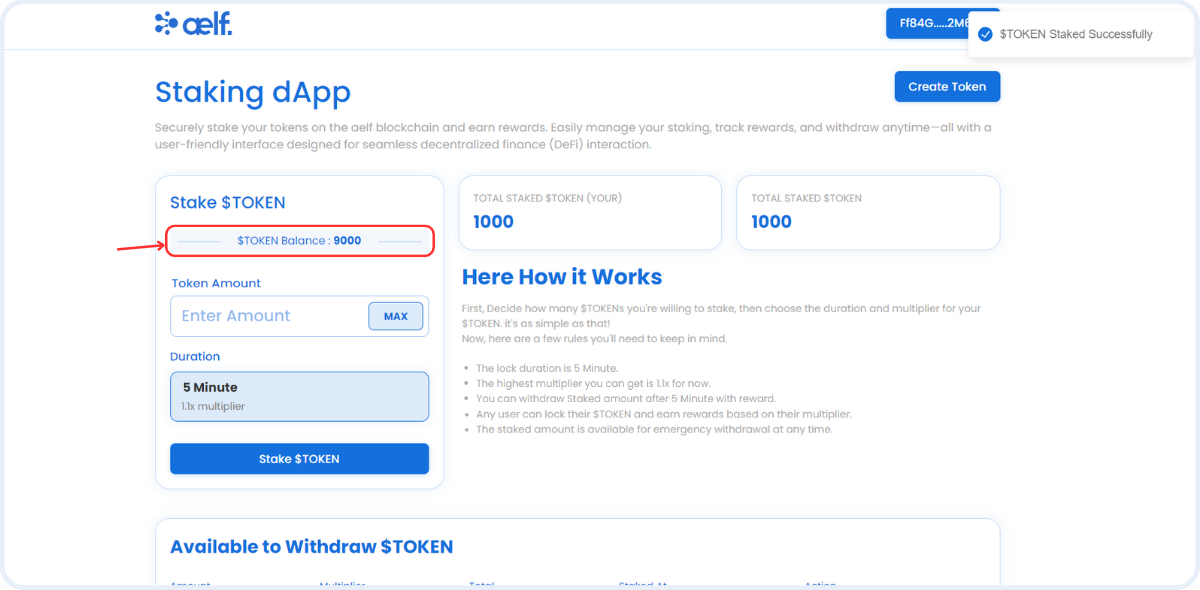
As we have completed all the necessary steps to stake the token, now it's time to withdraw the tokens.
- There are two ways to withdraw the staked amount.
- Emergency Withdraw Token : User can withdraw staked tokens at anytime before the staking (lock) time period ends.
- Withdraw Token : User can withdraw staked tokens once the lock time period is over.
Let's do Emergency Withdraw Token in the next step.
Emergency Withdraw Tokens
- After clicking on the staked token, A staked token entry will be visible on the Staked $TOKEN section like below.
- Click on Emergency Withdraw Button.
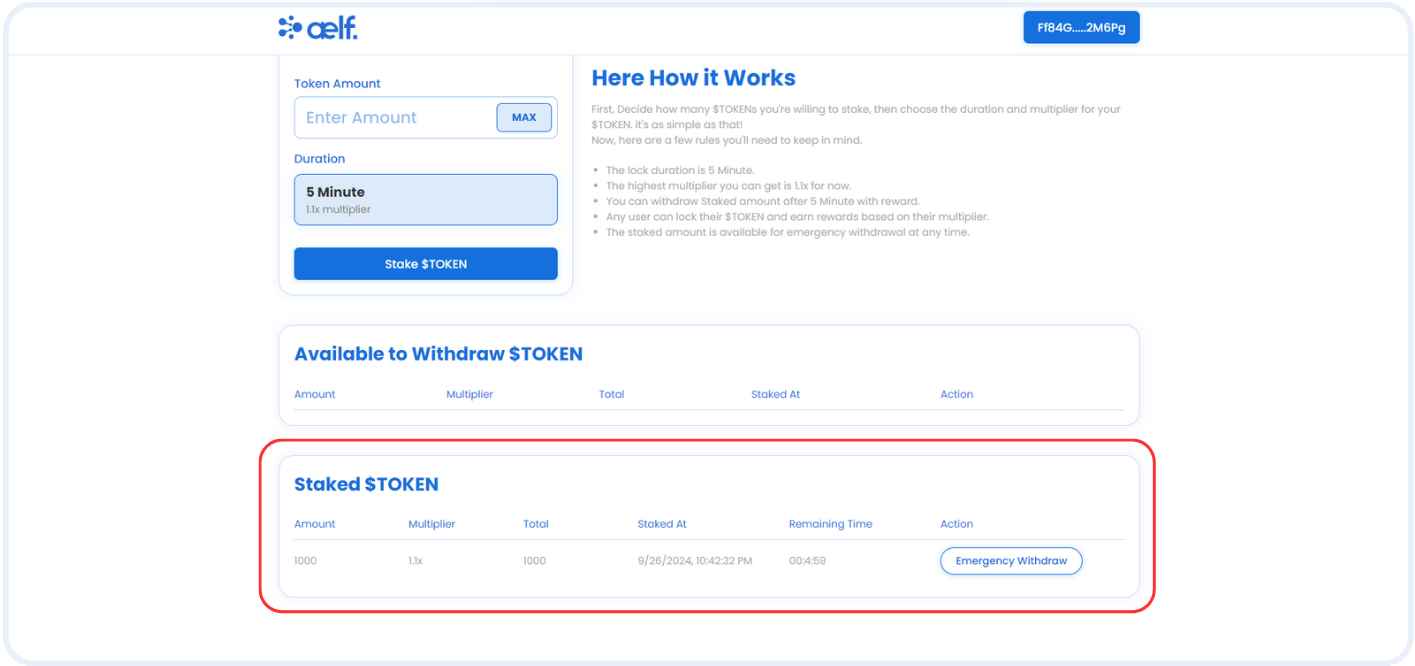
- Now, a transaction request will pop-up on the Portkey wallet.
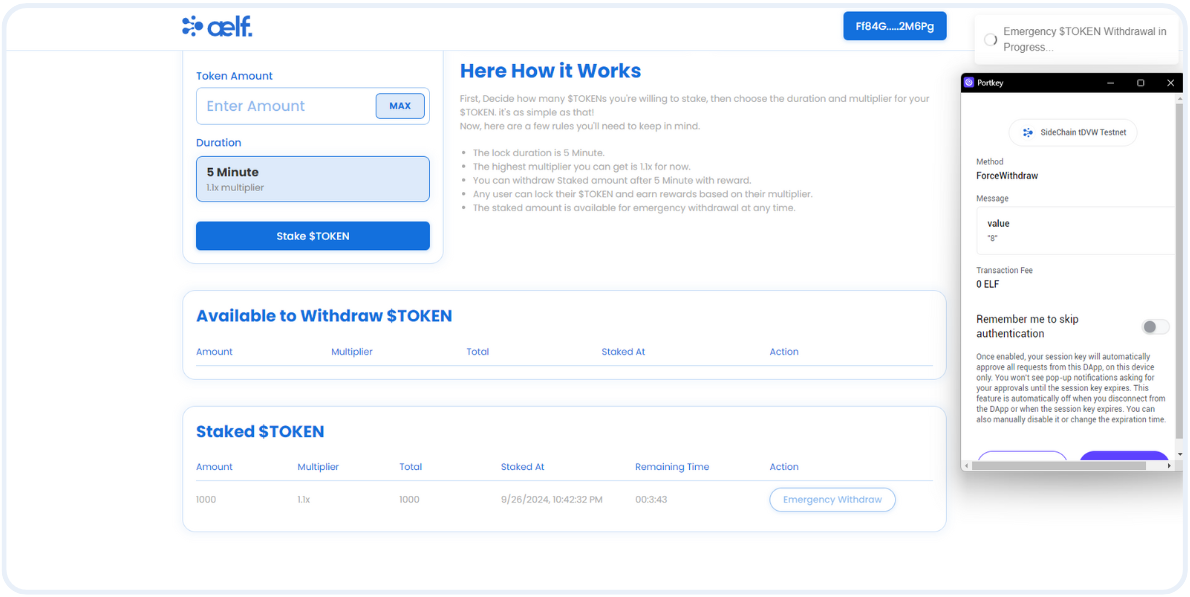
- The staked amount will be returned without any rewards and the token balance will be updated.
As we have completed Emergency Withdraw Tokens functioanlity. It's time to try Withdraw Token functionality.
Withdraw Token
-
First, the connected wallet needs to stake the tokens on the staking contract as we have already completed this during Stake Tokens step.
-
You need to wait till the lock time period is over for the staked amount.
-
After the lock period is over, you will be able to see your staked amount in Available to Withdraw $TOKEN section as shown below.
-
Click on Withdraw button to withdraw the amount including staking Rewards. 1.1 times the amount of the staked tokens.
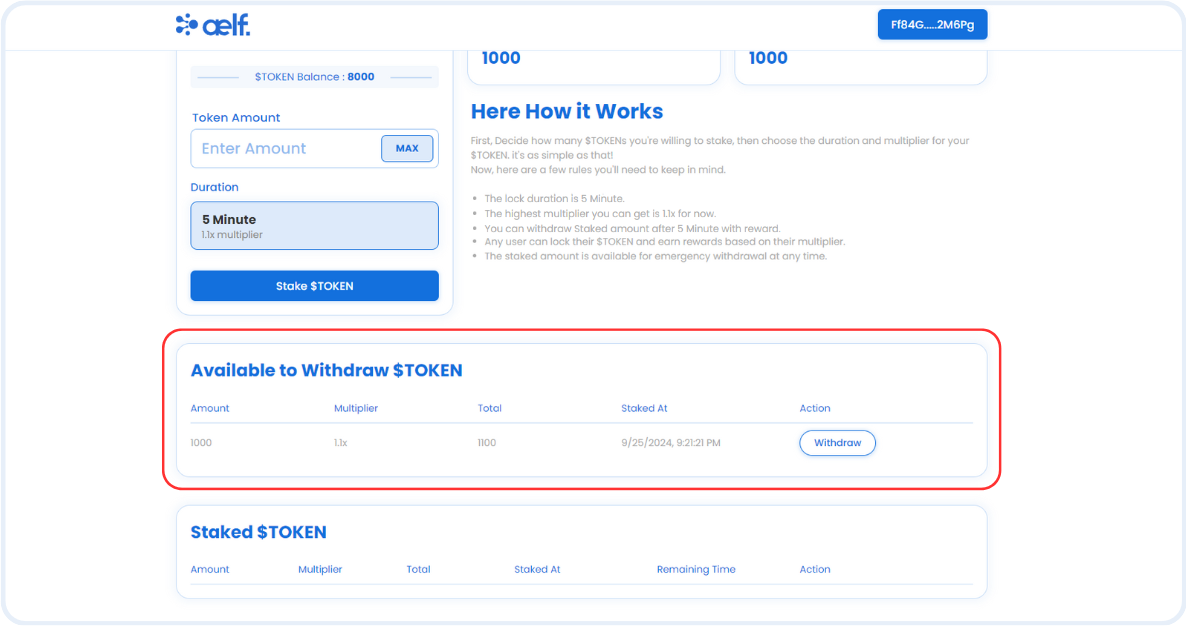
-
Now, You will get the transaction request on the Portkey wallet to withdraw the staked amount.
-
Click on the Sign button.
-
Your staked tokens including rewards will be transferred to the connected wallet once the withdrawal request completes.
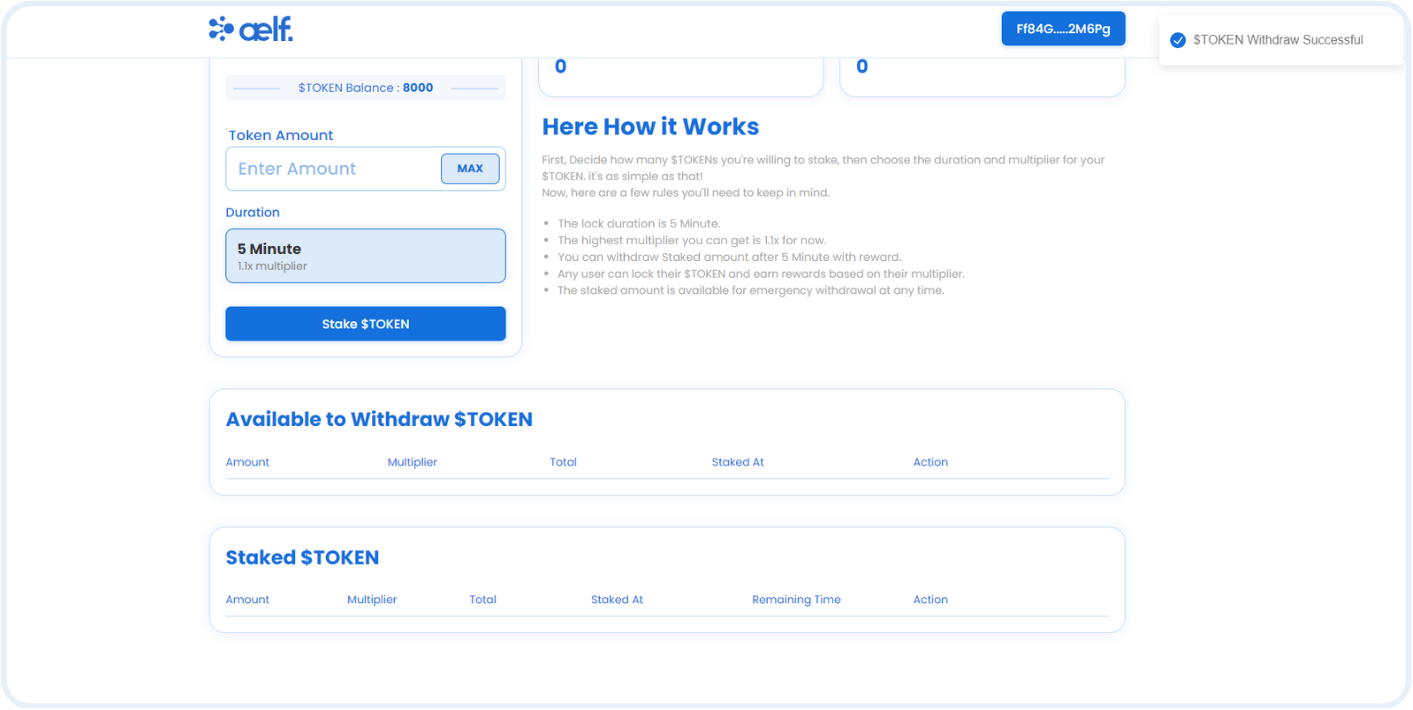
🎉 Congratulations Learners! You have successfully built your Staking dApp!
🎯 Conclusion
🎊 Congratulations on setting up your development environment and interacting with both the multi-token and staking smart contracts! 🎊 You've now built a solid foundation for handling advanced token operations and staking functionalities on the aelf blockchain. 🌟
📚 What You've Learned
Throughout this section, you've gained vital skills in:
-
🛠️ Setting Up Your Development Environment: You installed essential tools like the .NET SDK, aelf contract templates, and the aelf deploy tool to prepare for smart contract development.
-
📦 Installing Node.js, Yarn, and aelf-command: These tools enable efficient interaction with the aelf blockchain, facilitating wallet creation and transaction management.
-
💡 Getting Token Seed: You obtained a TOKEN seed from the testnet faucet, a fundamental step in creating fungible tokens.
-
🔧 Configuring Frontend Integration: You set up a frontend that interacts with both the multi-token and staking contracts, enabling user-friendly functionality including functions like token creation, token issuance, stake tokens, and withdraw tokens in your dApp.
🔍 Final Output
By now, you should have:
-
📜 Successfully set up your development environment and installed all required packages.
-
💻 Configured your frontend to interact with both the multi-token and staking smart contracts, enabling functionalities like creating tokens, issuing them on the dAppChain, staking, and withdrawing tokens.
➡️ What's Next?
With a comprehensive understanding of token creation, staking, and contract interaction, you're prepared to explore further aspects of blockchain development. Consider diving into:
-
📊 Advanced Smart Contract Logic: Add more complex features and security to your contracts.
-
Enhanced Staking Protocols: Learn about advanced staking mechanisms and rewards structures to elevate your dApp.
-
🌐 Cross-Chain Interoperability: Explore how aelf’s cross-chain capabilities enable seamless communication between different blockchains.
Keep experimenting and innovating with aelf! Your journey into decentralized finance and blockchain development is just getting started. 🚀
Happy coding and building on the aelf blockchain! 😊